Problem solving in work place

This document discusses problem solving in the workplace. It begins by outlining some key quotes about problem solving and decision making. It then defines what a problem is and introduces the concept of problem solving. Several common types of problems encountered in workplaces are described, such as communication, attitude, and performance issues. The document outlines a seven step problem solving process involving defining the problem, analyzing it, generating solutions, evaluating solutions, selecting the best solution, implementing it, and evaluating the results. Barriers to effective problem solving like failing to recognize the real problem or considering all consequences are also discussed. Read less


More Related Content
- 1. ? ? PROBLEMSOLVING IN WORK PLACE? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
- 2. "In any moment of decision the best thing you can do is the right thing, the next best thing is the wrong thing, and the worst thing you can do is nothing." (attributed to Theodore Roosevelt) DO NOT PUT A BAND AID – SOLVE THE ROOT OF THE PROBLEM “You can’t solve problems with the same thinking that created them” -Albert Einstein
- 3. WHAT IS A PROBLEM ??? • A problem is ▫ A present unsatisfactory state that needs to be changed to a desired state as soon as possible ▫ Some deviation from the expected standard which prevent the achievement of objectives
- 4. INTRODUCTION TO PROBLEM SOLVING…. • Problem solving… ▫ Is bridging the gap between the way things are and the way they ought to be ▫ It is focused on the past Usually analytical Operational Done at lower levels
- 5. A LITTLE ABOUT DECISION MAKING…. • Decision making… ▫ Is a broader concept ▫ It is the act of making a choice between two or more options ▫ It is focused on the future Often creative Directional Done at senior levels Problem solving is therefore ▫ part of decision making ▫ a subset of decision making
- 6. TYPES OF PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED AT THE WORKPLACE Problems abound in every workplace due to various issues such as the need to collaborate and work with various types of people, meet targets and deadlines, work within tight budgets, gain the endorsement and praise of supervisors work within the norms and culture of the organization etc.
- 7. TYPES OF PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED AT THE WORKPLACEThere are specific problems which are common to every workplace because workplaces are human institutions and human beings are the same every where. Communication problems Attitude problems Interpersonal challenges between supervisor and subordinate or among your subordinates Ethical problems Poor performance Discrimination and/or harassment
- 8. TYPES OF PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED AT THE WORKPLACE There are another set of problems that are peculiar to an organization for various reasons for example as a result of: Policies that are unique to your workplace Processes that should be followed for various work related issues Types of clients the organization provides services to Other constraints at work ie. Inadequate resources, equipment etc.
- 9. APPROACH TO PROBLEM SOLVING To effectively solve problems at the workplace, it is important to keep the following in mind: Problems are not manageable when they are conceived in large global terms: “Everything is going wrong.” “He will never change.” “There is no hope.” etc. You need to establish and obtain relevant facts. Problems should not be allowed to linger. Addressing issues as they occur is a much strategy than waiting for things to get better and work themselves out.
- 10. APPROACH TO PROBLEM SOLVING Practice fairness in solving problems Commend or criticize the team, (where relevant) not the players, and establish a culture of fairness in the decisions you make and the actions you take If there is any punishment, let it fit the crime Not too excessive, not too lenient
- 11. PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL In this approach, possible solutions are carefully evaluated & one of them is chosen for implementation. The situation is carefully monitored over time to ensure the initial & continued effectiveness of the solution. Therefore, problem solving for one situation contributes to the nurse’s knowledge for problem solving in other similar situations. 2
- 12. PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS 3 Problem definition Problem analysis Generating possible solutions Analyzin g the solution Selectin g the best solution s Impleme nting the solution Evaluatio n & revision
- 13. PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS Problem definition • In this first step, there is a need to write down what exactly the problem entails, which helps to identify the real problem that is under study & needs an immediate solution. Problem analysis • To analysis how the problem affects the researcher & his or her current situation & other people involved in the situation. • The gravity of the problem & all the factors that are contributing to the problem are determined 4
- 14. PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS Generating possible solutions • Focus must be on identifying & generating all possible solutions for a problem. • Each potential idea for solution of a problem must be considered without discarding it through value judgment. Analyzing the solutions • Various factors about each of the potential solutions are investigated, wherein all the positive & negative aspects of each solution are analyzed. 5
- 15. PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS Selecting the best solutions • An attempt is made to compare the available solutions, & eventually the best solutions is selected based on the careful judgment. Implementing the solutions • The final step of the problem-solving process is to practically solve the problem by implementing the selected solutions. 6
- 16. Evaluation and revision PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS • After implementation of the most potential solution, an evaluation is made to judge the effectiveness of the solution in resolving the problem. • It also helps to redefine the problem & revise the problem- solving process in case the initial solution fails to manage the problem effectively. 7
- 17. The problem solving model The importance of understanding and using a model is that the solution will be the result of facts and analysis rather than of opinions and feelings. Identification of the real problem is extremely important. If the wrong cause and solution for that cause is selected, the problem will still be there.
- 18. Barriers to Problem Solving Failure to recognize the problem- not sure what the problem is Conceiving the problem too narrowly, not sure what is happening Making a hasty choice, not sure what you want Failure to consider all consequences, not enough resources Failure to consider the feasibility of the solution
- 19. Barriers to Problem Solving Failure to know to communicate what is possible Failure to define what YOU did that was responsible for your success Team attitudes like complacency, ridiculing others’ ideas, lack of accountability, dysfunctions, fear of change, lack of trust and doubts Too many chefs in the kitchen Value judgment: Members afraid to be judged based on their skills

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Decision making & problem solving
Published by Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Decision making & problem solving"— Presentation transcript:

Management, Leadership, & Internal Organization………..
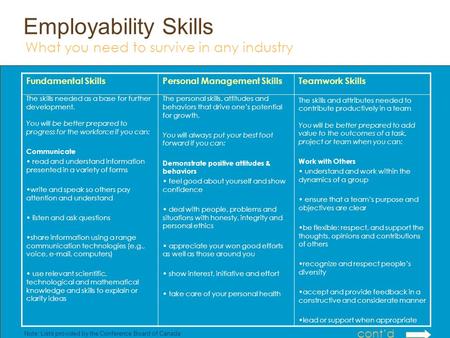
Note: Lists provided by the Conference Board of Canada

Chapter Ten Making Decisions. Chapter Ten Making Decisions.

Communicating for Results 9e 9 Key Ideas Defining small group Characteristics of successful problem-solving teams Group formats Small-Group Communication.
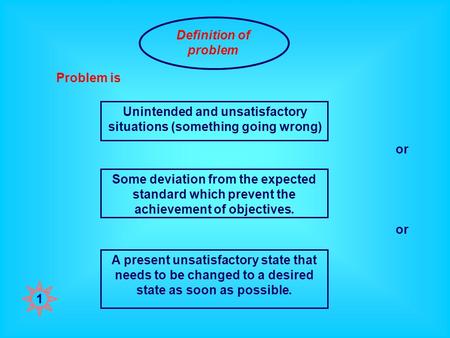
Definition of problem Unintended and unsatisfactory situations (something going wrong) Some deviation from the expected standard which prevent the achievement.

Decision Making, Learning, Creativity, and Entrepreneurship

What Is Perception, and Why Is It Important?

Managerial Decision Making Chapter 9. Copyright © 2005 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Managerial Decision Making.

8 Thinking Critically, Making Decisions, Solving Problems.

The Nature of Managerial Decision Making

7 Chapter Management, Leadership, and the Internal Organization

PLANNING in NURSING ADMINISTRATION DECISION MAKING & PROBLEM SOLVING.

Copyright c 2006 Oxford University Press 1 Chapter 7 Solving Problems and Making Decisions Problem solving is the communication that analyzes the problem.

Copyright © 2008 Allyn & Bacon Meetings: Forums for Problem Solving 11 CHAPTER Chapter Objectives This Multimedia product and its contents are protected.

Marketing CH. 4 Notes.

RESEARCH DESIGN.

Delmar Learning Copyright © 2003 Delmar Learning, a Thomson Learning company Nursing Leadership & Management Patricia Kelly-Heidenthal

Decision Making Dr Vasuprada Kartic NAC Batch IX PGDCPM.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Problem Solving and Decision Making
Jan 05, 2020
810 likes | 1.34k Views
Problem Solving and Decision Making. Problem A situation that exists when objectives are not being met. Problem Solving The process of taking corrective action to meet objectives. Decision Making The process of selecting an alternative course of action that will solve a problem.
Share Presentation
- decision making
- decision maker
- programmed decisions
- decision making conditions
- situational management decision making

Presentation Transcript
Problem Solving and Decision Making • Problem • A situation that exists when objectives are not being met. • Problem Solving • The process of taking corrective action to meet objectives. • Decision Making • The process of selecting an alternative course of action that will solve a problem. • Managers need to make proficient decisions while performing the functions of management.
Management, Decision Making, and Problem Solving • The Relationship Among Management Functions, Decision Making, and Problem Solving • Managers need to make proficient decisions while performing the functions of management.
Steps in Problem Solving Identify the problem Generate ideas Evaluate alternatives Choose among alternatives Implement chosen alternative Learn from feedback
The Decision-Making Model • A six-step model that when properly utilized increases chances of success in decision making and problem solving. Model 4–1
Decision-Making Styles • Reflexive Style • Makes quick decisions without taking the time to get all the information that may be needed and without considering all the alternatives. • Reflective Style • Takes plenty of time to make decision, gathering considerable information and analyzing several alternatives. • Consistent • Tends to make decisions without rushing or wasting time.
Types of Decisions • Programmed Decisions • Recurring or routine situations in which the decision maker should use decision rules or organizational policies and procedures to make the decision. • Nonprogrammed Decisions • Significant and nonrecurring and nonroutine situations in which the decision maker should use the decision-making model.
Decision-Making Structure Exhibit 4–1
Decision-Making Models • Rational Model (Classical Model) • The decision maker attempts to use optimizing, selecting the best possible alternative. • The Bounded Rationality Model • The decision maker uses satisficing, selecting the first alternative that meets the minimal criteria for solving the problem.
Which Decision Model to Use Exhibit 4–4a
Decision-Making Conditions • Certainty • Each alternative’s outcome is known in advance. • Risk • Probabilities can be assigned to each alternative. • Uncertainty • Lack of information or knowledge makes the each alternative unpredictable such that no probabilities can be determined.
Decision-Making Conditions Continuum Exhibit 4–4b
Potential Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Group Decision Making Exhibit 4–3
When to Use Group or Individual Decision Making Exhibit 4–4c
Define the Problem or Opportunity • Distinguish Symptoms from the Cause of the Problem • List the observable and describable occurrences (symptoms) that indicate a problem exists. • Determine the cause of the problem. • Removing the cause should cause the symptoms to disappear or cease. • Symptom: Customer dissatisfaction • Cause: Poorly trained employees • Solution: Implement customer relations training program for employees
Set Objectives and Criteria • Setting Objectives • Involves establishing clear objectives that will make for better decisions. • Objectives state what the decisions should accomplish in solving a problem or taking advantage of an opportunity. • Setting Criteria • Involves setting standards that an alternative must meet to be selected as the decision that will accomplish the objective.
Generate Creative Alternatives • Innovation • The implementation of a new idea • Product innovation (new things) • Process innovation (new way of doing things) • Creativity • A way of thinking that generates new ideas • The Creative Process • Preparation • Incubation and illumination • Evaluation
Stages in the Creative Process Become familiar with the problem; generate as many alternatives as possible. Take some time before working on the problem again to gain additional insight. Before implementing the solution, evaluate the alternative to be sure it is practical. Exhibit 4–5
Characteristics of Useful Information • Timeliness • Quality (Accuracy) • Completeness (Amount) • Relevance Exhibit 4–6
Group Decision-Making Techniques That Foster Creativity Exhibit 4–7
Generating Creative Alternatives • Brainstorming • The process of suggesting many possible alternatives without evaluation. • Synectics • The process of generating novel alternatives through role playing and fantasizing. • Nominal Grouping • The process of generating and evaluating alternatives using a structured voting method that includes listing, recording, clarification, ranking, discussion, and voting to select an alternative.
Generating Creative Alternatives • Consensus Mapping (Ringi) • The process of developing group agreement on a solution to a problem. • Delphi Technique • The process of using a series of confidential questionnaires posed to experts to refine a solution.
Responses That Kill Creativity Exhibit 4–8
Analyzing the Feasibility of Alternatives • Quantitative Techniques • Break-even analysis • Capital budgeting • Payback • Discounted cash flow • Linear programming • Queuing theory • Probability theory
Cost-Benefit (Pros and Cons) Analysis • Cost-Benefit Analysis • A technique for comparing the cost and benefit of each alternative course of action using subjective intuition and judgment along with math. • The Alternative Analysis Techniques Continuum: Exhibit 4–10
Plan, Implement, and Control • Plan • Develop a plan of action and a schedule of implementation. • Implement the Plan • Communicate and delegate for direct action. • Control • Use checkpoints to determine whether the alternative is solving the problem. • Avoid escalation of commitment to a bad alternative.
Decision Tree Exhibit 4–11
Situational Management: Decision Making Model 4–2a
Situational Management: Decision Making (cont’d) Model 4–2b
- More by User

Strategic Problem Solving and Decision Making
Strategic Problem Solving and Decision Making. Approaches for Bringing Strategic Focus to Organizational Problem Solving and Decision Making. “No problem is so large or complex that it can’t be run away from.” — Charlie Brown.
2.34k views • 35 slides

Problem Solving And Decision Making
Problem Solving And Decision Making. Chapter 8. Definition. Problem solving refers to active efforts to discover what must be done to achieve a goal that is not readily attainable. Types of Problems (Greeno). Problems of Inducing Structure Problems of Arrangement Problems of Transformation.
1.15k views • 13 slides

Problem Solving and Decision Making. Problem solving involves making a series of decisions: deciding that something is wrong, deciding what the problem is, and deciding how to solve it. . Successful problem solving depends on good decisions.
1.86k views • 59 slides


Problem Solving / Decision Making
Problem Solving / Decision Making. Kepner-Tregoe The New Rational Manager Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Contents. Conditions & Skills of Making Choices Major Elements of Decision Analysis The Techniques of Decision Analysis (DA). People and Decisions.
825 views • 30 slides

Managerial Decision Making and Problem Solving
Managerial Decision Making and Problem Solving . Lecture Notes 2 Sensitivity Analysis. Introduction. Sensitivity analysis (or post-optimality analysis) is used to determine how the optimal solution is affected by changes, within specified ranges, in: the objective function coefficients
826 views • 34 slides

Problem Solving Decision Making
?????(Problem) ??? ????????????????????????????????? ??? ??????????????????????????????????????. . . . ???????????????. ??????????????????. ?????. . ??????????? (Problem Solving)??????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????
610 views • 35 slides

Problem Solving and decision making
Your totem goes here, you may use a build if you desire. Problem Solving and decision making. Your name goes here Your course position goes here. LEARNING OBJECTIVES. As a result of this session, you will be able to: Analyze a problem and submit it to a systematic problem-solving process.
457 views • 19 slides

Decision making problem solving
1.09k views • 86 slides

Supervisory training Program. Learning today, leading tomorrow. Register Now!. Problem Solving and Decision Making. Any Date and Time AGC Chapter Headquarters. Learn how to improve: Problem prevention and anticipation Identifying problems Solving scheduling and technical problems
231 views • 1 slides

Problem Solving and Decision Making. Presented by Dianne Orfanos District Organizational Development 11/9/2010. Objectives. Determine personal decision making style Identify problem solving processes Identify problem solving tools Practice 1-2 decision-making tools.
1.07k views • 22 slides

Problem Solving and Decision Making. Ben Lilly. Objectives. Learn a systematic problem solving process Understand the relationship between Problem Solving and Project Planning Learn a Decision Making Process Put into action the skills the principles you have learned Practice Team Work
696 views • 16 slides

Problem Solving and Decision Making. FEM 3107/PEM 3501.
582 views • 33 slides

PROBLEM SOLVING AND DECISION MAKING
PROBLEM SOLVING AND DECISION MAKING. ICE BREAKER. ICEBREAKER. What is your leisure activity? Who , living or dead , do you most admire , and why? What is your greatest achievement? What are your positive qualities?
2.5k views • 139 slides

Problem Solving / Decision Making. Kepner-Tregoe The New Rational Manager Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Contents. Future Events and Their Consequences The Basic Activities A Different Kind of Process When to Use Problem (Opportunity) Analysis. The Future.
818 views • 21 slides

Problem Solving / Decision Making. Kepner-Tregoe The New Rational Manager Chapter 3. Chapter 3 Contents. Acquiring the Habit of Problem Solving PA Questioning at the Mgmt Level Abbreviated Use of PA When Actual has Never met Expected PA by a Team. PA Questioning at the Mgmt Level.
349 views • 11 slides

Managerial Decision Making and Problem Solving. Computer Lab Notes 1. Basic Excel functions and operators. Arithmetic Operations Addition of cells A1and B1: Subtracting cell B1 from A1: Multiplication of cell A1 by B1: Division of cell A1 by B1: Cell A1xraised to the power in cell B1:.
416 views • 22 slides

Problem Solving and Decision Making. 7 Steps of Problem Solving (First 5 steps are the process of decision making ) 1. Identify and define the problem. 2. Determine the set of alternative solutions. 3. Determine the criteria for evaluating alternatives. 4. Evaluate the alternatives.
1.32k views • 50 slides

PROBLEM-SOLVING and DECISION-MAKING TOOLS
PROBLEM-SOLVING and DECISION-MAKING TOOLS. Presented by: Karen Deering, Jon Ross, Mark Kesler. THE PDSA CYCLE. CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT CYCLE THE SEVEN PHASES TO THE PROBLEM SOLVING METHOD. 6 PRINCIPLES OF TQM. Mark…
1.08k views • 37 slides

Problem Solving and Decision Making. Presenter 1 Presenter 2. C7-129-15 Day 4. Albert Einstein once said…. “If I had an hour to solve a problem, I’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and 5 minutes thinking about solutions.”. Way back on Day 2….
563 views • 22 slides

Thinking: Problem Solving and Decision Making
Thinking: Problem Solving and Decision Making. Units of Thoughts. Concept A mental grouping based on shared similarity Categorizing items in one’s environment Prototype A typical best example incorporating the major features of a concept
595 views • 22 slides

Decision Making and Problem Solving
Decision Making and Problem Solving. Decision Making, Problem Solving and Conflict Resolution. Objectives To provide the learner with steps for effective decision making. To identify the barriers to effective decision making. To practice effective decision making and problem solving.
723 views • 29 slides

Managing Decision Making and Problem Solving
Managing Decision Making and Problem Solving. www.AssignmentPoint.com. After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Define decision making and discuss types of decisions and decision-making conditions.
240 views • 15 slides

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jul 12, 2013 · This document discusses problem solving and decision making at the workplace. It outlines a problem solving model involving 6 steps: 1) recognizing and defining the problem, 2) gathering information, 3) analyzing the information, 4) developing and selecting solutions, 5) implementing the solution, and 6) evaluating the solution.
Mar 29, 2015 · The decision making process involves defining the problem, analyzing it, generating possible solutions, analyzing the solutions, selecting the best option, and planning the next steps. Problem solving is related and involves working through the details of an issue to find a resolution.
Sep 19, 2018 · This document discusses problem solving in the workplace. It begins by outlining some key quotes about problem solving and decision making. It then defines what a problem is and introduces the concept of problem solving. Several common types of problems encountered in workplaces are described, such as communication, attitude, and performance ...
6.1 Learning Objectives Differentiate between programmed and nonprogrammed decisions. Explain the steps involved in making a nonprogrammed decision. Understand the major factors influencing decision making in organizations. Understand the nature of creativity and how it contributes to managerial work. Describe organizational programs for improving creativity. Implement several suggestions for ...
9 Many educators use the terms problem solving and decision making synonymously, but there is a small important difference between the two. Although decision making is the last step in the problem solving process, it is possible for decision making to occur without the full analysis required in problem solving.
Jan 5, 2020 · The Decision-Making Model • A six-step model that when properly utilized increases chances of success in decision making and problem solving. Model 4–1 Model 4–1 Decision-Making Styles • Reflexive Style • Makes quick decisions without taking the time to get all the information that may be needed and without considering all the ...