- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search


Neutralization Reaction at Home
Subject: Chemistry
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
18 May 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This activity is a simple experiment that allows students to investigate a neutralization reaction at home using vinegar and baking soda. Suitable for home learning or remote teaching.
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
skeptucator
I've been using your resources with my year 7 class to teach remotely - thank you for such excellent ideas and downloads :D
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

We aim at developing the scientific temperament among the students and society

Neutralization is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react quantitatively with each other resulting in salts and water as products. The reaction involves combination of H + and OH – ions resulting in formation of water.
Acid + Base (alkaline) → Salt + Water
H 2 SO 4 +2( NaOH) → Na 2 SO 4 + 2(H 2 O)
Sulphuric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide → Sodium Sulfate + Water
H + (aq) + OH – (aq) → H 2 O (l)
Phenolphthalein is an acid/base artificial indicator. It is colorless when it is added to an acid and changes color to pink when added to a base. Lime water is a calcium hydroxide solution, Ca(OH) 2 , which is a base, used in this experiment.
Do-it-yourself Experiment: Neutralization Reaction (Magic Breath)
Apparatus required:.

Precautions:
- Wear the safety glasses and hand gloves while doing the experiment.
- Do not breath-in through the straw as it would allow intake of the solution which can be dangerous.
Step wise Procedure of Neutralization Reaction
- Take 200 ml water in a transparent flask.
- Add 3 ml lime water (solution of calcium hydroxide) into water to make it a base.

CO 2 + H 2 O → H 2 CO 3 (carbonic acid)

H 2 CO 3 + Ca(OH) 2 → CaCO 3 + H 2 O


Applications of Neutralization Reaction:
- Treatment of Waste Water: The waste water from the industries is often toxic in nature and very harmful to the environment. This toxicity of the waste water needs to be neutralized with different chemicals like magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, etc. depending on the applications.
- Human Digestive System: The intestinal wall absorbs the nutrients with the help of alkaline environments. So, antacid bicarbonates are produced by the pancreas to cause this transformation to happen.
- Control of pH value of Soil: Neutralization of soil is necessary to promote the plant growth. Soil gets acidic nature due to acid rains. Liming process is employed in agriculture that uses calcium and magnesium carbonates to neutralize the soil and hence providing nutrients to promote the plant growth. Soil is also alkaline in some cases where calcium sulfate, gypsum and sulfur etc are used for neutralization.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Remember Me

Experiment Neutralization Reactions Experiments
Neutralization reactions.
Experiment #6 from Physical Science with Vernier
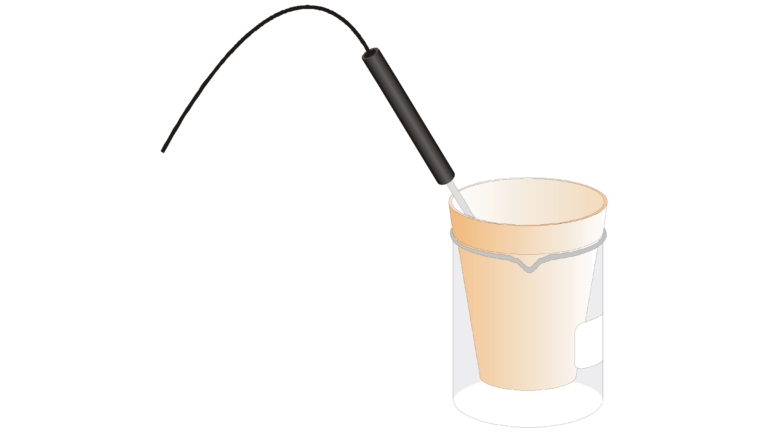
Introduction
If an acid is added to a base, a chemical reaction called neutralization occurs. An example is the reaction between nitric acid, HNO 3 , and the base potassium hydroxide, KOH.
Neutralization produces a salt and water. KNO 3 is the salt in the above reaction. Heat energy is generally released, and the amount of heat released depends upon the properties of the acid and the base. Temperature measurements, made with a Temperature Probe, can be used to study the heat effects of neutralization.
In this experiment, you will
- Use conductivity to determine the strengths of acids and bases.
- Use litmus paper to distinguish acids and bases.
- Measure temperatures of reactants and products of neutralization reactions.
- Study the relationship between acid and base strength and heat released during neutralization.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.

Ready to Experiment?
Ask an expert.
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email [email protected]
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #6 of Physical Science with Vernier . The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An entertaining twist on the classic neutralisation reaction experiment. John will inspire you with creative ideas for your Science lessons.Visit our shop to...
Neutralization Reaction at Home. Subject: Chemistry. Age range: 11-14. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. Videos. File previews. docx, 80.55 KB. This activity is a simple experiment that allows students to investigate a neutralization reaction at home using vinegar and baking soda. Suitable for home learning or remote teaching.
Add a spatula measure of ‘slaked lime’ to the vinegar solution and stir steadily for 10 seconds. Record the new temperature of the solution. Take a drop of the solution and place on the second piece of indicator paper on the spotting tile. Make sure you do not transfer solid particles of slaked lime. Record the pH found.
This video covers how to carry out the neutralization reaction between vinegar (acid) and baking soda (alkali) at home using vinegar and baking soda. It is a...
Upon immersing the baking soda in the vinegar a couple of chemical reactions occur: 1) The baking soda (base) and the vinegar (acid) react to form water (neutral pH), which is why we call this a neutralization reaction. 2) The baking soda contains a chemical known as bicarbonate (HCO3 -) that becomes H2CO3 (Carbonic acid) upon reacting with the ...
Neutralization Reaction: A neutralization reaction can be defined as a chemical reaction in which an acid and base quantitatively react together to form a sa...
Neutralisation reactions. A neutralisation reaction is one in which a base reacts with an acid to form water. A salt is also formed in this reaction. pH. The pH scale is an indication of the hydrogen ion concentration and runs from below 0 to above 14. Wales. GCSE. WJEC Chemistry. Unit 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS and ...
An acid and an alkali react to form a soluble salt in solution. In this experiment, students produce ammonium sulfate from the reaction between ammonia and sulfuric acid. They can then recover this salt by crystallisation. This is a well-tried standard class experiment, which should take no more than 30 minutes.
Neutralization is a chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react quantitatively with each other resulting in salts and water as products. The reaction involves combination of H + and OH – ions resulting in formation of water. Acid + Base (alkaline) → Salt + Water. H 2 SO 4 +2 ( NaOH) → Na 2 SO 4 + 2 (H 2 O)
If an acid is added to a base, a chemical reaction called neutralization occurs. An example is the reaction between nitric acid, HNO3, and the base potassium hydroxide, KOH. Neutralization produces a salt and water. KNO3 is the salt in the above reaction. Heat energy is generally released, and the amount of heat released depends upon the properties of the acid and the base. Temperature ...