

How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, how to write a case study in research..., online ai writing tools: cost-efficient help for dissertation..., how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.

Chapter 21. Conclusion: The Value of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is engaging research, in the best sense of the word.
A few of the meanings of engage = to attract or hold by influence or power; to hold the attention of; to induce to participate; to enter into contest with; to bring together or interlock; to deal with at length; to pledge oneself; to begin and carry on an enterprise; to take part or participate; to come together; engaged = to be actively involved in or committed; to greatly interest; to be embedded with. ( Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary )
There really is no “cookbook” for conducting qualitative research. Each study is unique because the social world is rich and full of wonders, and those of us who are curious about it have our own position in that world and our own understandings and experiences we bring with us when we seek to explore it. And yet even though our reports may be subjective, we can do what we can to make them honest and intelligible to everyone else. Learning how to do that is learning how to be a qualitative researcher rather than simply an amateur observer. Helping you understand that and getting you ready for doing so have been the goal of this book.

According to Lareau ( 2021:36 ), excellent qualitative work must include all the following elements: a clear contribution to new knowledge, a succinct assessment of previous literature that shows the holes in the literature, a research question that can be answered with the data in hand, a breadth and depth in the data collection, a clear exposition of the results, a deep analysis that links the evidence to the interpretation, an acknowledgment of disconfirming evidence, a discussion that uses the case as a springboard to reflect on more general concerns, and a full discussion of implications for ideas and practices. The emphasis on rigor, the clear contribution to new knowledge, and the reflection on more general concerns place qualitative research within the “scientific” camp vis-à-vis the “humanistic inquiry” camp of pure description or ideographic approaches. The attention to previous literature and filling the holes in what we know about a phenomenon or case or situation set qualitative research apart from otherwise excellent journalism, which makes no pretensions of writing to or for a larger body of knowledge.
In the magnificently engaging untextbook Rocking Qualitative Social Science , Ashley Rubin ( 2021 ) notes, “Rigorous research does not have to be rigid” ( 3 ). I agree with her claim that there are many ways to get to the top of the mountain, and you can have fun doing so. An ardent rock climber, Rubin calls her approach the Dirtbagger approach, a way of climbing the mountain that is creative, flexible, and definitely outside proscribed methods. Here are eleven lessons offered by Rubin in paraphrase form with commentary and direct quotes noted:
- There is no right way to do qualitative social science, “and people should choose the approach that works for them, for the particular project at hand, given whatever constraints and opportunities are happening in their life at the time. ( 252 )”
- Disagreements about what is proper qualitative research are distracting and misleading.
- Even though research questions are very important, they can and most likely will change during data collection or even data analysis—don’t worry about this.
- Your findings will have a bigger impact if you’ve connected them to previous literature; this shows that you are part of the larger conversation. This “anchor” can be a policy issue or a theoretical debate in the literature, but it need not be either. Sometimes what we do is really novel (but rarely—so always poke around and check before proceeding as if you are inventing the wheel).
- Although there are some rules you really must follow when designing your study (e.g., how to obtain informed consent, defining a sample), unexpected things often happen in the course of data collection that make a mockery of your original plans. Be flexible.
- Sometimes you have chosen a topic for some reason you can’t yet articulate to yourself—the subject or site just calls to you in some way. That’s fine. But you will still need to justify your choice in some way (hint: see number 4 above).
- Pay close attention to your sample: “Think about what you are leaving out, what your data allow you to observe, and what you can do to fill in some of those blanks” (252). And when you can’t fill them in, be honest about this when writing about the limitations of your study.
- Even if you are doing interviews, archival research, focus groups, or any other method of data collection that does not actually require “going into the field,” you can still approach your work as fieldwork. This means taking fieldnotes or memos about what you are observing and how you are reacting and processing those observations or interviews or interactions or documents. Remember that you yourself are the instrument of data collection, so keep a reflective eye on yourself throughout.
- Memo, memo, memo. There is no magic about how data become findings. It takes a lot of work, a lot of reflection, a lot of writing. Analytic memos are the helpful bridge between all that raw data and the presented findings.
- Rubin strongly rejects the idea that qualitative research cannot make causal claims. I would agree, but only to a point. We don’t make the kinds of predictive causal claims you see in quantitative research, and it can confuse you and lead you down some unpromising paths if you think you can. That said, qualitative research can help demonstrate the causal mechanisms by which something happens. Qualitative research is also helpful in exploring alternative explanations and counterfactuals. If you want to know more about qualitative research and causality, I encourage you to read chapter 10 of Rubin’s text.
- Some people are still skeptical about the value of qualitative research because they don’t understand the rigor required of it and confuse it with journalism or even fiction writing. You are just going to have to deal with this—maybe even people sitting on your committee are going to question your research. So be prepared to defend qualitative research by knowing the common misconceptions and criticisms and how to respond to them. We’ve talked a bit about these in chapter 20, and I also encourage you to read chapter 10 of Rubin’s text for more.

Hopefully, by the time you have reached the end of this book, you will have done a bit of your own qualitative research—maybe you’ve conducted an interview or practiced taking fieldnotes. You may have read some examples of excellent qualitative research and have (hopefully!) come to appreciate the value of this approach. This is a good time, then, to take a step back and think about the ways that qualitative research is valuable, distinct and different from both quantitative methods and humanistic (nonscientific) inquiry.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study?
Across all Western countries, we can observe a strong statistical relationship between young people’s educational attainment and their parent’s level of education. If you have at least one parent who went to university, your own chances of going to and graduating from university are much higher compared to not having university-educated parents. Why this happens is much less clear… This is where qualitative research becomes important: to help us get a clearer understanding of the dynamics that lead to this observed statistical relationship.
In my own research, I go a step further and look at young men and women who have crossed this barrier: they have become the first in their family to go to university. I am interested in finding out why and how first-in-family university students made it to university and how being at university is experienced. In-depth interviews allow me to learn about hopes, aspirations, fears, struggles, resilience and success. Interviews give participants an opportunity to tell their stories in their own words while also validating their experiences.
I often ask the young people I interview what being in my studies means to them. As one of my participants told me, it is good to know that “people like me are worth studying.” I cannot think of a better way to explain why qualitative research is important.
-Wolfgang Lehman, author of Education and Society: Canadian Perspectives
For me personally, the real value of the qualitative approach is that it helps me address the concerns I have about the social world—how people make sense of their lives, how they create strategies to deal with unfair circumstances or systems of oppression, and why they are motivated to act in some situations but not others. Surveys and other forms of large impersonal data collection simply do not allow me to get at these concerns. I appreciate other forms of research for other kinds of questions. This ecumenical approach has served me well in my own career as a sociologist—I’ve used surveys of students to help me describe classed pathways through college and into the workforce, supplemented by interviews and focus groups that help me explain and understand the patterns uncovered by quantitative methods ( Hurst 2019 ). My goal for this book has not been to convince you to become a qualitative researcher exclusively but rather to understand and appreciate its value under the right circumstances (e.g., with the right questions and concerns).
In the same way that we would not use a screwdriver to hammer a nail into the wall, we don’t want to misuse the tools we have at hand. Nor should we critique the screwdriver for its failure to do the hammer’s job. Qualitative research is not about generating predictions or demonstrating causality. We can never statistically generalize our findings from a small sample of people in a particular context to the world at large. But that doesn’t mean we can’t generate better understandings of how the world works, despite “small” samples. Excellent qualitative research does a great job describing (whether through “thick description” or illustrative quotes) a phenomenon, case, or setting and generates deeper insight into the social world through the development of new concepts or identification of patterns and relationships that were previously unknown to us. The two components—accurate description and theoretical insight—are generated together through the iterative process of data analysis, which itself is based on a solid foundation of data collection. And along the way, we can have some fun and meet some interesting people!

Supplement: Twenty Great (engaging, insightful) Books Based on Qualitative Research
Armstrong, Elizabeth A. and Laura T. Hamilton. 2015. Paying for the Party: How College Maintains Inequality . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Bourgois, Phillipe and Jeffrey Schonberg. 2009. Righteous Dopefiend . Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
DiTomaso, Nancy. 2013. The American Non-dilemma: Racial Inequality without Racism . Thousand Oaks, CA; SAGE.
Ehrenreich, Barbara. 2010. Nickel and Dimed: On (Not) Getting By in America . New York: Metropolitan Books.
Fine, Gary Alan. 2018. Talking Art: The Culture of Practice and the Practice of Culture in MFA Education . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ghodsee, Kristen Rogheh. 2011. Lost in Transition: Ethnographies of Everyday Life after Communism . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Gowan, Teresa. 2010. Hobos, Hustlers, and Backsliders: Homeless in San Francisco . Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Graeber, David. 2013. The Democracy Project: A History, a Crisis, a Movement . New York: Spiegel & Grau.
Grazian, David. 2015. American Zoo: A Sociological Safari . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Hartigan, John. 1999. Racial Situations: Class Predicaments of Whiteness in Detroit . Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press.
Ho, Karen Zouwen. 2009. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street. Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Hochschild, Arlie Russell. 2018. Strangers in Their Own Land: Anger and Mourning on the American Right . New York: New Press.
Lamont, Michèle. 1994. Money, Morals, and Manners: The Culture of the French and the American Upper-Middle Class . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Lareau, Annette. 2011. Unequal Childhoods: Class, Race, and Family Life. 2nd ed with an Update a Decade Later. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Leondar-Wright, Betsy. 2014. Missing Class: Strengthening Social Movement Groups by Seeing Class Cultures . Ithaca, NY: ILR Press.
Macleod, Jay. 2008. Ain’t No Makin’ It: Aspirations and Attainment in a Low-Income Neighborhood . 3rd ed. New York: Routledge.
Newman, Katherine T. 2000. No Shame in My Game: The Working Poor in the Inner City . 3rd ed. New York: Vintage Press.
Sherman, Rachel. 2006. Class Acts: Service and Inequality in Luxury Hotels . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Streib, Jessi. 2015. The Power of the Past: Understanding Cross-Class Marriages . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Stuber, Jenny M. 2011. Inside the College Gates: How Class and Culture Matter in Higher Education . Lanham, Md.: Lexington Books.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry that seeks to understand human experiences, behaviors, and interactions by exploring them in-depth. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data, qualitative research delves into meanings, perceptions, and subjective experiences. It is widely used in fields such as sociology, psychology, education, healthcare, and business to uncover insights that are difficult to capture through numerical data.
This article explores the methods of qualitative research, types of qualitative analysis, and a comprehensive guide to conducting a qualitative study.

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a non-numerical method of data collection and analysis that focuses on understanding phenomena from the perspective of participants. It prioritizes depth over breadth and aims to explore the “why” and “how” behind human behaviors and social phenomena.
For example, qualitative research might examine how individuals cope with chronic illness by conducting interviews to explore their experiences and emotions in detail.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
- Exploratory Nature: Focuses on exploring new areas of study or understanding complex phenomena.
- Contextual Understanding: Emphasizes the importance of context in interpreting findings.
- Subjectivity: Values participants’ perspectives and experiences as central to the research.
- Flexibility: Allows for adjustments to research design based on emerging insights.
- Rich Data: Produces detailed and nuanced descriptions rather than numerical summaries.
Methods of Qualitative Research
1. interviews.
Interviews involve one-on-one conversations between the researcher and participants to gather in-depth insights.
- Types: Structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interviews.
- Example: Interviewing teachers to understand their experiences with online education.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups consist of facilitated discussions with small groups of participants to explore shared experiences or perspectives.
- Example: Conducting a focus group with patients to understand their satisfaction with healthcare services.
3. Observation
Observation involves studying participants in their natural environment to capture behaviors, interactions, and contexts.
- Types: Participant observation (researcher participates) and non-participant observation (researcher observes without involvement).
- Example: Observing interactions in a classroom to understand teaching dynamics.
4. Case Studies
Case studies provide an in-depth examination of a single individual, group, event, or organization.
- Example: Analyzing the impact of a leadership change within a specific company.
5. Ethnography
Ethnography focuses on studying cultural practices and social norms by immersing the researcher in the community.
- Example: Exploring the cultural traditions of an indigenous group through prolonged fieldwork.
6. Document Analysis
Document analysis involves analyzing written or visual materials, such as reports, diaries, photographs, or social media posts.
- Example: Reviewing company policies to understand workplace diversity practices.
7. Narrative Research
Narrative research examines personal stories and experiences to understand individual perspectives.
- Example: Analyzing the life stories of refugees to explore their resilience and adaptation processes.
Types of Qualitative Data Analysis
1. thematic analysis.
Thematic analysis involves identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within qualitative data.
- Steps: Familiarization, coding, theme identification, and interpretation.
- Example: Analyzing interview transcripts to uncover themes related to work-life balance.
2. Content Analysis
Content analysis systematically categorizes textual or visual data to identify patterns and themes.
- Example: Analyzing social media comments to explore public opinions on environmental policies.
3. Grounded Theory
Grounded theory focuses on developing a theory grounded in the data collected.
- Steps: Open coding, axial coding, and selective coding.
- Example: Developing a theory about customer satisfaction based on retail feedback.
4. Narrative Analysis
Narrative analysis examines the structure and content of personal stories to uncover meaning.
- Example: Analyzing interviews with survivors of natural disasters to understand coping strategies.
5. Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis explores how language is used in specific contexts to construct meaning and social realities.
- Example: Analyzing political speeches to identify persuasive strategies.
6. Framework Analysis
Framework analysis uses a structured approach to analyze data within a thematic framework.
- Example: Evaluating healthcare professionals’ experiences with new policies using predefined themes.
7. Phenomenological Analysis
Phenomenological analysis focuses on understanding the lived experiences of participants.
- Example: Exploring the experiences of first-time parents to understand emotional transitions.
Guide to Conducting Qualitative Research
Step 1: define the research problem.
Clearly articulate the purpose of your study and the research questions you aim to address.
- Example: “What are the experiences of remote workers during the COVID-19 pandemic?”
Step 2: Choose a Research Method
Select a method that aligns with your research objectives and the nature of the phenomenon.
- Example: Conducting semi-structured interviews to gather personal insights.
Step 3: Identify Participants
Choose participants who can provide rich and relevant data for your study.
- Example: Selecting remote workers from diverse industries to capture varied perspectives.
Step 4: Collect Data
Use the chosen method to gather detailed and context-rich data.
- Example: Conducting interviews via video calls and recording responses for analysis.
Step 5: Analyze Data
Apply an appropriate qualitative analysis method to identify patterns, themes, or insights.
- Example: Using thematic analysis to group common challenges faced by remote workers.
Step 6: Interpret Findings
Contextualize your findings within the existing literature and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Example: Comparing your findings on remote work challenges with studies conducted pre-pandemic.
Step 7: Present Results
Communicate your results clearly, using direct quotes, narratives, or visualizations to support your findings.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Rich Insights: Provides deep understanding of complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Adapts to the research context and emerging findings.
- Contextual Detail: Captures the nuances of participants’ experiences and environments.
- Exploratory Nature: Ideal for exploring new or poorly understood topics.
Challenges of Qualitative Research
- Time-Intensive: Data collection and analysis can be lengthy processes.
- Subjectivity: Risk of researcher bias influencing data interpretation.
- Generalizability: Findings are context-specific and may not apply universally.
- Data Management: Handling and analyzing large volumes of qualitative data can be challenging.
Applications of Qualitative Research
- Healthcare: Understanding patient experiences with chronic illnesses.
- Education: Exploring teacher perceptions of new classroom technologies.
- Marketing: Investigating consumer attitudes toward a brand.
- Social Work: Analyzing community responses to social programs.
- Psychology: Examining coping mechanisms among individuals facing trauma.
Qualitative research is a powerful method for exploring the human experience and understanding complex social phenomena. By employing diverse methods such as interviews, focus groups, and ethnography, and using robust analytical techniques, qualitative researchers uncover rich, detailed insights that are essential for addressing real-world challenges. Although it requires careful planning, execution, and interpretation, qualitative research offers unparalleled depth and contextual understanding, making it indispensable across disciplines.
- Creswell, J. W., & Poth, C. N. (2018). Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Flick, U. (2018). An Introduction to Qualitative Research . Sage Publications.
- Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2017). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research . Sage Publications.
- Merriam, S. B. (2009). Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation . Jossey-Bass.
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Transformative Design – Methods, Types, Guide


Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Basic Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Applied Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Resources
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading your paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of the research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable based on your analysis, where you explain the need for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice [e.g., "The finding that the location of health care facilities negatively impacts child obesity rates in certain young adults suggests the need for more nuanced training of nutritionists in..."].
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past studies about the topic [e.g., "This study makes an important contribution to the problem of technical job training needs in rural areas of the state by documenting how..."]
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant or requires further investigation [e.g., "These findings contribute new insights concerning how factors related to economic uncertainty can lead to stalled peace negotiations in regions where..."].
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective [e.g., "By using a case study approach to examine the relationship between the religious beliefs of Central American immigrants and supporting clean energy, this study reveals important connections that can be used to..."].
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information, which should be avoided, but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study [e.g., "By applying Game Theory to the concept of trade-offs in how countries negotiate global business deals, this study offers a new approach to the dynamics of...].
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of your main argument(s) strengths and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and the necessity of examining the research problem in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., describe what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem, but that further analysis should take place that was beyond the initial scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to reflect and think introspectively about the topic, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your paper examines a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not addressing to the problem proactively based on the evidence presented in your study.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from a source cited in your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in a new or important way.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [topic studied within the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move the discussion from specific [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize the structure of your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific method of analysis and the discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative or surprising results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long, but it often represents the key takeaway for your reader.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out due to unforeseen factors or unanticipated variables. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader concerning the validity and realiability of your research.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This is why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources that haven't been referenced elsewhere in your paper. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you have presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Nov 28, 2024 1:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Commentary: Writing and Evaluating Qualitative Research Reports
Yelena p wu , phd, deborah thompson , phd, rd, karen j aroian , phd, rn, faan, elizabeth l mcquaid , phd, abpp, janet a deatrick , phd, faan.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
All correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Yelena P. Wu, PHD, Division of Public Health, Department of Family and Preventive Medicine, University of Utah, 375 Chipeta Way, Suite A, Salt Lake City, UT 84108. E-mail: [email protected]
Corresponding author.
Received 2015 Nov 6; Revised 2016 Mar 21; Accepted 2016 Mar 25; Issue date 2016 Jun.
Objective To provide an overview of qualitative methods, particularly for reviewers and authors who may be less familiar with qualitative research. Methods A question and answer format is used to address considerations for writing and evaluating qualitative research. Results and Conclusions When producing qualitative research, individuals are encouraged to address the qualitative research considerations raised and to explicitly identify the systematic strategies used to ensure rigor in study design and methods, analysis, and presentation of findings. Increasing capacity for review and publication of qualitative research within pediatric psychology will advance the field’s ability to gain a better understanding of the specific needs of pediatric populations, tailor interventions more effectively, and promote optimal health.
Keywords: methods, patient-centered, qualitative, theme
The Journal of Pediatric Psychology (JPP) has a long history of emphasizing high-quality, methodologically rigorous research in social and behavioral aspects of children’s health ( Palermo, 2013 , 2014 ). Traditionally, research published in JPP has focused on quantitative methodologies. Qualitative approaches are of interest to pediatric psychologists given the important role of qualitative research in developing new theories ( Kelly & Ganong, 2011 ), illustrating important clinical themes ( Kars, Grypdonck, de Bock, & van Delden, 2015 ), developing new instruments ( Thompson, Bhatt, & Watson, 2013 ), understanding patients’ and families’ perspectives and needs ( Bevans, Gardner, Pajer, Riley, & Forrest, 2013 ; Lyons, Goodwin, McCreanor, & Griffin, 2015 ), and documenting new or rarely examined issues ( Haukeland, Fjermestad, Mossige, & Vatne, 2015 ; Valenzuela et al., 2011 ). Further, these methods are integral to intervention development ( Minges et al., 2015 ; Thompson et al., 2007 ) and understanding intervention outcomes ( de Visser et al., 2015 ; Hess & Straub, 2011 ). For example, when designing an intervention, qualitative research can identify patient and family preferences for and perspectives on desirable intervention characteristics and perceived needs ( Cassidy et al., 2013 ; Hess & Straub, 2011 ; Thompson, 2014 ), which may lead to a more targeted, effective intervention.
Both qualitative and quantitative approaches are concerned with issues such as generalizability of study findings (e.g., to whom the study findings can be applied) and rigor. However, qualitative and quantitative methods have different approaches to these issues. The purpose of qualitative research is to contribute knowledge or understanding by describing phenomenon within certain groups or populations of interest. As such, the purpose of qualitative research is not to provide generalizable findings. Instead, qualitative research has a discovery focus and often uses an iterative approach. Thus, qualitative work is often foundational to future qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods studies.
At the time of this writing, three of six current calls for papers for special issues of JPP specifically note that manuscripts incorporating qualitative approaches would be welcomed. Despite apparent openness to broadening JPP’s emphasis beyond its traditional quantitative approach, few published articles have used qualitative methods. For example, of 232 research articles published in JPP from 2012 to 2014 (excluding commentaries and reviews), only five used qualitative methods (2% of articles).
The goal of the current article is to present considerations for writing and evaluating qualitative research within the context of pediatric psychology to provide a framework for writing and reviewing manuscripts reporting qualitative findings. The current article may be especially useful to reviewers and authors who are less familiar with qualitative methods. The tenets presented here are grounded in the well-established literature on reporting and evaluating qualitative research, including guidelines and checklists ( Eakin & Mykhalovskiy, 2003 ; Elo et al., 2014 ; Mays & Pope, 2000 ; Tong, Sainsbury, & Craig, 2007 ). For example, the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research checklist describes essential elements for reporting qualitative findings ( Tong et al., 2007 ). Although the considerations presented in the current manuscript have broad applicability to many fields, examples were purposively selected for the field of pediatric psychology.
Our goal is that this article will stimulate publication of more qualitative research in pediatric psychology and allied fields. More specifically, the goal is to encourage high-quality qualitative research by addressing key issues involved in conducting qualitative studies, and the process of conducting, reporting, and evaluating qualitative findings. Readers interested in more in-depth information on designing and implementing qualitative studies, relevant theoretical frameworks and approaches, and analytic approaches are referred to the well-developed literature in this area ( Clark, 2003 ; Corbin & Strauss, 2008 ; Creswell, 1994 ; Eakin & Mykhalovskiy, 2003 ; Elo et al., 2014 ; Mays & Pope, 2000 ; Miles, Huberman, & Saldaña, 2013 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ; Saldaña, 2012 ; Sandelowski, 1995 , 2010 ; Tong et al., 2007 ; Yin, 2015 ). Researchers new to qualitative research are also encouraged to obtain specialized training in qualitative methods and/or to collaborate with a qualitative expert in an effort to ensure rigor (i.e., validity).
We begin the article with a definition of qualitative research and an overview of the concept of rigor. While we recognize that qualitative methods comprise multiple and distinct approaches with unique purposes, we present an overview of considerations for writing and evaluating qualitative research that cut across qualitative methods. Specifically, we present basic principles in three broad areas: (1) study design and methods, (2) analytic considerations, and (3) presentation of findings (see Table 1 for a summary of the principles addressed in each area). Each area is addressed using a “question and answer” format. We present a brief explanation of each question, options for how one could address the issue raised, and a suggested recommendation. We recognize, however, that there are no absolute “right” or “wrong” answers and that the most “right” answer for each situation depends on the specific study and its purpose. In fact, our strongest recommendation is that authors of qualitative research manuscripts be explicit about their rationale for design, analytic choices, and strategies so that readers and reviewers can evaluate the rationale and rigor of the study methods.
Summary of Overarching Principles to Address in Qualitative Research Manuscripts
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative methods are used across many areas of health research, including health psychology ( Gough & Deatrick, 2015 ), to study the meaning of people’s lives in their real-world roles, represent their views and perspectives, identify important contextual conditions, discover new or additional insights about existing social and behavioral concepts, and acknowledge the contribution of multiple perspectives ( Yin, 2015 ). Qualitative research is a family of approaches rather than a single approach. There are multiple and distinct qualitative methodologies or stances (e.g., constructivism, post-positivism, critical theory), each with different underlying ontological and epistemological assumptions ( Lincoln, Lynham, & Guba, 2011 ). However, certain features are common to most qualitative approaches and distinguish qualitative research from quantitative research ( Creswell, 1994 ).
Key to all qualitative methodologies is that multiple perspectives about a phenomenon of interest are essential, and that those perspectives are best inductively derived or discovered from people with personal experience regarding that phenomenon. These perspectives or definitions may differ from “conventional wisdom.” Thus, meanings need to be discovered from the population under study to ensure optimal understanding. For instance, in a recent qualitative study about texting while driving, adolescents said that they did not approve of texting while driving. The investigators, however, discovered that the respondents did not consider themselves driving while a vehicle was stopped at a red light. In other words, the respondents did approve of texting while stopped at a red light. In addition, the adolescents said that they highly valued being constantly connected via texting. Thus, what is meant by “driving” and the value of “being connected” need to be considered when approaching the issue of texting while driving with adolescents ( McDonald & Sommers, 2015 ).
Qualitative methods are also distinct from a mixed-method approach (i.e., integration of qualitative and quantitative approaches; Creswell, 2013b ). A mixed-methods study may include a first phase of quantitative data collection that provides results that inform a second phase of the study that includes qualitative data collection, or vice versa. A mixed-methods study may also include concurrent quantitative and qualitative data collection. The timing, priority, and stage of integration of the two approaches (quantitative and qualitative) are complex and vary depending on the research question; they also dictate how to attend to differing qualitative and quantitative principles ( Creswell et al., 2011 ). Understanding the basic tenets of qualitative research is preliminary to integrating qualitative research with another approach that has different tenets. A full discussion of the integration of qualitative and quantitative research approaches is beyond the scope of this article. Readers interested in the topic are referred to one of the many excellent resources on the topic ( Creswell, 2013b ).
What Are Typical Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative research questions are typically open-ended and are framed in the spirit of discovery and exploration and to address existing knowledge gaps. The current manuscript provides exemplar pediatric qualitative studies that illustrate key issues that arise when reporting and evaluating qualitative studies. Example research questions that are contained in the studies cited in the current manuscript are presented in Table 2 .
Example Qualitative Research Questions From the Pediatric Literature
What Are Rigor and Transparency in Qualitative Research?
There are several overarching principles with unique application in qualitative research, including definitions of scientific rigor and the importance of transparency. Quantitative research generally uses the terms reliability and validity to describe the rigor of research, while in qualitative research, rigor refers to the goal of seeking to understand the tacit knowledge of participants’ conception of reality ( Polanyi, 1958 ). For example, Haukeland and colleagues (2015) used qualitative analysis to identify themes describing the emotional experiences of a unique and understudied population—pediatric siblings of children with rare medical conditions such as Turner syndrome and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Within this context, the authors’ rendering of the diverse and contradictory emotions experienced by siblings of children with these rare conditions represents “rigor” within a qualitative framework.
While debate exists regarding the terminology describing and strategies for strengthening scientific rigor in qualitative studies ( Guba, 1981 ; Morse, 2015a , 2015b ; Sandelowski, 1993a ; Whittemore, Chase, & Mandle, 2001 ), little debate exists regarding the importance of explaining strategies used to strengthen rigor. Such strategies should be appropriate for the specific study; therefore, it is wise to clearly describe what is relevant for each study. For example, in terms of strengthening credibility or the plausibility of data analysis and interpretation, prolonged engagement with participants is appropriate when conducting an observational study (e.g., observations of parent–child mealtime interactions; Hughes et al., 2011 ; Power et al., 2015 ). For an interview-only study, however, it would be more practical to strengthen credibility through other strategies (e.g., keeping detailed field notes about the interviews included in the analysis).
Dependability is the stability of a data analysis protocol. For instance, stepwise development of a coding system from an “a priori” list of codes based on the underlying conceptual framework or existing literature (e.g., creating initial codes for potential barriers to medication adherence based on prior studies) may be essential for analysis of data from semi-structured interviews using multiple coders. But this may not be the ideal strategy if the purpose is to inductively derive all possible coding categories directly from data in an area where little is known. For some research questions, the strategy may be to strengthen confirmability or to verify a specific phenomenon of interest using different sources of data before generating conclusions. This process, which is commonly referred to in the research literature as triangulation, may also include collecting different types of data (e.g., interview data, observational data), using multiple coders to incorporate different ways of interpreting the data, or using multiple theories ( Krefting, 1991 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Alternatively, another investigator may use triangulation to provide complementarity data ( Krefting, 1991 ) to garner additional information to deepen understanding. Because the purpose of qualitative research is to discover multiple perspectives about a phenomenon, it is not necessarily appropriate to attain concordance across studies or investigators when independently analyzing data. Some qualitative experts also believe that it is inappropriate to use triangulation to confirm findings, but this debate has not been resolved within the field ( Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ; Tobin & Begley, 2004 ). More agreement exists, however, regarding the value of triangulation to complement, deepen, or expand understanding of a particular topic or issue ( Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Finally, instead of basing a study on a sample that allows for generalizing statistical results to other populations, investigators in qualitative research studies are focused on designing a study and conveying the results so that the reader understands the transferability of the results. Strategies for transferability may include explanations of how the sample was selected and descriptive characteristics of study participants, which provides a context for the results and enables readers to decide if other samples share critical attributes. A study is deemed transferable if relevant contextual features are common to both the study sample and the larger population.
Strategies to enhance rigor should be used systematically across each phase of a study. That is, rigor needs to be identified, managed, and documented throughout the research process: during the preparation phase (data collection and sampling), organization phase (analysis and interpretation), and reporting phase (manuscript or final report; Elo et al., 2014 ). From this perspective, the strategies help strengthen the trustworthiness of the overall study (i.e., to what extent the study findings are worth heeding; Eakin & Mykhalovskiy, 2003 ; Lincoln & Guba, 1985 ).
A good example of managing and documenting rigor and trustworthiness can be found in a study of family treatment decisions for children with cancer ( Kelly & Ganong, 2011 ). The researchers describe how they promoted the rigor of the study and strengthening its credibility by triangulating data sources (e.g., obtaining data from children’s custodial parents, stepparents, etc.), debriefing (e.g., holding detailed conversations with colleagues about the data and interpretations of the data), member checking (i.e., presenting preliminary findings to participants to obtain their feedback and interpretation), and reviewing study procedure decisions and analytic procedures with a second party.
Transparency is another key concept in written reports of qualitative research. In other words, enough detail should be provided for the reader to understand what was done and why ( Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Examples of information that should be included are a clear rationale for selecting a particular population or people with certain characteristics, the research question being investigated, and a meaningful explanation of why this research question was selected (i.e., the gap in knowledge or understanding that is being investigated; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Clearly describing recruitment, enrollment, data collection, and data analysis or extraction methods are equally important ( Dixon-Woods, Shaw, Agarwal, & Smith, 2004 ). Coherency among methods and transparency about research decisions adds to the robustness of qualitative research ( Tobin & Begley, 2004 ) and provides a context for understanding the findings and their implications.
Study Design and Methods
Is qualitative research hypothesis driven.
In contrast to quantitative research, qualitative research is not typically hypothesis driven ( Creswell, 1994 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). A risk associated with using hypotheses in qualitative research is that the findings could be biased by the hypotheses. Alternatively, qualitative research is exploratory and typically guided by a research question or conceptual framework rather than hypotheses ( Creswell, 1994 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). As previously stated, the goal of qualitative research is to increase understanding in areas where little is known by developing deeper insight into complex situations or processes. According to Richards and Morse (2013) , “If you know what you are likely to find, … you should not be working qualitatively” (p. 28). Thus, we do not recommend that a hypothesis be stated in manuscripts presenting qualitative data.
What Is the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research?
Consistent with the exploratory nature of qualitative research, one particular qualitative method, grounded theory, is used specifically for discovering substantive theory (i.e., working theories of action or processes developed for a specific area of concern; Bryant & Charmaz, 2010 ; Glaser & Strauss, 1967 ). This method uses a series of structured steps to break down qualitative data into codes, organize the codes into conceptual categories, and link the categories into a theory that explains the phenomenon under study. For example, Kelly and Ganong (2011) used grounded theory methods to produce a substantive theory about how single and re-partnered parents (e.g., households with a step-parent) made treatment decisions for children with childhood cancer. The theory of decision making developed in this study included “moving to place,” which described the ways in which parents from different family structures (e.g., single and re-partnered parents) were involved in the child’s treatment decision-making. The resulting theory also delineated the causal conditions, context, and intervening factors that contributed to the strategies used for moving to place.
Theories may be used in other types of qualitative research as well, serving as the impetus or organizing framework for the study ( Sandelowski, 1993b ). For example, Izaguirre and Keefer (2014) used Social Cognitive Theory ( Bandura, 1986 ) to investigate self-efficacy among adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease. The impetus for selecting the theory was to inform the development of a self-efficacy measure for adolescent self-management. In another study on health care transition in youth with Type 1 Diabetes ( Pierce, Wysocki, & Aroian, 2016 ), the investigators adapted a social-ecological model—the Socio-ecological Model of Adolescent and Young Adult Transition Readiness (SMART) model ( Schwartz, Tuchman, Hobbie, & Ginsberg, 2011 )—to their study population ( Pierce & Wysocki, 2015 ). Pierce et al. (2016) are currently using the adapted SMART model to focus their data collection and structure the preliminary analysis of their data about diabetes health care transition.
Regardless of whether theory is induced from data or selected in advance to guide the study, consistent with the principle of transparency , its role should be clearly identified and justified in the research publication ( Bradbury-Jones, Taylor, & Herber, 2014 ; Kelly, 2010 ). Methodological congruence is an important guiding principle in this regard ( Richards & Morse, 2013 ). If a theory frames the study at the outset, it should guide and direct all phases. The resulting publication(s) should relate the phenomenon of interest and the research question(s) to the theory and specify how the theory guided data collection and analysis. The publication(s) should also discuss how the theory fits with the finished product. For instance, authors should describe how the theory provided a framework for the presentation of the findings and discuss the findings in context with the relevant theoretical literature.
A study examining parents’ motivations to promote vegetable consumption in their children ( Hingle et al., 2012 ) provides an example of methodological congruence. The investigators adapted the Model of Goal Directed Behavior ( Bagozzi & Pieters, 1998 ) for parenting practices relevant to vegetable consumption (Model of Goal Directed Vegetable Parenting Practices; MGDVPP). Consistent with the adapted theoretical model and in keeping with the congruence principle, interviews were guided by the theoretical constructs contained within the MGDVPP, including parents’ attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control related to promoting vegetable consumption in children ( Hingle et al., 2012 ). The study discovered that the adapted model successfully identified parents’ motivations to encourage their children to eat more vegetables.
The use of the theory should be consistent with the basic goal of qualitative research, which is discovery. Alternatively stated, theories should be used as broad orienting frameworks for exploring topical areas without imposing preconceived ideas and biases. The theory should be consistent with the study findings and not be used to force-fit the researcher’s interpretation of the data ( Sandelowski, 1993b ). Divergence from the theory when it does not fit the study findings is illustrated in a qualitative study of hypertension prevention beliefs in Hispanics ( Aroian, Peters, Rudner, & Waser, 2012 ). This study used the Theory of Planned Behavior as a guiding theoretical framework but found that coding separately for normative and control beliefs was not the best organizing schema for presenting the study findings. When divergence from the original theory occurs, the research report should explain and justify how and why the theory was modified ( Bradbury-Jones et al., 2014 ).
What Are Typical Sampling Methods in Qualitative Studies?
Qualitative sampling methods should be “purposeful” ( Coyne, 1997 ; Patton, 2015 ; Tuckett, 2004 ). Purposeful sampling is based on the study purpose and investigator judgments about which people and settings will provide the richest information for the research questions. The logic underlying this type of sampling differs from the logic underlying quantitative sampling ( Patton, 2015 ). Quantitative research strives for empirical generalization. In qualitative studies, generalizability beyond the study sample is typically not the intent; rather, the focus is on deriving depth and context-embedded meaning for the relevant study population.
Purposeful sampling is a broad term. Theoretical sampling is one particular type of purposeful sampling unique to grounded theory methods ( Coyne, 1997 ). In theoretical sampling, study participants are chosen according to theoretical categories that emerge from ongoing data collection and analyses ( Bryant & Charmaz, 2010 ). Data collection and analysis are conducted concurrently to allow generating and testing hypotheses that emerge from analyzing incoming data. The following example from the previously mentioned qualitative interview study about transition from pediatric to adult care in adolescents with type 1 diabetes ( Pierce et al., 2016 ) illustrates the process of theoretical sampling: An adolescent study participant stated that he was “turned off” by the “childish” posters in his pediatrician’s office. He elaborated that he welcomed transitioning to adult care because his diabetes was discovered when he was 18, an age when he reportedly felt more “mature” than most pediatric patients. These data were coded as “developmental misfit” and prompted a tentative hypothesis about developmental stage at entry for pediatric diabetes care and readiness for health care transition. Examining this hypothesis prompted seeking study participants who varied according to age or developmental stage at time of diagnosis to examine the theoretical relevance of an emerging theme about developmental fit.
Not all purposeful sampling, however, is “theoretical.” For example, ethnographic studies typically seek to understand a group’s cultural beliefs and practices ( Creswell, 2013a ). Consistent with this purpose, researchers conducting an ethnographic study might purposefully select study participants according to specific characteristics that reflect the social roles and positions in a given group or society (e.g., socioeconomic status, education; Johnson, 1990 ).
Random sampling is generally not used in qualitative research. Random selection requires a sufficiently large sample to maximize the potential for chance and, as will be discussed below, sample size is intentionally small in qualitative studies. However, random sampling may be used to verify or clarify findings ( Patton, 2015 ). Validating study findings with a randomly selected subsample can be used to address the possibility that a researcher is inadvertently giving greater attention to cases that reinforce his or her preconceived ideas.
Regardless of the sampling method used, qualitative researchers should clearly describe the sampling strategy and justify how it fits the study when reporting study findings (transparency). A common error is to refer to theoretical sampling when the cases were not chosen according to emerging theoretical concepts. Another common error is to apply sampling principles from quantitative research (e.g., cluster sampling) to convince skeptical reviewers about the rigor or validity of qualitative research. Rigor is best achieved by being purposeful, making sound decisions, and articulating the rationale for those decisions. As mentioned earlier in the discussion of transferability , qualitative researchers are encouraged to describe their methods of sample selection and descriptive characteristics about their sample so that readers and reviewers can judge how the current sample may differ from others. Understanding the characteristics of each qualitative study sample is essential for the iterative nature of qualitative research whereby qualitative findings inform the development of future qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods studies. Reviewers should evaluate sampling decisions based on how they fit the study purpose and how they influence the quality of the end product.
What Sample Size Is Needed for Qualitative Research?
No definitive rules exist about sample size in qualitative research. However, sample sizes are typically smaller than those in quantitative studies ( Patton, 2015 ). Small samples often generate a large volume of data and information-rich cases, ultimately leading to insight regarding the phenomenon under study ( Patton, 2015 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Sample sizes of 20–30 cases are typical, but a qualitative sample can be even smaller under some circumstances ( Mason, 2010 ).
Sample size adequacy is evaluated based on the quality of the study findings, specifically the full development of categories and inter-relationships or the adequacy of information about the phenomenon under study ( Corbin & Strauss, 2008 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Small sample sizes are of concern if they do not result in these outcomes. Data saturation (i.e., the point at which no new information, categories, or themes emerge) is often used to judge informational adequacy ( Morgan, 1998 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). Although enough participants should be included to obtain saturation ( Morgan, 1998 ), informational adequacy pertains to more than sample size. It is also a function of the quality of the data, which is influenced by study participant characteristics (e.g., cognitive ability, knowledge, representativeness) and the researcher’s data-gathering skills and analytical ability to generate meaningful findings ( Morse, 2015b ; Patton, 2015 ).
Sample size is also influenced by type of qualitative research, the study purpose, the sample, the depth and complexity of the topic investigated, and the method of data collection. In general, the more heterogeneous the sample, the larger the sample size, particularly if the goal is to investigate similarities and differences by specific characteristics ( Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). For instance, in a study to conduct an initial exploration of factors underlying parents’ motivations to use good parenting practices, theoretical saturation (i.e., the point at which no new information, categories, or themes emerge) was obtained with a small sample ( n = 15), most likely because the study was limited to parents of young children ( Hingle et al., 2012 ). If the goal of the study had been, for example, to identify racial/ethnic, gender, or age differences in food parenting practices, a larger sample would likely be needed to obtain saturation or informational adequacy.
Studies that seek to understand maximum variation in a phenomenon might also need a larger sample than one that is seeking to understand extreme or atypical cases. For example, a qualitative study of diet and physical activity in young Australian men conducted focus groups to identify perceived motivators and barriers to healthy eating and physical activity and examine the influence of body weight on their perceptions. Examining the influence of body weight status required 10 focus groups to allow for group assignment based on body mass index ( Ashton et al., 2015 ). More specifically, 61 men were assigned to a healthy-weight focus group ( n = 3), an overweight/obese focus group ( n = 3), or a mixed-weight focus group ( n = 4). Had the researcher not been interested in whether facilitators and barriers differed by weight status, its likely theoretical saturation could have been obtained with fewer groups. Depth of inquiry also influences sample size ( Sandelowski, 1995 ). For instance, an in-depth analysis of an intervention for children with cancer and their families included 16 family members from three families. Study data comprised 52 hrs of videotaped intervention sessions and 10 interviews ( West, Bell, Woodgate, & Moules, 2015 ). Depth was obtained through multiple data points and types of data, which justified sampling only a few families.
Authors of publications describing qualitative findings should show evidence that the data were “saturated” by a sample with sufficient variation to permit detailing shared and divergent perspectives, meanings, or experiences about the topic of inquiry. Decisions related to the sample (e.g., targeted recruitment) should be detailed in publications so that peer reviewers have the context for evaluating the sample and determining how the sample influenced the study findings ( Patton, 2015 ).
Qualitative Data Analysis
When conducting qualitative research, voluminous amounts of data are gathered and must be prepared (i.e., transcribed) and managed. During the analytic process, data are systematically transformed through identifying, defining, interpreting, and describing findings that are meant to comprehensively describe the phenomenon or the abstract qualities that they have in common. The process should be systematic ( dependability ) and well-documented in the analysis section of a qualitative manuscript. For example, Kelly and Ganong (2011) , in their study of medical treatment decisions made by families of children with cancer, described their analytic procedure by outlining their approach to coding and use of memoing (e.g., keeping careful notes about emerging ideas about the data throughout the analytic process), comparative analysis (e.g., comparing data against one another and looking for similarities and differences), and diagram drawing (e.g., pictorially representing the data structure, including relationships between codes).
How Should Researchers Document Coding Reliability?
Because the intent of qualitative research is to account for multiple perspectives, the goal of qualitative analysis is to comprehensively incorporate those perspectives into discernible findings. Researchers accustomed to doing quantitative studies may expect authors to quantify interrater reliability (e.g., kappa statistic) but this is not typical in qualitative research. Rather, the emphasis in qualitative research is on (1) training those gathering data to be rigorous and produce high-quality data and on (2) using systematic processes to document key decisions (e.g., code book), clear direction, and open communication among team members during data analysis. The goal is to make the most of the collective insight of the investigative team to triangulate or complement each other’s efforts to process and interpret the data. Instead of evaluating if two independent raters came to the same numeric rating, reviewers of qualitative manuscripts should judge to what extent the overall process of coding, data management, and data interpretation were systematic and rigorous. Authors of qualitative reports should articulate their coding procedures for others to evaluate. Together, these strategies promote trustworthiness of the study findings.
An example of how these processes are described in the report of a qualitative study is as follows:
The first two authors independently applied the categories to a sample of two interviews and compared their application of the categories to identify lack of clarity and overlap in categories. The investigators created a code book that contained a definition of categories, guidelines for their application, and excerpts of data exemplifying the categories. The first two authors independently coded the data and compared how they applied the categories to the data and resolved any differences during biweekly meetings. ATLAS.ti, version 6.2, was used to document and accommodate ongoing changes and additions to the coding structure ( Palma et al., 2015 , p. 224).
Do I Need to Use a Specialized Qualitative Data Software Program for Analysis?
Multiple computer software packages for qualitative data analysis are currently available ( Silver & Lewins, 2014 ; Yin, 2015 ). These packages allow the researcher to import qualitative data (e.g., interview transcripts) into the software program and organize data segments (e.g., delineate which interview excerpts are relevant to particular themes). Qualitative analysis software can be useful for organizing and sorting through data, including during the analysis phase. Some software programs also offer sophisticated coding and visualization capabilities that facilitate and enhance interpretation and understanding. For example, if data segments are coded by specific characteristics (e.g., gender, race/ethnicity), the data can be sorted and analyzed by these characteristics, which may contribute to an understanding of whether and/or how a particular phenomenon may vary by these characteristics.
The strength of computer software packages for qualitative data analysis is their potential to contribute to methodological rigor by organizing the data for systematic analyses ( John & Johnson, 2000 ; MacMillan & Koenig, 2004 ). However, the programs do not replace the researchers’ analyses. The researcher or research team is ultimately responsible for analyzing the data, identifying the themes and patterns, and placing the findings within the context of the literature. In other words, qualitative data analysis software programs contribute to, but do not ensure scientific rigor or “objectivity” in, the analytic process. In fact, using a software program for analysis is not essential if the researcher demonstrates the use of alternative tools and procedures for rigor.
Presentation of Findings
Should there be overlap between presentation of themes in the results and discussion sections.
Qualitative papers sometimes combine results and discussion into one section to provide a cohesive presentation of the findings along with meaningful linkages to the existing literature ( Burnard, 2004 ; Burnard, Gill, Stewart, Treasure, & Chadwick, 2008 ). Although doing so is an acceptable method for reporting qualitative findings, some journals prefer the two sections to be distinct.
When the journal style is to distinguish the two sections, the results section should describe the findings, that is, the themes, while the discussion section should pull the themes together to make larger-level conclusions and place the findings within the context of the existing literature. For instance, the findings section of a study of how rural African-American adolescents, parents, and community leaders perceived obesity and topics for a proposed obesity prevention program, contained a description of themes about adolescent eating patterns, body shape, and feedback on the proposed weight gain prevention program according to each subset of participants (i.e., adolescents, parents, community leaders). The discussion section then put these themes within the context of findings from prior qualitative and intervention studies in related populations ( Cassidy et al., 2013 ). In the Discussion, when making linkages to the existing literature, it is important to avoid the temptation to extrapolate beyond the findings or to over-interpret them ( Burnard, 2004 ). Linkages between the findings and the existing literature should be supported by ample evidence to avoid spurious or misleading connections ( Burnard, 2004 ).
What Should I Include in the Results Section?
The results section of a qualitative research report is likely to contain more material than customary in quantitative research reports. Findings in a qualitative research paper typically include researcher interpretations of the data as well as data exemplars and the logic that led to researcher interpretations ( Sandelowski & Barroso, 2002 ). Interpretation pertains to the researcher breaking down and recombining the data and creating new meanings (e.g., abstract categories, themes, conceptual models). Select quotes from interviews or other types of data (e.g., participant observation, focus groups) are presented to illustrate or support researcher interpretations. Researchers trained in the quantitative tradition, where interpretation is restricted to the discussion section, may find this surprising; however, in qualitative methods, researcher interpretations represent an important component of the study results. The presentation of the findings, including researcher interpretations (e.g., themes) and data (e.g., quotes) supporting those interpretations, adds to the trustworthiness of the study ( Elo et al., 2014 ).
The Results section should contain a balance between data illustrations (i.e., quotes) and researcher interpretations ( Lofland & Lofland, 2006 ; Sandelowski, 1998 ). Because interpretation arises out of the data, description and interpretation should be combined. Description should be sufficient to support researcher interpretations, and quotes should be used judiciously ( Morrow, 2005 ; Sandelowski, 1994 ). Not every theme needs to be supported by multiple quotes. Rather, quotes should be carefully selected to provide “voice” to the participants and to help the reader understand the phenomenon from the participant’s perspective within the context of the researcher’s interpretation ( Morrow, 2005 ; Ritchie & Lewis, 2003 ). For example, researchers who developed a grounded theory of sexual risk behavior of urban American Indian adolescent girls identified desire for better opportunities as a key deterrent to neighborhood norms for early sexual activity. They illustrated this theme with the following quote: “I don’t want to live in the ‘hood and all that…My sisters are stuck there because they had babies. That isn’t going to happen to me” ( Saftner, Martyn, Momper, Loveland-Cherry, & Low, 2015 , p. 372).
There is no precise formula for the proportion of description to interpretation. Both descriptive and analytic excess should be avoided ( Lofland & Lofland, 2006 ). The former pertains to presentation of unedited field notes or interview transcripts rather than selecting and connecting data to analytic concepts that explain or summarize the data. The latter pertains to focusing on the mechanics of analysis and interpretation without substantiating researcher interpretations with quotes. Reviewer requests for methodological rigor can result in researchers writing qualitative research papers that suffer from analytic excess ( Sandelowski & Barroso, 2002 ). Page limitations of most journals provide a safeguard against descriptive excess, but page limitations should not circumvent researchers from providing the basis for their interpretations.
Additional potential problems with qualitative results sections include under-elaboration, where themes are too few and not clearly defined. The opposite problem, over-elaboration, pertains to too many analytic distinctions that could be collapsed under a higher level of abstraction. Quotes can also be under- or over-interpreted. Care should be taken to ensure the quote(s) selected clearly support the theme to which they are attached. And finally, findings from a qualitative study should be interesting and make clear contributions to the literature ( Lofland & Lofland, 2006 ; Morse, 2015b ).
Should I Quantify My Results? (e.g., Frequency With Which Themes Were Endorsed)
There is controversy over whether to quantify qualitative findings, such as providing counts for the frequency with which particular themes are endorsed by study participants ( Morgan, 1993 ; Sandelowski, 2001 ). Qualitative papers usually report themes and patterns that emerge from the data without quantification ( Dey, 1993 ). However, it is possible to quantify qualitative findings, such as in qualitative content analysis. Qualitative content analysis is a method through which a researcher identifies the frequency with which a phenomenon, such as specific words, phrases, or concepts, is mentioned ( Elo et al., 2014 ; Morgan, 1993 ). Although this method may appeal to quantitative reviewers, it is important to note that this method only fits specific study purposes, such as studies that investigate the language used by a particular group when communicating about a specific topic. In addition, results may be quantified to provide information on whether themes appeared to be common or atypical. Authors should avoid using imprecise language, such as “some participants” or “many participants.” A good example of quantification of results to illustrate more or less typical themes comes from a manuscript describing a qualitative study of school nurses’ perceived barriers to addressing obesity with students and their families. The authors described that all but one nurse reported not having the resources they needed to discuss weight with students and families whereas one-quarter of nurses reported not feeling competent to discuss weight issues ( Steele et al., 2011 ). If quantification of findings is used, authors should provide justification that explains how quantification is consistent with the aims or goals of the study ( Sandelowski, 2001 ).
Conclusions
This article highlighted key theoretical and logistical considerations that arise in designing, conducting, and reporting qualitative research studies (see Table 1 for a summary). This type of research is vital for obtaining patient, family, community, and other stakeholder perspectives about their needs and interests, and will become increasingly critical as our models of health care delivery evolve. For example, qualitative research could contribute to the study of health care providers and systems with the goal of optimizing our health care delivery models. Given the increasing diversity of the populations we serve, qualitative research will also be critical in providing guidance in how to tailor health interventions to key characteristics and increase the likelihood of acceptable, effective treatment approaches. For example, applying qualitative research methods could enhance our understanding of refugee experiences in our health care system, clarify treatment preferences for emerging adults in the midst of health care transitions, examine satisfaction with health care delivery, and evaluate the applicability of our theoretical models of health behavior changes across racial and ethnic groups. Incorporating patient perspectives into treatment is essential to meeting this nation’s priority on patient-centered health care ( Institute of Medicine Committee on Quality of Health Care in America, 2001 ). Authors of qualitative studies who address the methodological choices addressed in this review will make important contributions to the field of pediatric psychology. Qualitative findings will lead to a more informed field that addresses the needs of a wide range of patient populations and produces effective and acceptable population-specific interventions to promote health.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Bridget Grahmann for her assistance with manuscript preparation.
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health (K07CA196985 to Y.W.). This work is a publication of the United States Department of Agriculture/Agricultural Research Center (USDA/ARS), Children’s Nutrition Research Center, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas. It is also a publication of the USDA/ARS, Children’s Nutrition Research Center, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, and funded in part with federal funds from the USDA/ARS under Cooperative Agreement No. 58‐6250‐0‐008 (to D.T.). The contents of this publication do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the USDA, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement from the U.S. government. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Conflicts of interest : None declared.
- Aroian K. J., Peters R. M., Rudner N., Waser L. (2012). Hypertension prevention beliefs of hispanics. Journal of Transcultural Nursing , 23, 134–142. doi:10.1177/1043659611433871. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashton L. M., Hutchesson M. J., Rollo M. E., Morgan P. J., Thompson D. I., Collins C. E. (2015). Young adult males’ motivators and perceived barriers towards eating healthily and being active: A qualitative study. The International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity , 12, 93 doi:10.1186/s12966‐015‐0257‐6. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bagozzi R., Pieters R. (1998). Goal-directed emotions. Cognition & Emotion , 12(1), 1–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bandura A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bevans K. B., Gardner W., Pajer K., Riley A. W., Forrest C. B. (2013). Qualitative development of the PROMIS ® pediatric stress response item banks. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 38, 173–191. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jss107. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bradbury-Jones C., Taylor J., Herber O. (2014). How theory is used and articulated in qualitative research: Development of a new typology. Social Science and Medicine , 120, 135–141. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.09.014. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bryant A., Charmaz K. (2010). The Sage handbook of grounded theory. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Burnard P. (2004). Writing a qualitative research report. Nurse Education Today , 24, 174–179. doi:10.1016/j.nedt.2003.11.005. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burnard P., Gill P., Stewart K., Treasure E., Chadwick B. (2008). Analysing and presenting qualitative data. British Dental Journal , 204, 429–432. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.2008.292. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cassidy O., Sbrocco T., Vannucci A., Nelson B., Jackson-Bowen D., Heimdal J., Heimdal J., Mirza N., Wilfley D. E., Osborn R., Shomaker L. B., Young J. F., Waldron H., Carter M., Tanofsky-Kraff M., (2013). Adapting interpersonal psychotherapy for the prevention of excessive weight gain in rural African American girls. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 38, 965–977. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jst029. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark J. (2003). How to peer review a qualitative manuscript. Peer Review in Health Sciences, 2, 219–235. [ Google Scholar ]
- Corbin S., Strauss A. (2008). Basics of qualitative research (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coyne I. T. (1997). Sampling in qualitative research. Purposeful and theoretical sampling; merging or clear boundaries? Journal of Advanced Nursing , 26, 623–630. doi:10.1046/j.1365‐2648.1997.t01‐25‐00999.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W. (1994). Research design: Qualitative & quantitative approaches. Journal of Marketing Research , 33, 252 doi:10.2307/3152153. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W. (2013a). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W. (2013b). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W., Klassen A. C., Plano Clark V. L., Smith K. C.;for the Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research. (2011). Best practices for mixed methods research in the health sciences. Retrieved from National Institutes of Health: http://obssr.od.nih.gov/mixed_methods_research .
- de Visser R. O., Graber R., Hart A., Abraham C., Scanlon T., Watten P., Memon A. (2015). Using qualitative methods within a mixed-methods approach to developing and evaluating interventions to address harmful alcohol use among young people. Health Psychology , 34, 349–360. doi:10.1037/hea0000163. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dey I. (1993). Qualitative data analysis: A user-friendly guide for social scientists. New York, NY: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Shaw R. L., Agarwal S., Smith J. A. (2004). The problem of appraising qualitative research. Quality and Safety in Health Care , 13, 223–225. doi:10.1136/qhc.13.3.223. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eakin J. M., Mykhalovskiy E. (2003). Reframing the evaluation of qualitative health research: Reflections on a review of appraisal guidelines in the health sciences. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice , 9, 187–194. doi:10.1046/j.1365‐2753.2003.00392.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elo S., Kääriäinen M., Kanste O., Pölkki T., Utriainen K., Kyngäs H. (2014). Qualitative content analysis: A focus on trustworthiness. SAGE Open , 4(1), 1–10. doi:10.1177/2158244014522633. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser B., Strauss A. (1967). The discovery grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative inquiry. Nursing Research , 17, 364 doi:10.1097/00006199‐196807000‐00014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gough B., Deatrick J. A. (2015). Qualitative health psychology research: Diversity, power, and impact. Health Psychology , 34, 289–292. doi:10.1037/hea0000206. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guba E. G. (1981). Criteria for assessing the trustworthiness of naturalistic inquiries. Educational Communication and Technology , 29, 75–91. doi:10.1007/BF02766777. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haukeland Y. B., Fjermestad K. W., Mossige S., Vatne T. M. (2015). Emotional experiences among siblings of children with rare disorders. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 40, 12–20. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsv022. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hess J. S., Straub D. M. (2011). Brief report: Preliminary findings from a pilot health care transition education intervention for adolescents and young adults with special health care needs. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 36, 172–178. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsq091. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hingle M., Beltran A., O’Connor T., Thompson D., Baranowski J., Baranowski T. (2012). A model of goal directed vegetable parenting practices. Appetite , 58, 444–449. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2011.12.011. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hughes S. O., Power T. G., Papaioannou M. A., Cross M. B., Nicklas T. A., Hall S. K., Shewchuk R. M. (2011). Emotional climate, feeding practices, and feeding styles: An observational analysis of the dinner meal in Head Start families. The International Journal of Behavavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity , 8, 60 doi:10.1186/1479‐5868‐8‐60. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Medicine Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. (2001). Crossing the quality chasm: A new health system for the 21st century. National Academies Press. Washington, DC. [ Google Scholar ]
- Izaguirre M. R., Keefer L. (2014). Development of a self-efficacy scale for adolescents and young adults with inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition , 59, 29–32. doi:10.1097/mpg.0000000000000357. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- John W. S., Johnson P. (2000). The pros and cons of data analysis software for qualitative research. Journal of Nursing Scholarship , 32, 393–397. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson J. C. (1990). Selecting ethnographic informants. Sage Publications. Thousand Oaks, CA. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kars M. C., Grypdonck M. H., de Bock L. C., van Delden J. J. (2015). The parents’ ability to attend to the “voice of their child” with incurable cancer during the palliative phase. Health Psychology , 34, 446–452. doi:10.1037/hea0000166. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kelly K., Ganong L. (2011). Moving to place: Childhood cancer treatment decision making in single-parent and repartnered family structures. Qualitative Health Research , 21, 349–364. doi:10.1177/1049732310385823. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kelly M. (2010). The role of theory in qualitative health research. Family Practice , 27, 285–290. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmp077. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krefting L. (1991). Rigor in qualitative research: The assessment of trustworthiness. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy , 45, 214–222. doi:10.5014/ajot.45.3.214. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y. S., Guba E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y. S., Lynham S. A., Guba E. G. (2011). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences, revisited. In Denzin N. K., Lincoln Y. S. (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (4th ed., pp. 97–128). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lofland J., Lofland L. H. (2006). Analyzing social settings: A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing Company. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lyons A. C., Goodwin I., McCreanor T., Griffin C. (2015). Social networking and young adults’ drinking practices: Innovative qualitative methods for health behavior research. Health Psychology , 34, 293–302. doi:10.1037/hea0000168. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- MacMillan K., Koenig T. (2004). The wow factor: Preconceptions and expectations for data analysis software in qualitative research. Social Science Computer Review , 22, 179–186. doi:10.1177/0894439303262625. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason M. (Producer). (2010). Sample size and saturation in PhD studies using qualitative interviews. Forum: Qualitative Social Research. Retrieved from http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:0114-fqs100387 .
- Mays N., Pope C. (2000). Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. British Medical Journal , 320, 50 doi:10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McDonald C. C., Sommers M. S. (2015). Teen drivers’ perceptions of inattention and cell phone use while eriving. Traffic Injury Prevention , 16(Suppl 2), S52–S58. doi:10.1080/15389588.2015.1062886. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles M. B., Huberman A. M., Saldaña J. (2013). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Minges K. E., Owen N., Salmon J., Chao A., Dunstan D. W., Whittemore R. (2015). Reducing youth screen time: Qualitative metasynthesis of findings on barriers and facilitators. Health Psychology , 34, 381–397. doi:10.1037/hea0000172. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L. (1993). Qualitative content analysis: A guide to paths not taken. Qualitative Health Research , 3, 112–121. doi:10.1177/104973239300300107. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D. L. (1998). Planning Focus Groups: Focus Group Kit #2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrow S. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology , 52, 250–260. doi:10.1037/0022‐0167.52.2.250. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse J. M. (2015a). Critical analysis of strategies for determining rigor in qualitative inquiry. Qualitative Health Research , 25, 1212–1222. doi:10.1177/1049732315588501. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse J. M. (2015b). Data were saturated. Qualitative Health Research , 25, 587–588. doi:10.1177/1049732315576699. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palermo T. M. (2013). New guidelines for publishing review articles in JPP: Systematic reviews and topical reviews. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 38, 5–9. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jss124. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palermo T. M. (2014). Evidence-based interventions in pediatric psychology: Progress over the decades. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 39, 753–762. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsu048. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Palma E., Deatrick J., Hobbie W., Ogle S., Kobayashi K., Maldonado L. (2015). Maternal caregiving demands for adolescent and young adult survivors of pediatric brain tumors. Oncology Nursing Forum , 42, 222–229. doi:10.1188/15.ONF.. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pierce J. S., Wysocki T. (2015). Topical Review: Advancing research on the transition to adult care for type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 40, 1041–1047. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsv064. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pierce J. S., Wysocki T., Aroian K. (2016). Multiple stakeholder perspectives on health care transition outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes. Unpublished data. [ Google Scholar ]
- Polanyi M. (1958). Personal knowledge. New York, NY: Harper & Row. [ Google Scholar ]
- Power T. G., Hughes S. O., Goodell L. S., Johnson S. L., Duran J. A., Williams K., Beck A. D., Frankel L. A. (2015). Feeding practices of low-income mothers: How do they compare to current recommendations? The International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity , 12, 34 doi:10.1186/s12966‐015‐0179‐3. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Richards L., Morse J. M. (2013). Readdme first for a user’s guide to qualitative methods (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie J., Lewis J. (Eds.). (2003). Qualitative research practice: A guide for social science students and researchers. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saftner M. A., Martyn K. K., Momper S. L., Loveland-Cherry C. J., Low L. K. (2015). Urban American Indian adolescent girls framing sexual risk behavior. Journal of Transcultural Nursing, 26, 365–375. doi:10.1177/1043659614524789. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saldaña J. (2012). The coding manual for qualitative researchers. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (1993a). Rigor or rigor mortis: The problem of rigor in qualitative research revisited. Advances in Nursing Science , 16, 1–8. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (1993b). Theory unmasked: The uses and guises of theory in qualitative research. Research in Nursing & Health , 16, 213–218. doi:10.1002/nur.4770160308. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (1994). The use of quotes in qualitative research. Research in Nursing and Health , 17, 479–482. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (1995). Sample size in qualitative research. Research in Nursing and Health , 18, 179–183. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (1998). Writing a good read: Strategies for re-presenting qualitative data. Research in Nursing and Health , 21, 375–382. doi:10.1016/s1361‐3111(98)80052‐6. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (2001). Real qualitative researchers do not count: The use of numbers in qualitative research. Research in Nursing and Health , 24, 230–240. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. (2010). What’s in a name? Qualitative description revisited. Research in Nursing and Health , 33, 77–84. doi:10.1002/nur.20362.. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M., Barroso J. (2002). Finding the findings in qualitative studies. Journal of Nursing Scholarship , 34, 213–219. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz L. A., Tuchman L. K., Hobbie W. L., Ginsberg J. P. (2011). A social-ecological model of readiness for transition to adult-oriented care for adolescents and young adults with chronic health conditions. Child: Care, Health, and Development , 37, 883–895. doi:10.1111/j.1365‐2214.2011.01282.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Silver C., Lewins A. (2014). Using software in qualitative research: A step-by-step guide (2nd ed.). London: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Steele R. G., Wu Y. P., Jensen C. D., Pankey S., Davis A. M., Aylward B. S. (2011). School nurses’ perceived barriers to discussing weight with children and their families: A qualitative approach. Journal of School Health , 81, 128–137. doi:10.1111/j.1746‐1561.2010.00571.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thompson D. (2014). Talk to me, please!: The importance of qualitative research to games for health. Games for Health: Research, Development, and Clinical Applications , 3, 117–118. doi:10.1089/g4h.2014.0023. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thompson D., Baranowski T., Buday R., Baranowski J., Juliano M., Frazior M., Wilsdon J., Jago R. (2007). In pursuit of change: Youth response to intensive goal setting embedded in a serious video game. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology , 1, 907–917. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thompson D., Bhatt R., Watson K. (2013). Physical activity problem-solving inventory for adolescents: Development and initial validation. Pediatric Exercise Science , 25, 448–467. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tobin G. A., Begley C. M. (2004). Methodological rigour within a qualitative framework. Journal of Advanced Nursing , 48, 388–396. doi:10.1111/j.1365‐2648.2004.03207.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tong A., Sainsbury P., Craig J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care , 19, 349–357. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzm042. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tuckett A. G. (2004). Qualitative research sampling: The very real complexities. Nurse Researcher , 12, 47–61. doi:10.7748/nr2004.07.12.1.47.c5930. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valenzuela J. M., Buchanan C. L., Radcliffe J., Ambrose C., Hawkins L. A., Tanney M., Rudy B. J. (2011). Transition to adult services among behaviorally infected adolescents with HIV—a qualitative study. Journal of Pediatric Psychology , 36, 134–140. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsp051. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- West C. H., Bell J. M., Woodgate R. L., Moules N. J. (2015). Waiting to return to normal: An exploration of family systems intervention in childhood cancer. Journal of Family Nursing , 21, 261–294. doi:10.1177/1074840715576795. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whittemore R., Chase S. K., Mandle C. L. (2001). Validity in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research , 11, 522–537. doi:10.1177/104973201129119299. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. K. (2015). Qualitative research from start to finish (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (219.0 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
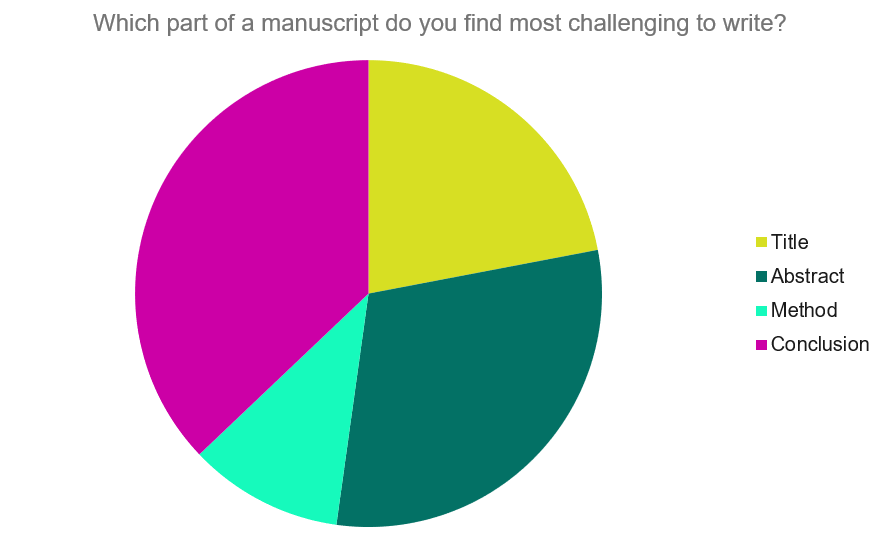
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
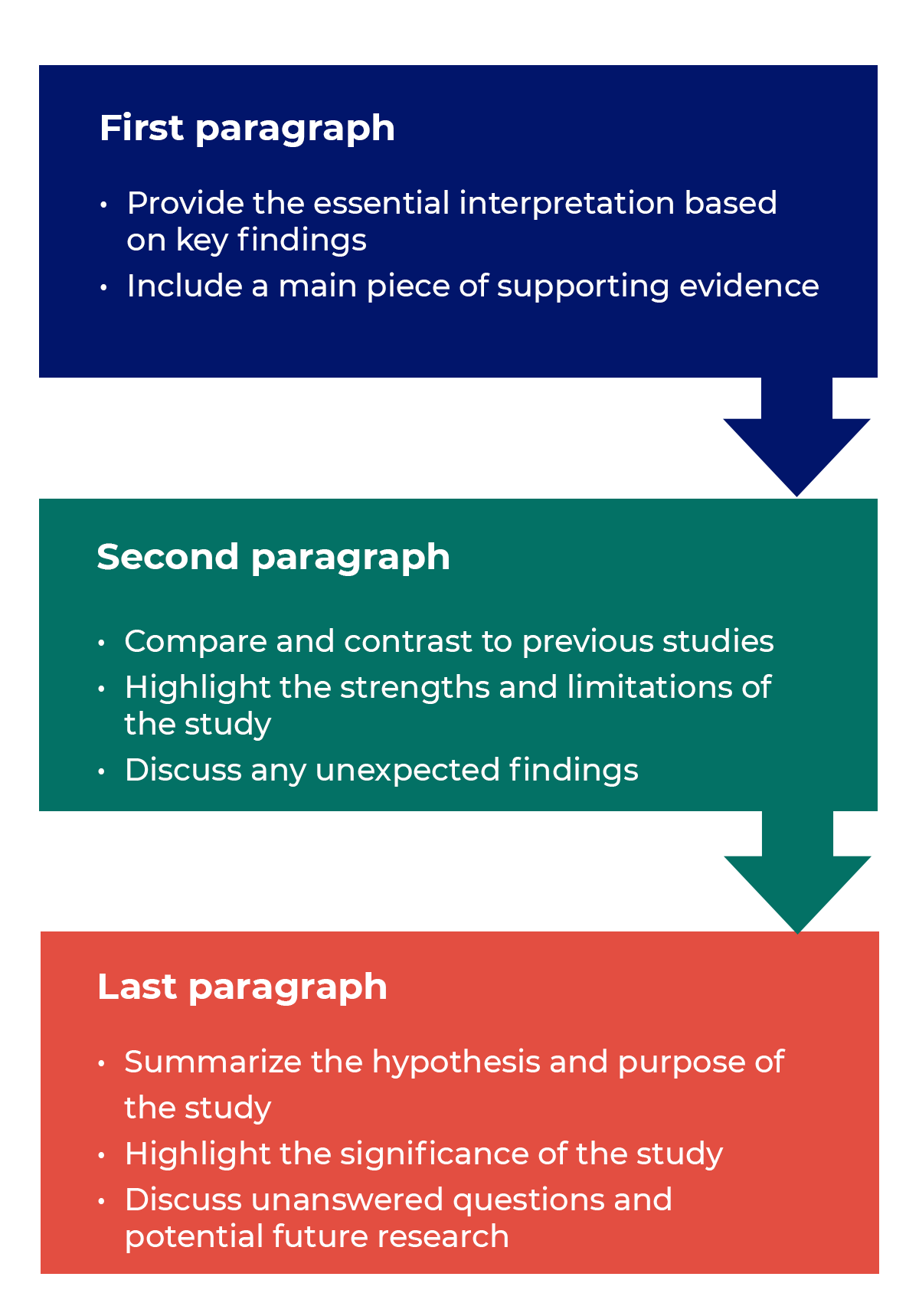
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, a two-or-three paragraph conclusion may be required.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with several important opportunities to demonstrate your overall understanding of the research problem to the reader. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key points in your analysis or findings.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger implications of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly answer the "so what?" question by placing the study within the context of past research about the topic you've investigated.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers you a chance to elaborate on the significance of your findings.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing/contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2018/07/conclusions_uwmadison_writingcenter_aug2012.pdf I. General Rules
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- State your conclusions in clear, simple language.
- Do not simply reiterate your results or the discussion.
- Indicate opportunities for future research, as long as you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Make sure, however, that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings because this reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your essay.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data.
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented, or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have done will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way.
NOTE : Don't delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply not to guess at possible outcomes.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following.
- If your essay deals with a contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion to lend authority to the conclusion you have reached [a good place to look is research from your literature review].
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to drive home the ultimate point of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point with a relevant narrative drawn from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you introduced in your introduction, but add further insight that is derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results to reframe it in new ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a strong, succient statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid Failure to be concise The conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too long often have unnecessary detail. The conclusion section is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, etc. that you make. Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from general [the field of study] to specific [your research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from specific [your research problem] back to general [your field, i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In other words, the conclusion is where you place your research within a larger context. Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. Problems, drawbacks, and challenges encountered during your study should be included as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative results [findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section of your paper. In the conclusion, use the negative results as an opportunity to explain how they provide information on which future research can be based. Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits back into your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize it briefly and directly. Often this element of your conclusion is only a few sentences long. Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine your original objectives in your introduction, as these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you now know a good deal about it, perhaps even more than your professor! Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches...."
Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions . Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization . Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining to read, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your Conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. If you have new information to present, add it to the Discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no actual new information is introduced, the conclusion is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; it's where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate your understanding of the material that you’ve presented, and locate your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Having said that, the conclusion of a qualitative study can at times be quite detailed. This would depend on the complexity of the study. A questionnaire about likes and dislikes is simpler to score, interpret, and infer than a focus group, interview, or case study.
When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1. Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem. Recommend specific course (s) of action.
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study? Across all Western countries, we can observe a strong statistical relationship between young people’s educational attainment and their parent’s level of education.
The content of the conclusion varies depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument through engagement with sources. The steps below show you how to construct an effective conclusion for either type of research paper.
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry that seeks to understand human experiences, behaviors, and interactions by exploring them in-depth. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data, qualitative research delves into meanings, perceptions, and subjective experiences.
A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of the research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable based on your analysis, where you explain the need for future research.
Results and Conclusions When producing qualitative research, individuals are encouraged to address the qualitative research considerations raised and to explicitly identify the systematic strategies used to ensure rigor in study design and methods, analysis, and presentation of findings.
How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic? Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies? How can future research build on these observations?
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules: State your conclusions in clear, simple language. Do not simply reiterate your results or the discussion. Indicate opportunities for future research, as long as you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper.
Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5–7% of your overall word count. An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research.