

Harriet Tubman

Tubman was born into slavery in 1822, and later escaped from Dorchester County, Maryland to Philadelphia where she lived as a freewoman
Once free, Tubman dedicated her life to the abolition of slavery as a conductor on the Underground Railroad. She brought approximately 70 enslaved African Americans to freedom in the north
Tubman remained a philanthropist well into her later years, founding the Home for Aged & Indigent Negroes and supporting women’s rights
"I had reasoned this out in my mind; there was one of two things I had the right to, liberty or death; if I could have one, I would have the other.” – Harriet Tubman, 1886
Early life .
Born Araminta Ross (and affectionately called "Minty") in March of 1822 to parents Harriet (Rit) Green Ross and Benjamin Ross, Tubman was one of nine children. The Ross family were enslaved in Dorchester County, Maryland. Chattel slavery determined that Black people were property that were bought and sold. The children of enslaved women were also considered enslaved, regardless of whether their fathers were enslaved or not. Such was the case for Tubman and her siblings as Benjamin was free, but Rit was not (University at Buffalo). The Ross’ enslaver, Edward Brodess, did not allow the family to remain together and worked to split them up through the assignment of work. Separated from Benjamin Ross at a young age, Rit, Araminta and her siblings worked on a different farm owned by the Brodesses in Bucktown, Maryland (NPS n.d.).
In 1828 at the age of six, Brodess rented out Tubman at his whim to provide childcare for nearby overseers. Compensation for her work would go to Brodess and time periods for how long she would be rented out would vary. This work separated her from her mother and siblings for extended periods of time. Tubman's life would change forever at the age of 13. In 1835, while she was running errands at a local store, she witnessed another enslaved person’s attempted escape (Owens 2022). She refused to assist the freedom seeker's enslaver in capturing the fugitive. As the enslaver became desperate in their attempt to recapture the freedom seeker, he threw a two pound weight. Rather than hitting the intended target, he struck Tubman in the back of the head and fractured her skull.
She teetered between life and death. Her mother Rit nursed Tubman back to health as much as she could given their limited resources (NPS n.d.). After the incident, physical pain became a consistent part of Tubman’s life. She experienced chronic pain from headaches and uncontrollable bouts of seizures, which Tubman herself referred to as “sleeping spells," (PBS 2022). Historians now know that Tubman had narcolepsy, which is a “chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain's ability to control sleep-wake cycles” (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke n.d.).
Tubman’s place in disability history is often overlooked. It is important to note that narcolepsy was a prominent part of both her identity and story. Vivid visions of freedom came to her while experiencing these seizures (PBS 2022). As a result of her visions, her disability is often associated with her religiosity. However, Tubman’s dedication to her faith and her experience with chronic pain hold equal weight. Both elements were key in her determination to seek liberation for the enslaved. Historian Deidre Cooper Owens spoke to the importance of Tubman’s disability in her essay "Harriet Tubman’s Disability and Why it Matters." Cooper-Owens highlighted that, “she offered up a version of freedom where a disabled Black woman sat at the center of it, where Black women were liberators, and where liberation was communal and democratic” (Owens 2022).
Journey to Freedom
The pain of separation from her family and the cruelty of slavery never left Tubman. Forced back to the fields immediately after her injury, Tubman recounted: “there I worked with the blood and sweat rolling down my face til I couldn’t see” (Wickenden 2021). She became determined to find some sense of autonomy wherever she could, despite the confines of enslavement (NPS n.d.). She negotiated with her enslaver to select her own work assignments. He agreed so long as she paid him a yearly fee. From then on, Tubman hired herself out on her own terms.
With new tasks came the exploration of new geographic areas. Dorchester County’s environment is marshland (NPCA n.d.). As such, the duties given to the enslaved in this area were unique to the landscape of Maryland’s Eastern Shore. Tubman became familiar with the intricacies of the environment through these tasks. Down the line, her familiarity with Dorchester County would be key in her journey to freedom.
In an unexpected turn of events, one assignment required her to work alongside her father in the timber fields. Not only did this allow her to spend time with him despite years of separation, but also to work alongside Black sailors. As regular travelers along the East Coast, these men were well connected. They shared their knowledge of the surrounding areas with Tubman and assisted her in tapping into a network of those also seeking liberation (Wickenden 2021). It was around this time that she met her future husband, freedman John Tubman. The couple married in 1844 when Tubman was 22 years old. Upon their union, she changed her name from Araminta “Minty” Ross, to Harriet (likely after her mother) Tubman (NPS n.d.).
Tubman cherished moments spent with her father and her time as a newlywed. However, her enslaver Brodess struggled financially and found himself in debt in 1849. He decided to sell more of his enslaved workers as a financial solution. Tubman discovered that Brodess’s financial troubles were likely to lead to the sale of her and her brothers, Ben and Henry (Wickenden 2021). Even Brodess’s death in 1849 did not alleviate Tubman’s fear of the sale and Tubman sought to make her dreams of freedom a reality. She saw her future clearly, detailing to biographer Sarah Hopkins Bradford what she envisioned as she crossed the Mason-Dixon line that separates Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia: “and on the other side of that line were green fields, and lovely flowers, and beautiful white ladies who stretched out their arms to me over the line” (Tubman, 1869).
Making use of her wealth of knowledge gained over the years, Tubman set her sights on escaping to Philadelphia. The Abolitionist Movement, which was prominent in the city, meant she was sure to find allies and like-minded confidants (University at Buffalo n.d.). After developing a route, the journey with her brothers began. While on the journey, the trio caught word that Eliza Broddess, Brodess’s widow, placed an ad in the paper calling for their return (Balkansky 2020). Tubman’s brothers decided to return to the plantation for fear of capture and subsequent punishment. Not the slightest bit discouraged, the visions that came to Tubman during narcoleptic bouts assured her she would be free (Wickenden 2021). She pressed onward alone, guided to Pennsylvania by the stars.
The Moses of Her People: Conducting the Underground Railroad
With the help of abolitionists along the way, Tubman journeyed from the Brodess’ farm in Maryland to Pennsylvania. In Philadelphia, she made connections with abolitionists, namely William Still, a conductor on the Underground Railroad (Larson 2004). Tubman learned more about the Underground Railroad from Still. Often misunderstood as a railroad with tracks and trains, the Underground Railroad (UGRR) actually refers to various safehouses in which abolitionists provided sanctuary for freedom seekers. “Conductors” led the journeys to freedom, while “Station Masters” hosted freedom seekers within their homes, churches, or other safe spaces. The more Tubman learned, the more her desire to see her family free grew. She decided to return for them in 1850.
After a successful first trip in which she brought both family and friends to freedom, she became a Conductor on the UGRR. She succeeded in her second journey as well and, on her third in 1851, Tubman returned for her husband, John. She quickly discovered that he thought she was dead and had remarried. John’s new wife was pregnant. Though heartbroken, Tubman’s commitment to freedom knew no bounds. She offered to take the couple to freedom, but John refused.
In 1850, Congressional passage of the Fugitive Slave Act changed the calculus for Conductors like Tubman. The Act “stipulated that it was illegal for any citizen to assist an escaped slave and demanded that if an escaped slave was sighted, he or she should be apprehended and turned in to the authorities for deportation back to the ‘rightful’ owner down south. Any United States Marshall who refused to return a runaway slave would pay a hefty penalty of $1,000,” (University at Buffalo n.d.). Many freedom seekers opted to flee to Canada instead of the northern US as a result. Tubman conducted eleven trips from Maryland to St. Catherines, Ontario, Canada between 1850 and 1860. All of these journeys–19 in total– over the years made Tubman a hero, with many African Americans–both free and enslaved–dubbing her “Moses” after the biblical figure (Library of Congress 1998 and Balkansky 2020).
While widely celebrated within her own community, Tubman was infamous among enslavers. Many called for her capture with bounties upwards of $40,000, which would be approximately $1,573,056.41 in today’s dollars. Between 1850 to 1860, Tubman brought approximately 70 individuals (including her parents, Rit and Ben) to freedom. Tubman spoke proudly of her accomplishments and famously stated, “I never ran my train off the track and I never lost a passenger” (Prescod-Weinstein 2022).
General Tubman: The Union Spy
In 1857, after working to free her parents, Tubman initially brought them to Canada with her but ultimately settled in Auburn, New York. Auburn was a hotbed of abolition and felt like an ideal place for Tubman and her family to settle. Frances Seward, abolitionist wife of Senator (and later Secretary of State under President Abraham Lincoln) William H. Seward, offered Tubman land in Auburn (University at Buffalo n.d.). This further encouraged the family to stay. Though Tubman had her freedom, the fight for the liberation of the enslaved still called to her.
In 1857, she met abolitionist John Brown. Brown was outspoken in his support of antislavery and, though unpopular among white southerners, his efforts were largely supported by those in the North. Tubman and Brown formed a close friendship, with Brown dubbing her “General Tubman” (NPS n.d.). She once claimed to have seen him in many of her narcoleptic dreams before meeting him. The pair worked together, including on Brown’s plans for the raid on Harpers Ferry, (now West) Virginia; Tubman provided her geographical expertise and recruited formerly enslaved people to assist in the raid. While planned as a way to steal guns and start a revolt to free enslaved people across the South, the raid ultimately ended in failure. An army unit, led by future Confederate General Robert E. Lee, captured Brown and put him on trial for "treason, murder, and inciting a slave rebellion" (NPS n.d.). Brown was hung shortly thereafter. Tubman was not in attendance at his hanging due to illness.
In April 1861, the American Civil War broke out over the issue of slavery. Tubman saw an opportunity to get involved, enlisting in the Union (Northern) Army as a nurse where she cared for wounded soldiers with natural remedies (University at Buffalo n.d.). In 1863, Tubman took on the role of a scout and organized a group of spies. She recruited enslaved people interested in assisting the Union. Tubman helped Colonel James Montgomery coordinate the Combahee River Raid in South Carolina, which aimed to “harass whites and rescue freed slaves” (University at Buffalo n.d.). The raid was wildly successful with Montgomery’s troops burning down many plantations and freeing approximately 750 enslaved people. (NPS n.d.). With their newfound freedom, many of the formerly enslaved men opted to join the Union’s fight against the Confederacy (the South). To date, Tubman is recognized as the first woman in US history to both plan and lead a military raid. In June 2021, the Army inducted her into the Military Intelligence Corps (Lacdan 2023).

Later Life and Legacy
During her time with the Union Army, Tubman met her second husband, Nelson Davis. The couple married in 1869 in Auburn, NY where he, Tubman, and her freed family members (one of which was their adopted daughter, Gertie), would live out their days (NPS n.d.). Nelson built the family a home, which still stands as of 2024. It is also in Auburn where Tubman founded the Home for the Aged, an institution that provided care for those with “paralysis, epilepsy, and those with vision impairment and blindness,” (Shoot 2021).

A staunch supporter of the suffrage movement , Tubman worked alongside various upstate-NY based suffragists, such as Lucretia Mott , Susan B. Anthony , and Elizabeth Cady Stanton . The interests of abolitionists were aligned closely with those of suffragists, with both movements concerned with autonomy and freedom. Later in life, Tubman attended various women’s rights conferences (Balkansky 2020). She also collaborated with the AME Zion Church, helping them raise money to build their church in Auburn (NPS n.d.). As collaborative partners, the church then supported Tubman’s dream of making the Home for the Aged a reality.
Nelson Davis passed away in 1888. In his absence, Tubman continued to dedicate her final 25 years to philanthropic efforts. In 1913, at the age of 91, Harriet Tubman died of pneumonia in the Home for the Aged & Indigent Negroes. In her final words, Tubman called upon her faith and made reference to John 14:3 in the Bible. She stated, “I go away to prepare a place for you, that where I am you also may be” (Larson 2004, p. 289). She was laid to rest in the Fort Hill Cemetery in Auburn.
Of service to her community until the very end, Harriet Tubman’s legacy remains relevant. In 2024, the United States Mint launched the 2024 Harriet Tubman Commemorative Coin Program . On Veteran's Day that same year, the Governor of Maryland recognized Tubman as "one of the greatest authors of the American story" and posthumously named Tubman a one-star brigadier general (Dvorak 2024). Continued discussions about and homages to Tubman stems from her powerful narrative of taking control of her own destiny and ultimately forging a path for others. She is celebrated not only for the hundreds of enslaved that she freed over the course of her lifetime, but for all of those who still look to her story for guidance. Just as she looked to the North Star to carry her to freedom, her work and values remain a guiding light to many to continue onward–no matter how harrowing the path ahead.
Primary Source Analysis Strategies
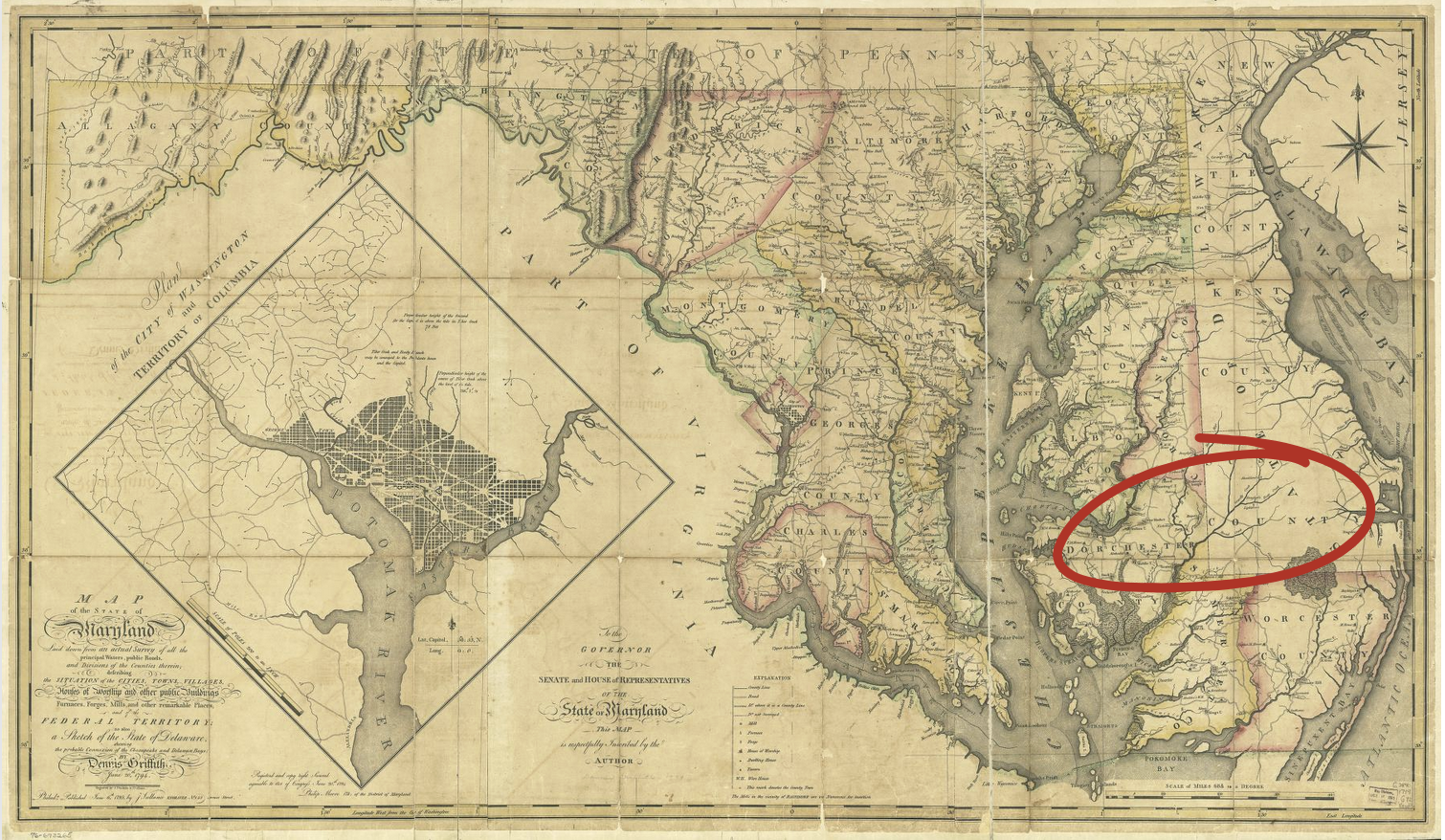
Map of Maryland
Caption: This map highlights in red Dorchester County, Maryland. Located right along the coast, it has direct access to water.
Analysis Questions:
At first glance, what do you notice about the map? Now, examine the map closely. What do you notice that you did not see the first time?
Who is the intended audience of this map?
Spot Dorchester County. What does being able to locate it on a map make you wonder?
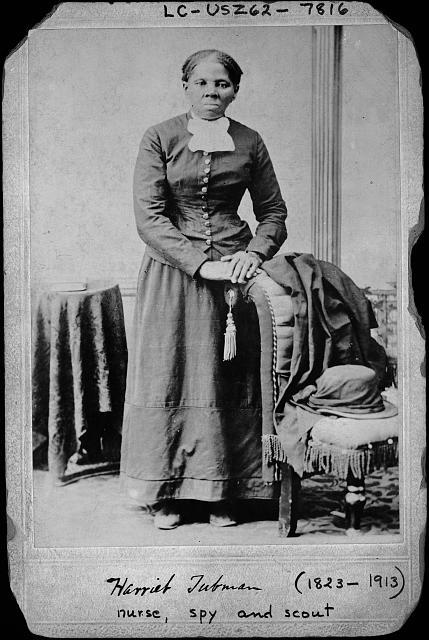
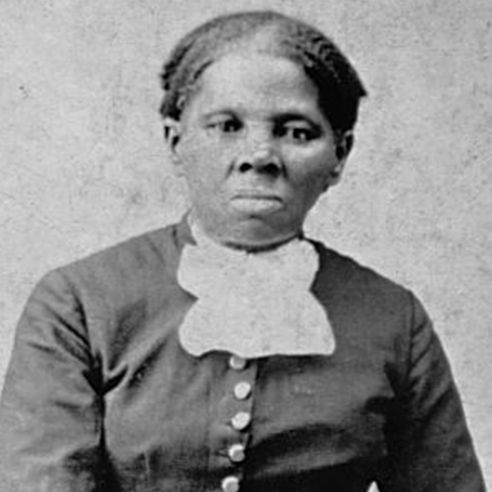
Portrait of Harriet Tubman
Caption: Tubman is seen posing for a portrait sometime between 1871 and 1876, expression neutral while she rests her hands on a chair. The bottom of the image reads “Harriet Tubman (1822-1913)” and “Nurse, spy and scout”.
What is the first thing you notice when looking at this image? Why do you think you might have gravitated towards that first?
Based on the events mentioned in the biography between 1871 and 1876 (when this image was thought to be taken), why might Tubman have had this portrait taken?
What do you notice about her appearance (her attire, hair, etc)?
The caption “nurse, spy and scout” omits words such as “conductor, abolitionist, formerly enslaved” etc. Do you believe Tubman would have agreed with the caption? If she dictated it herself, why do you think she might have wanted to be known by those three labels?
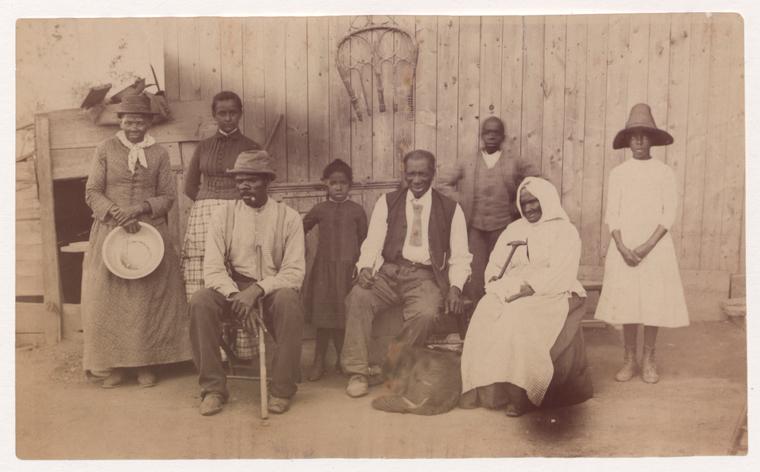
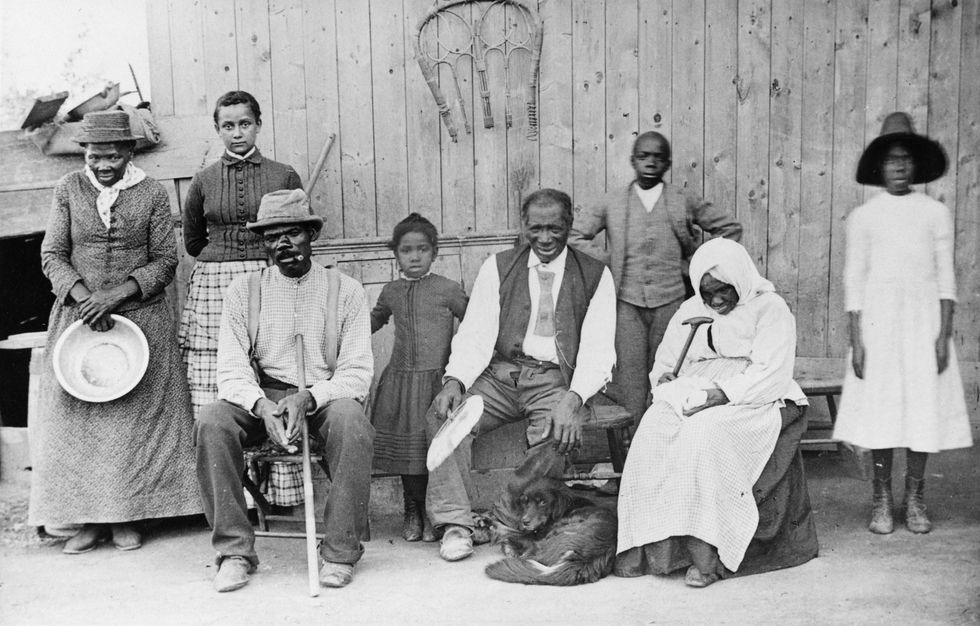
Harriet Tubman and her family
Caption: Tubman (on the far left) is photographed alongside her husband Nelson Davis, adopted child Gertie, and various other family members. This photograph was taken in Auburn, NY on the Tubman-Davis property.
Analysis Questions:
When examining this photo of Tubman surrounded by family, what questions come to mind?
Reflect on Tubman’s journey to freedom. What is the significance of this image of her photographed with so many of her family members?
In comparison to the previous images of Tubman, what differences do you notice in how she appears in this photograph?
Educator Notes
"Teacher's Guide Analyzing Primary Sources," Library of Congress
This resource outlines different lenses that students can examine through primary resources through. There is no specific order to use the columns in. The questions students develop through their examination are meant to encourage further research and curiosity. Educators can then propose other activities (as outlined in the resource) that help students further contextualize different - but related - primary sources
"Primary Source Analysis Tool," Library of Congress
This is a blank version of the previous link. Educators can create their own specific sample questions (most likely based on the medium of the primary source to have students answer in each column, or simply have students fill out this document with the guidance of the original document.
"Teacher's Guide Analyzing Maps," Library of Congress
Similar to the first resource, this document specifically focuses on how to analyze maps. The questions highlighted in each column still use the “Observe, Reflect, Question” model, but allow students to further hone in on the unique features of maps - such as the one featured in this biography.
- Lacdan, Joe. “Army Honors Female Combat Pioneer, Renowned Abolitionist.” www.army.mil. August 25, 2023. https://www.army.mil/article/269360/army_honors_female_combat_pioneer_renowned_abolitionist .
- Balkansky, Arlene. Harriet Tubman: Conductor on the Underground Railroad. June 16, 2020. https://blogs.loc.gov/headlinesandheroes/2020/06/harriet-tubman-conductor-on-the-underground-railroad/
- Dvorak, Petula. Harriet Tubman Becomes a One-Star General in Maryland, 160 Years Late. November 11, 2024. https://www.washingtonpost.com/dc-md-va/2024/11/11/harriet-tubman-brigadier-general-civil-war-underground-railroad/
- “Harriet Tubman’s Story.” National Parks Conservation Association. n.d. https://www.npca.org/articles/2162-harriet-tubman-s-story .
- Harriet Tubman Timeline. University at Buffalo. n.d. http://math.buffalo.edu/~sww/0history/hwny-tubman.html.
- “Tubman.” National Parks Service. n.d. https://www.nps.gov/hatu/learn/historyculture/htubman.htm .
- Larson, Kate Clifford, Bound for the Promised Land: Harriet Tubman, Portrait of an American Hero . New York, Ballantine, 2004.
- London, Nicole, Stanley, Nelson and Christopher, Haley. 2022. Harriet Tubman: Visions of Freedom . [San Francisco, California, USA]: PBS.
- Owens, D. C. Harriet Tubman’s disability and why it matters. Ms. Magazine. February 10, 2022. https://msmagazine.com/2022/02/10/harriet-tubman-disability-democracy/
- Prescod-Weinstein, Dr. Chanda. “Harriet Tubman, Astronomer Extraordinaire.” Ms. Magazine, February 3, 2023. https://msmagazine.com/2022/02/03/harriet-tubman-astronomer-underground-railroad-north-star-nasa/ .
- Shoot, B. (2021). The brain injury that helped end slavery. Folks. n.d. https://folks.pillpack.com/brain-injury-helped-end-slavery/
- “The African American Odyssey: A Quest for Full Citizenship Abolition, Anti-Slavery Movements, and the Rise of the Sectional Controversy.” Library of Congress, February 9, 1998. https://www.loc.gov/exhibits/african-american-odyssey/abolition.html .
- “When John Brown Met Harriet Tubman.” National Parks Service. n.d. https://www.nps.gov/hafe/learn/historyculture/when-john-brown-met-harriet-tubman.htm .
- Wickenden, Dorothy. “Liberty or Death: On the Prophetic Visions and Unflinching Will of Harriet Tubman.” Literary Hub, March 31, 2021. https://lithub.com/liberty-or-death-on-the-prophetic-visions-and-unflinching-will-of-harriet-tubman/ .
- http://www.math.buffalo.edu/~sww/0history/hwny-tubman.html
Image Citations
- Griffith, Dennis, James Thackara, and J Vallance. Map of the State of Maryland laid down from an actual survey of all the principal waters, public roads, and divisions of the counties therein; describing the situation of the cities, towns, villages, houses of worship and other public buildings, furnaces, forges, mills, and other remarkable places; and of the Federal Territory; as also a sketch of the State of Delaware shewing the probable connexion of the Chesapeake and Delaware Bays. [Philadelphia, J. Vallance, 1794] Map. https://www.loc.gov/item/76693265/ .
- Lindsley, Harvey B, photographer. Harriet Tubman, full-length portrait, standing with hands on back of a chair. , ca. 1871. [Between and 1876] Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2003674596/ .
- Powelson, Benjamin F, photographer. Portrait of Harriet Tubman / Powelson, photographer, 77 Genesee St., Auburn, New York. New York, 1868. [Auburn, N.Y.: Benjamin Powelson, or 1869] Photograph. https://www.loc.gov/item/2018645050/ .
- United States Mint. Harriet Tubman 2024 Proof Silver Dollar Coin. 2024. https://catalog.usmint.gov/harriet-tubman-2024-proof-silver-dollar-coin-24CL.html?cgid=harriet-tubman-commemorative-coins#start= 1
- Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture, Photographs and Prints Division, The New York Public Library. "Harriet Tubman; Gertie Davis; Nelson Davis; Lee Cheney; "Pop" Alexander; Walter Green; Sarah Parker; and Dora Stewart " New York Public Library Digital Collections. https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/510d47df-793f-a3d9-e040-e00a18064a99
MLA – Dawson, Shay. "Harriet Tubman-Davis." National Women's History Museum. National Women's History Museum, 2024. Date accessed.
Chicago - Dawson, Shay. “Harriet Tubman-Davis" National Women's History Museum. 2024. www.womenshistory.org/education-resources/biographies/ harriet-tubman .
- Bradford, Sarah Hopkins. Harriet, the Moses of Her People. Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press, 2012. muse.jhu.edu/book/19228 .
- Hobson, Janell, Michelle D. Commander, Dr. Chanda Prescod-Weinstein, Dr. Kate Clifford Larson, Deirdre Cooper Owens, Dr. Edda L. Fields-Black, Janell Hobson, et al. “The Harriet Tubman Bicentennial Project.” Ms. Magazine, February 1, 2023. https://msmagazine.com/tubman200/ .
- Library of Congress. Research guides: Harriet Tubman: Topics in Chronicling America: Search Strategies & Selected Articles. N.d. https://guides.loc.gov/chronicling-america-harriet-tubman/selected-articles.

This biography is sponsored in part by the Library of Congress Teaching with Primary Sources Eastern Region Program, coordinated by Waynesburg University. Content created and featured in partnership with the TPS program does not indicate an endorsement by the Library of Congress.
For further information or questions, please contact [email protected] .
Related Biographies

Stacey Abrams

Abigail Smith Adams

Jane Addams

Toshiko Akiyoshi
Related background, native women and anti-colonialism in the arc of us history, exploring maria tallchief: a dance journey through history, voices of change: analyzing speeches by lgbtq+ women, “when we sing, we announce our existence”: bernice johnson reagon and the american spiritual'.
Home / A Nation Divided, 1832-1877 / Civil War / Life Story: Harriet Tubman
Life Story: Harriet Tubman (ca. 1820–1913)
Freedom fighter.
The story of the Underground Railroad’s most famous conductor and Civil War soldier.
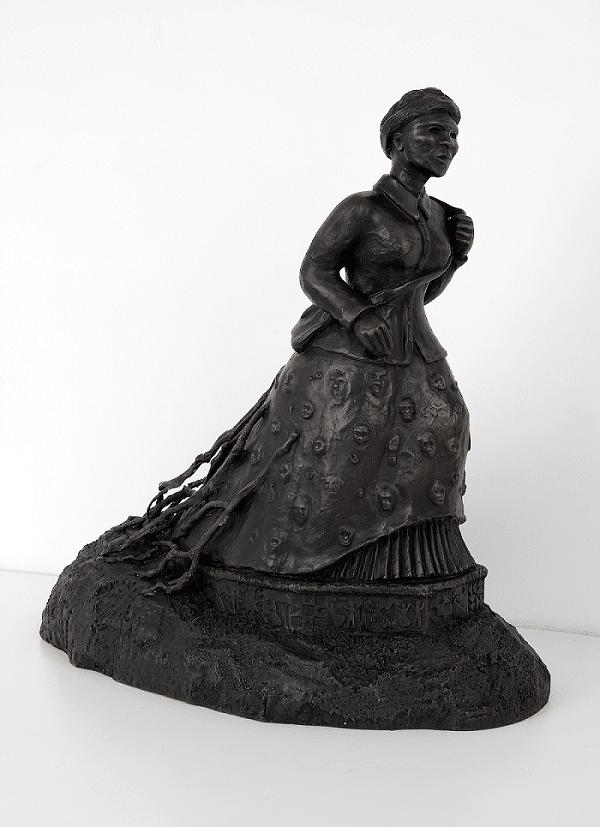

Maquette for “Swing Low, a Harriet Tubman memorial”
Alison Saar, Maquette for “Swing Low: A Harriet Tubman memorial,” 2007. New-York Historical Society, Purchase.
Harriet Tubman was born around the year 1820 in Dorchester County, Maryland. Her parents named her Araminta Ross. Her mother, Harriet Green, was an enslaved woman owned by Mary Pattinson Brodess. Her father, Ben Ross, was an enslaved man owned by Anthony Thompson. They were brought together when Mary and Anthony got married. Ben and Harriet had nine children.
Araminta inherited the status of enslaved person from her mother. She was put to work around the age of five. When she was young, her enslaver’s son sold three of Araminta’s sisters to distant plantations, breaking up her family. Araminta’s mother fought successfully to keep the rest of her children with her, but Araminta learned as a child that her life would never be secure so long as she was enslaved.
Araminta suffered violence at the hands of her enslavers and other white people in her community. Her body was scarred from beatings. When she was a teenager, an overseer in town hit her in the head with a two-pound weight. Because of this attack, Araminta suffered from seizures, severe headaches, and narcolepsy for the rest of her life.
Araminta married John Tubman, a local free Black man, in 1844. The marriage did not change her legal status and she remained enslaved. Around the time of her marriage, she took the name Harriet, probably in honor of her mother. In 1849, she learned that her enslaver was planning to sell her. She decided to take her own freedom rather than submit. John did not join her and eventually remarried. Her brothers set off with her but grew frightened and returned to the plantation. Harriet continued on her own. She was aided by abolitionists who belonged to the Underground Railroad network. When she reached Philadelphia, in the free state of Pennsylvania, she found a job and started a new life.
Harriet’s fame spread throughout the country, and she began to speak at abolitionist events. At the height of her fame, governments in the South offered rewards totaling $40,000 for her capture.
In 1850, Harriet learned that her niece Kessiah was going to be sold. She traveled back to Maryland and helped Kessiah and her family escape to Philadelphia. This was the first of 19 trips Harriet made to guide her family, friends, and anyone else who wanted to use the Underground Railroad to take their own freedom. After the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 made it impossible for escaped slaves to live safely in Northern states, Harriet changed her route and brought people all the way to Canada.
Harriet was militant in her approach to guiding people on the Underground Railroad. She carried a gun and threatened to kill any person who wanted to turn back and endanger the group. She used a tonic to put babies into a deep sleep, so their cries would not draw attention during nighttime travels. She is estimated to have saved about 70 to 80 people, including her elderly parents. Her fame spread throughout the country, and she began to speak at abolitionist events. At the height of her fame, governments in the South offered rewards totaling $40,000 for her capture. Militant abolitionist John Brown admired her greatly. He called her “General Tubman” and consulted with her before conducting his raid on Harper’s Ferry. Harriet and John both believed that extreme acts were necessary to end slavery in the United States.
When the Civil War broke out in 1861, Harriet focused her efforts on supporting the Union Army. She was assigned to the 2 nd South Carolina Colored Troops under Colonel James Montgomery. She was given the jobs of cook and nurse because of her race and sex, but Harriet was soon performing more militaristic duties. Her knowledge of the local terrain and her Underground Railroad contacts made her an ideal spy. Her race and sex made it easy for her to slip behind Confederate lines to gather information. She did not abandon her efforts to help enslaved people—she helped the enslaved people who escaped during the war find shelter and safety. But despite all of her work, Harriet was paid very little. She supplemented her income by selling baked goods to Union soldiers.
On June 2, 1863, Harriet became the first woman to lead Union troops into battle. Based on information she had gathered, she led a group of Colonel Montgomery’s troops in a raid down the Combahee River. They destroyed Confederate Army ammunition depots and storage houses and burned several large plantations. They liberated 750 people from slavery in a single night.
When the war ended, Harriet settled in Auburn, New York, on land she had purchased before the war. Her parents and family were already living there. In 1868, she applied for a military pension but was denied, although Black male spies and soldiers received them. In 1869, she married a Black Civil War veteran named Nelson Davis, and in 1874, they adopted a baby girl named Gertie. It was only after Nelson’s death in 1888 that Harriet began to receive a widow’s pension from the government.
Harriet remained politically active after the war. She joined Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton in their campaign for women’s rights. She attended the founding meeting of the National Association of Colored Women in 1896, where she met and supported Ida B. Wells . Yet Harriet never had enough money to live comfortably. In 1898, she petitioned the government for her military pension and back pay, but instead they increased her widow’s pension from $8 to $20 a month.
Harriet never stopped working to improve her community and country. In 1908, she opened the Tubman Home for Aged and Indigent Negroes, a charity home that she hoped would carry on her work after her death. She died there in 1913 surrounded by friends and family.
- abolitionist: A person who fought to end slavery in the United States.
- ammunition: Explosive items used by the military.
- Confederate: Relating to the group of states that seceded from the United States before the Civil War in order to preserve slavery.
- contraband: The name the Union Army gave to all enslaved people who were liberated or escaped to Union lines during the American Civil War.
- Fugitive Slave Act of 1850: A law that required Northern states to return runaway enslaved people to their enslavers.
- narcolepsy: A condition that causes a person to fall into a deep sleep without warning.
- overseer: A person who was in charge of supervising the work of enslaved people.
- pension: A sum of money regularly paid to a former soldier for life in recognition of their service.
- Underground Railroad: A network of safe houses that helped enslaved people travel to freedom.
- Union: The name for the states that remained a part of the United State during the Civil War.
Discussion Questions
- How did Harriet Tubman’s childhood affect her choices as an adult?
- What extreme actions did Harriet Tubman take to dismantle slavery in the United States?
- How did Harriet support the Union war effort? What recognition did she receive for her actions?
- How did Harriet Tubman’s race and sex affect her opportunities in life?
Suggested Activities
- APUSH Connection: 5.8 Military Conflict in the Civil War
- Harriet Tubman existed at an intersection of a variety of oppressed identities: Black, woman, poor, and dis/abled. Be sure to highlight each of these aspects of her identity when teaching her story.
- After reading this life story, invite students to read the record of Harriet Tubman’s recollections of her early work guiding people to freedom. Why are all the sources we have on her life second hand? How does this complicate learning her story?
- Most biographies of Harriet Tubman minimize her role in the American Civil War. Ask students to consider why this might be the case, and why it is important to include this part of her story. Use this life story to move students beyond the typical narrative of Harriet Tubman’s life and legacy.
- Invite students to watch the film Harriet and consider how filmmakers adapted Harriet Tubman’s life for the big screen. What changes did they make? What do these choices reveal?
- Invite students to research the story of John Brown and write an essay considering why he and Harriet Tubman admired each other’s approach to abolition.
- To learn more about Black women’s role in the post-Civil War fight for women’s rights, visit “All Bound Up Together.”
- Harriet Tubman dedicated her final years to provide a safe home for her family and vulnerable members of her community. To learn more about Black women’s role in post-war community-building, read Life Story: Louisa Smith , Information Wanted , Life Story: Matilda Hughes , and Life Story: Elizabeth Keckley .
- Harriet Tubman was one of many Black women abolitionists operating in the antebellum period. After reading this story, invite students to learn more about the experience of Black women anti-slavery activists in the antebellum period, and compare the challenges and experiences of each: Elizabeth Jennings , Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl , Salem Female Anti-Slavery Society , Resistance , Harriet Robinson Scott , and Sojourner Truth .
- Harriet Tubman’s story illustrates one way women could take an active role in the American Civil War. For a larger lesson on this topic, teach this life story together with any of the following: Nursing , Women’s War Production , Sanitary Fairs , Smuggling , and Women Soldiers .
ACTIVISM AND SOCIAL CHANGE; POWER AND POLITICS
New-York Historical Society Curriculum Library Connections
- For more about the effects of the Fugitive Slave Law, see New York Divided .
- For more about Black Americans’ experiences after the Civil War, explore Black Citizenship in the Age of Jim Crow .
Quick Links

Major support for Women & the American Story provided by

Additional support provided by

Lead support for New-York Historical’s teacher programs provided by

- Plan Your Visit
- Group Visits
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Accessibility Options
- Sweet Home Café
- Museum Store
- Museum Maps
- Search the Collection
- Initiatives
- Museum Centers
- Publications
- Digital Resource Guide
- The Searchable Museum
- Exhibitions
- Freedmen's Bureau Search Portal
- Early Childhood
- Talking About Race
- Digital Learning
- Strategic Partnerships
- Ways to Give
- Internships & Fellowships
- Today at the Museum
- Upcoming Events
- Ongoing Tours & Activities
- Past Events
- Host an Event at NMAAHC
- About the Museum
- The Building
- Meet Our Curators
- Founding Donors
- Corporate Leadership Councils
- NMAAHC Annual Reports
Harriet Tubman

Harriet Tubman has been known by many names—Araminta, Moses, conductor, daughter, sister, wife, mother, aunt. All encompass the intersecting identities and experiences that Harriet Tubman encompassed over her lifespan. In March 2022, on the bicentennial of her birth, we look beyond these names to capture not only Harriet Tubman the icon, but Harriet the woman, and Harriet’s legacy of care, activism and bravery that influenced Black women across time.
Objects related to Harriet’s life highlight her impact on her contemporaries—such as the shawl gifted to her by Queen Victoria to acknowledge her international impact. Personal objects like her hymnal reveal her domestic life as a wife and mother, and the devout religious beliefs that inspired her to “conduct” hundreds of African Americans to freedom from bondage.
We use the video player Able Player to provide captions and audio descriptions. Able Player performs best using web browsers Google Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. If you are using Safari as your browser, use the play button to continue the video after each audio description. We apologize for the inconvenience.
In the years after her death in 1913, Harriet became a feminist icon for Black women’s organizations, and Black women artists including Betye Sarr, Alison Saar, Bisa Butler, Faith Ringgold and Elizabeth Catlett saw in Harriet the inspiration for the courage and creativity to document the struggle for equality as Black and as women. A pioneer in what it means to be regarded as an icon, Harriet Tubman served as a physical manifestation of liberation for many. On the bicentennial of her birth, this dynamic woman of many trades continues to be revered as an American hero and a symbol of freedom.

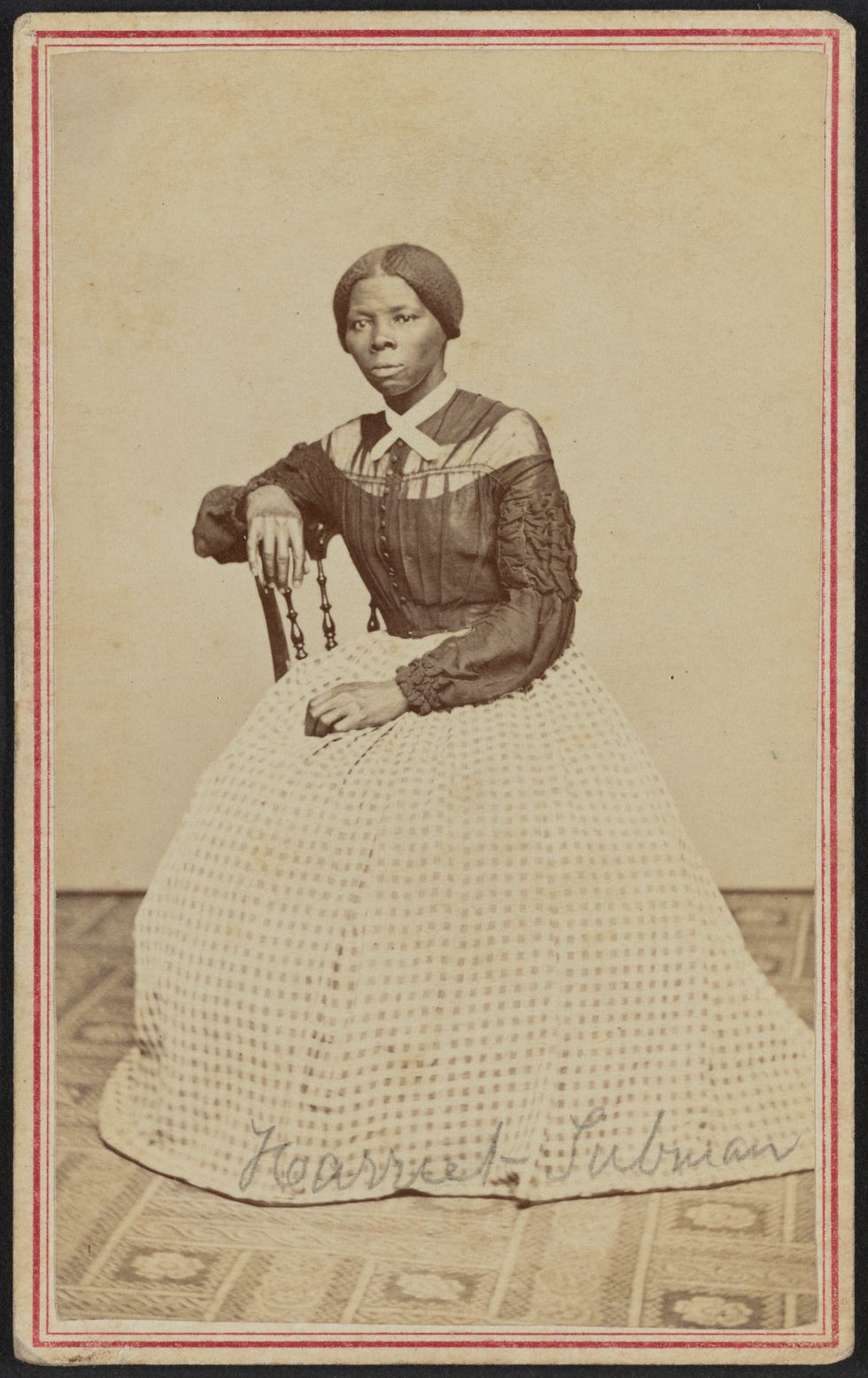
Carte-de-visite portrait of Harriet Tubman, 1868–69. Photograph by Benjamin F. Powelson.
Best known as the enslaved woman who brought emancipation to anyone who crossed her path, the legacy of Harriet Tubman’s lifework has inspired countless people across generations and geographic locations. Tubman was born into chattel slavery as Araminta “Minty” Ross in Dorchester County, Maryland, around 1822. Tubman was put into labor at an early age, and by the age of ten, she was hired out as a woodcutter, pest trapper and field worker. She preferred these jobs over domestic tasks in the “big house” under the scrutiny of her white mistress. Tubman’s strength of character was visible at this early stage. At age twelve, her intervention in a violent exchange between an overseer and a fugitive slave left her with substantial injuries.
After being struck on the head with a large iron weight, Tubman began suffering from severe headaches and a chronic sleep disorder called narcolepsy. In addition to her sudden attacks of sleep, she also experienced vivid religious dreams and hallucinations throughout her life. This injury left her anything but impaired.
In her final years on the plantation before escaping, Tubman became a familiar figure in the fields. A primed field hand, she was described as a “small, muscular woman” standing at 4’11”, yet carrying half cords of wood like any other man in the fields. She was often seen with her skirt looped around her waist and a vividly colored bandanna tied around her head.

In Harriet Tubman I Helped Hundreds to Freedom , 1946–47; printed 1989. Created by Elizabeth Catlett. 2017.21.7
In Harriet Tubman I Helped Hundreds to Freedom
This 1946–47 linocut expresses the major themes that connect the large body of work Elizabeth Catlett (1915–2012) produced during her lifetime: race and feminism. Her medium of choice changed from sculpture to printmaking after moving to Mexico to join the leftist art collective, the Taller de Gráfica Popular (TGP). Catlett’s artistry and politics inspired her linocuts featuring prominent Black people and themes. Much of the work she produced during her time in Mexico reflected the radical, worker-centered activism of the TGP and the Civil Rights Movement in the United States.
This linocut of Harriet Tubman from the series " The Black Woman (formerly the Negro Woman) " reveals Catlett’s desire to explore these major issues through the lens of Black women. We see Tubman in the simple attire that reflects the homespun clothing of enslaved women and the Black women sharecroppers of the 1940s, which collapses the historical narrative to show how long Black women have struggled against oppression. Tubman’s sinewy arm points towards freedom for the hundreds of Black people who come behind her, pointing to her strength and the weariness of the labor of this long journey.
God’s time [Emancipation] is always near. He set the North Star in the heavens; He gave me the strength in my limbs; He meant I should be free. Harriet Tubman to Ednah Dow Cheney New York City, ca. 1859
During this period, the dream of freedom had spread across antebellum plantations and Tubman’s visions were no different. First, her father was set free when she was about eighteen, and then she also learned that the last will of her previous owner manumitted Tubman’s family. However, her new owner refused to acknowledge this and Tubman’s mother, Tubman herself and her siblings remained in bondage.
Her desire for freedom only grew over the years, particularly after marrying John Tubman, a freedman. The threat of her family’s separation and her difficult marriage forced Tubman to take action. On September 17, 1849, Tubman and her two brothers set out to escape the plantation, heading north. Her brothers soon turned back, and Tubman completed her journey alone with the help of the Underground Railroad on the nearly hundred-mile journey to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. But her dreams of flying over corn and cotton, the North Star beckoning, did not end with her finding liberty.
Between 1850 and 1860, Tubman made over a dozen journeys across the Mason-Dixon line, guiding family and friends from slavery to freedom. During this time, her captaincy earned her the nickname “Moses," after the religious leader. The 1850 Fugitive Slave Act passed by Congress created a more dangerous journey for any enslaved person traveling northbound. With the government compelling northern law enforcement to now capture free Black Americans, Tubman’s strategies as a conductor became more militant and she began carrying a firearm for protection.
I was the conductor of the Underground Railroad for eight years, and I can say what most conductors can't say — I never ran my train off the track and I never lost a passenger. Harriet Tubman Suffrage Convention, New York, 1896

Golden Legacy Illustrated History Magazine: The Saga of Harriet Tubman, "The Moses of Her People," Vol. 2, 1967. Published by Fitzgerald Publishing Co. 2019.22.12
The Saga of Harriet Tubman, "The Moses of Her People"
The Golden Legacy Illustrated History Magazine is a graphic novel series published by Bertram A. Fitzgerald. These graphic novels were produced between 1966 and 1976 to “ implant pride and self-esteem in black youth while dispelling myths in others. ” “We believe this can be accomplished through our visual presentation of worldwide achievements in an effortless and enjoyable manner with a magazine which can be widely distributed.”
This issue about Harriet Tubman was written by Joan Bacchus Maynard , an artist, community organizer and preservationist who was a member of the grassroots organization to save Weeksville, a neighborhood in Brooklyn, New York, founded by free African Americans. Tubman is depicted on the cover as a fierce and courageous figure, and the danger of her work as conductor is palpable in the rifle she carries to protect herself and those she leads to freedom.
Through her friendship with fellow abolitionists such as Frederick Douglass, Tubman created her own network within the Underground Railroad. After a decade as a conductor, Tubman was called to action when the American Civil War began in 1861. She proved herself resourceful as a nurse, and she treated Union soldiers and fugitive African Americans alike using the medicinal value of native plants, a skill she learned as a young, enslaved woman working in the woods. After just two years of service, Harriet was tasked with moving behind enemy lines to gather intelligence from a web of informants. First a nurse, laundress and cook, now a spy and scout, Harriet Tubman also became the first woman in US history to lead a military expedition when she led Black troops in the Combahee River Raid in South Carolina in 1863.
I had reasoned this out in my mind; there was one of two things I had a right to, liberty, or death; if I could not have one, I would have the other; for no man should take me alive; I should fight for my liberty as long as my strength lasted, and when the time came for me to go, the Lord would let them take me. Harriet Tubman to Sarah Bradford Harriet, The Moses of Her People (1886)
Despite her renown and her heroism, Tubman was only paid $200 for the entirety of her service—less than half of what her white male counterparts received monthly. Additional compensation from the government came several decades later in the form of a pension as the widow of Nelson Davis, a Black union soldier she married after the war rather than for her own service. After the introduction of a bill by a Republican congressmember to grant Tubman a pension, President William McKinley later signed a bill granting Tubman a pension for her role as an Army nurse. Financial issues throughout the remainder of her life did not stop Tubman from lending her service to anyone in need. In 1896, on the land adjacent to her home, Harriet’s open-door policy flowered into the Harriet Tubman Home for the Aged and Indigent Colored People, where she spent her remaining years until her death in 1913. This home, located in Auburn, New York, a city about an hour outside of Syracuse and near Seneca Falls—the recognized birthplace of American feminism and women’s rights—became a site of pilgrimage for African Americans.
Angela Tate, Curator at the National Museum of African American History and Culture gives a deeper look into objects related to Harriet Tubman's life.

Postcard for the Harriet Tubman Home for the Aged

Pinback button for the Harriet Tubman Home

Brick from the Harriet Tubman Home
The NMAAHC bridges the connection between emancipation and modern-day freedom struggles in the collection of Harriet Tubman’s personal effects. In 2009, Charles L. Blockson, a historian and expert on the Underground Railroad, donated to the Museum a collection of items relating to Harriet Tubman’s life and legacy that were collected and given to him by Tubman’s descendants. Items such as a fork and knife from the Tubman household demystify and ground Tubman, giving her a sense of personhood.

Knife and fork from the Tubman household, 1870s.

Apron owned by Harriet Tubman, 1870–1913.

Handkerchief owned by Harriet Tubman, 1870s–1913.
The legacy of Harriet Tubman holds multitudes. Myths and legends about her acts of valor on the Underground Railroad have inspired artists to retrace her courage and skill in works of art. Tubman’s name readily evokes the image of strength (as seen in the christening of a cargo ship named after her in World War II ) and the complexities of being a Black woman—a pillar of courage to the public and a place of refuge for one’s family, friends and community.

Gospel Hymns No. 2 , 1876. Personal hymnal of Harriet Tubman. 2009.50.25
Harriet Tubman was a hero and icon during her lifetime and afterwards. Objects in the Museum's collection tell the story of her life at home with family and the accolades she received from the public. Her personal piety formed the basis of her pursuit of freedom and to go back and conduct others to freedom. Tubman’s small 8 x 5 inch hymnal is inscribed with the names of its two owners: Harriet Tubman and her great-niece Eva Northup. Though Tubman never learned to read, her spiritual beliefs were strengthened by the hymns and spirituals associated with African American uplift and freedom. Tubman’s favorite hymn was “Swing Low, Sweet Chariot,” a hymn associated with the hidden messages between conductors on the Underground Railroad and the bondspeople traveling through it. The importance of this hymn to Tubman’s legacy is present in Alison Saar’s sculpture titled after the song.

Swing Low: Harriet Tubman Memorial, 2007. Created by Alison Saar. 2011.63
Swing Low: Harriet Tubman Memorial
Alison Saar (b. 1956), is a Los Angeles-based sculptor and mixed media artist who focuses on women and the African diaspora. This sculpture is titled after a Negro spiritual “Swing Low, Sweet Chariot,” which expresses a longing for a return to heaven. But it could also be a song of liberation, where the lyrics held coded messages that told of when Underground Railroad conductors like Harriet Tubman would arrive to assist in stealing away to freedom. This is a small-scale version of Saar’s 13 feet tall monument to Harriet Tubman that stands in Harriet Tubman Memorial Plaza, in south Harlem at St. Nicholas Avenue and Frederick Douglass Boulevard at West 122nd Street. Saar depicts Tubman "not as the conductor of the Underground Railroad, but as the train itself, an unstoppable locomotive.” Tubman’s forward motion tears up the roots of slavery. The skirt of her dress holds chains, knives, glass bottles and the faces of those she led to freedom.
Interview with Alison Saar, the artist who created "Swing Low: A Memorial to Harriet Tubman" at West 122nd Street, St. Nicholas Avenue and Frederick Douglass Boulevard.

Photograph album owned by Emily Howland showing the last page featuring a photograph of Harriet Tubman.
In 2017, the common image of Harriet Tubman—that of an elderly woman in a white shawl—was forever changed with the discovery of a never-before-seen photograph of Tubman from the late 1860s at the back of a photo album owned by Emily Howland. Howland was a philanthropist, suffragist and educator who was also active in abolitionist circles. In 2017, her photo album was acquired jointly by the NMAAHC and the Library of Congress. Of the nearly fifty photographs of abolitionists, educators and statesmen included in the albums pages, there was the newly discovered photograph of Harriet Tubman. The carte-de-visite portrait of Harriet Tubman was taken in Auburn, New York, when Tubman was in her mid-forties. This image of Tubman at the height of her powers is especially interesting when noting how stylish she appears to be. She drapes her ruffled arm gracefully across a chair and the other rests on her checked skirt and she appears solemn yet assured.

I Go To Prepare A Place For You , 2021. Created by Bisa Butler. 2021.38

I Go To Prepare A Place For You
Bisa Butler, an artist who uses textiles and quilting to share stories of African American history and culture, used Benjamin Powelson's portrait of Tubman from the Howland Album to recreate her vibrancy and strength. The quilt’s symbolism displays Tubman's need to conceal herself, her personality, and to express her religious beliefs. According to Butler , the sunflower motif is intended to “acknowledge Harriet Tubman’s reliance (and that of many people escaping slavery) on the North Star to help point the way towards freedom. The sun is also a star, and the sunflower symbolizes that guiding light. The sunflower is known as a spiritual and devotional flower because they follow the sun as it moves from East to West in the sky. The sunflowers appear to worship the sun and I use that to indicate Tubman’s devout faith.”
Portraits of Harriet Tubman in the NMAAHC collection document her as a woman, as a wife and mother, and as a caretaker. Observing these images of Tubman at different stages of her life provides further context for her story and legacy. These images give the famed Underground Railroad conductor a more tangible connection to the significant role of Black women’s activism and highlights the way images shape how we remember important Black women.

Harriet Tubman, 1871–76; printed later. Photograph by Harvey B. Lindsley.

Postcard of Harriet Tubman, Nelson Davis, and daughter Gertie, ca. 1887; printed later. Photograph by William Haight Cheney.

Albumen print of Harriet Tubman, ca. 1908; printed ca. 1920. Photograph by Tarby Studios.

Photographic postcard of Harriet Tubman, 1911–12; printed 1917–30.
The NMAAHC shares the story of Harriet Tubman through its collections relating to her life, her activism, her strength and her community. The materials here provide a second glance at what we think we know and celebrate about Tubman on the 200th anniversary of her birth.
Browse Objects in the NMAAHC Collection Relating to Harriet Tubman
Written by Angela Tate, Curator of Women’s History, and Romya-Jenevieve Jerry, Annie Bell Shepherd Curatorial Intern in African American Women’s History Published on March 4, 2022
https://www.militarytimes.com/military-honor/black-military-history/2018/02/07/general-tubman-female-abolitionist-was-also-a-secret-military-weapon/
http://www.harriet-tubman.org/
https://nmaahc.si.edu/about/news/album-previously-unknown-photo-young-harriet-tubman-go-public-view-first-time
https://nmaahc.si.edu/explore/stories/combahee-ferry-raid

Share Your Story
Because of Harriet, we understand there is always a path forward. Because of Harriet, we are empowered to be bold and confident against all odds. As you reflect on Tubman’s life and legacy, share who you are because of Harriet on social media using #HiddenHerstory.
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Harriet Tubman
By: History.com Editors
Updated: February 20, 2024 | Original: October 29, 2009

Harriet Tubman was an escaped enslaved woman who became a “conductor” on the Underground Railroad, leading enslaved people to freedom before the Civil War, all while carrying a bounty on her head. But she was also a nurse, a Union spy and a women’s suffrage supporter. Tubman is one of the most recognized icons in American history and her legacy has inspired countless people from every race and background.
When Was Harriet Tubman Born?
Harriet Tubman was born around 1820 on a plantation in Dorchester County, Maryland. Her parents, Harriet (“Rit”) Green and Benjamin Ross, named her Araminta Ross and called her “Minty.”
Rit worked as a cook in the plantation’s “big house,” and Benjamin was a timber worker. Araminta later changed her first name to Harriet in honor of her mother.
Harriet had eight brothers and sisters, but the realities of slavery eventually forced many of them apart, despite Rit’s attempts to keep the family together. When Harriet was five years old, she was rented out as a nursemaid where she was whipped when the baby cried, leaving her with permanent emotional and physical scars.
Around age seven Harriet was rented out to a planter to set muskrat traps and was later rented out as a field hand. She later said she preferred physical plantation work to indoor domestic chores.
A Good Deed Gone Bad
Harriet’s desire for justice became apparent at age 12 when she spotted an overseer about to throw a heavy weight at a fugitive. Harriet stepped between the enslaved person and the overseer—the weight struck her head.
She later said about the incident, “The weight broke my skull … They carried me to the house all bleeding and fainting. I had no bed, no place to lie down on at all, and they laid me on the seat of the loom, and I stayed there all day and the next.”
Harriet’s good deed left her with headaches and narcolepsy the rest of her life, causing her to fall into a deep sleep at random. She also started having vivid dreams and hallucinations which she often claimed were religious visions (she was a staunch Christian). Her infirmity made her unattractive to potential slave buyers and renters.
Escape from Slavery
In 1840, Harriet’s father was set free and Harriet learned that Rit’s owner’s last will had set Rit and her children, including Harriet, free. But Rit’s new owner refused to recognize the will and kept Rit, Harriet and the rest of her children in bondage.
Around 1844, Harriet married John Tubman, a free Black man, and changed her last name from Ross to Tubman. The marriage was not good, and the knowledge that two of her brothers—Ben and Henry—were about to be sold provoked Harriet to plan an escape.

After the Underground Railroad, Harriet Tubman Led a Brazen Civil War Raid
Tubman applied intelligence she learned as an Underground Railroad conductor to lead the Combahee Ferry Raid that freed more than 700 from slavery.
6 Strategies Harriet Tubman and Others Used to Escape Along the Underground Railroad
From elaborate disguises to communicating in code to fighting back, enslaved people found multiple paths to freedom.
Harriet Tubman: 8 Facts About the Daring Abolitionist
Born into slavery, Harriet Tubman escaped to freedom in the North in 1849 and then risked her life to lead other enslaved people to freedom.
Harriet Tubman: Underground Railroad
On September 17, 1849, Harriet, Ben and Henry escaped their Maryland plantation. The brothers, however, changed their minds and went back. With the help of the Underground Railroad , Harriet persevered and traveled 90 miles north to Pennsylvania and freedom.
Tubman found work as a housekeeper in Philadelphia, but she wasn’t satisfied living free on her own—she wanted freedom for her loved ones and friends, too.
She soon returned to the south to lead her niece and her niece’s children to Philadelphia via the Underground Railroad. At one point, she tried to bring her husband John north, but he’d remarried and chose to stay in Maryland with his new wife.
Fugitive Slave Act
The 1850 Fugitive Slave Act allowed fugitive and freed workers in the north to be captured and enslaved. This made Harriet’s role as an Underground Railroad conductor much harder and forced her to lead enslaved people further north to Canada, traveling at night, usually in the spring or fall when the days were shorter.
She carried a gun for both her own protection and to “encourage” her charges who might be having second thoughts. She often drugged babies and young children to prevent slave catchers from hearing their cries.
Over the next 10 years, Harriet befriended other abolitionists such as Frederick Douglass , Thomas Garrett and Martha Coffin Wright, and established her own Underground Railroad network. It’s widely reported she emancipated 300 enslaved people; however, those numbers may have been estimated and exaggerated by her biographer Sarah Bradford, since Harriet herself claimed the numbers were much lower.
Nevertheless, it’s believed Harriet personally led at least 70 enslaved people to freedom, including her elderly parents, and instructed dozens of others on how to escape on their own. She claimed, “I never ran my train off the track and I never lost a passenger.”
Harriet Tubman's Civil War Service
When the Civil War broke out in 1861, Harriet found new ways to fight slavery. She was recruited to assist fugitive enslaved people at Fort Monroe and worked as a nurse, cook and laundress. Harriet used her knowledge of herbal medicines to help treat sick soldiers and fugitive enslaved people.
In 1863, Harriet became head of an espionage and scout network for the Union Army. She provided crucial intelligence to Union commanders about Confederate Army supply routes and troops and helped liberate enslaved people to form Black Union regiments.
Though just over five feet tall, she was a force to be reckoned with, although it took over three decades for the government to recognize her military contributions and award her financially.
Harriet Tubman’s Later Years
After the Civil War, Harriet settled with family and friends on land she owned in Auburn, New York . She married former enslaved man and Civil War veteran Nelson Davis in 1869 (her husband John had died 1867) and they adopted a little girl named Gertie a few years later.
Harriet had an open-door policy for anyone in need. She supported her philanthropy efforts by selling her home-grown produce, raising pigs and accepting donations and loans from friends. She remained illiterate yet toured parts of the northeast speaking on behalf of the women’s suffrage movement and worked with noted suffrage leader Susan B. Anthony .
In 1896, Harriet purchased land adjacent to her home and opened the Harriet Tubman Home for Aged and Indigent Colored People. The head injury she suffered in her youth continued to plague her and she endured brain surgery to help relieve her symptoms. But her health continued to deteriorate and eventually forced her to move into her namesake rest home in 1911.
Pneumonia took Harriet Tubman’s life on March 10, 1913, but her legacy lives on. Schools and museums bear her name and her story has been revisited in books, movies and documentaries.
Harriet Tubman: $20 Bill
Tubman even had a World War II Liberty ship named after her, the SS Harriet Tubman.
In 2016, the United States Treasury announced that Harriet’s image will replace that of former President and slaveowner Andrew Jackson on the $20 bill. Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin (who served under President Trump) later announced the new bill would be delayed until at least 2026. In January 2021, President Biden's administration announced it would speed up the design process to mint the bills honoring Tubman's legacy.

HISTORY Vault: Black History
Watch acclaimed Black History documentaries on HISTORY Vault.
Early Life. Harriet Tubman Historical Society.
General Tubman: Female Abolitionist was Also a Secret Military Weapon. Military Times.
Harriet Tubman Biography. Biography.
Harriet Tubman Home for the Aged, Residence, and Thompson AME Zion Church. National Park Service.
Harriet Tubman Myths and Facts. Bound for the Promised Land: Harriet Tubman Portrait of An American Hero by Kate Clifford Larson, Ph.D.
Harriet Tubman. National Park Service .
Harriet Tubman. National Women’s History Museum.
Harriet Tubman: The Moses of Her People. Harriet Tubman Historical Society.
Harriet Tubman Underground Railroad. National Park Service.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
African American Heritage

Harriet Tubman (c. March 1822 - March 10, 1913)
Harriet Tubman, born Araminta Ross in Dorchester County, Maryland, was one of the most famous conductors on the Underground Railroad, an abolitionist, suffragist, activist, and served in the Civil War as leader, nurse, cook, scout, and spy. Tubman was arguably the most successful individual who personally led enslaved people to freedom through her service on the Underground Railroad, and during the Civil War, she was given the moniker "Moses."
Tubman's early life was spent enslaved in the Eastern Shore region of Maryland, where she was made to do various tasks including childcare, plowing, and working on the wharf. Three of her sisters were sold and separated from the family during her childhood, but her parents, Rit and Ben Ross, continued to resist and keep the remaining family together. In 1849, Harriet Tubman escaped to Philadelphia, but would return to Maryland many times to recover her family and reunite them in freedom.
During the Civil War, Tubman served in South Carolina as a nurse, cook, and spy. She also became the only woman to lead a military action during the War when she led Black troops in the Combahee River Raid on June 2, 1863. The raid involved small ships and troops who destroyed roadways, and burned plantations, and collected supplies of livestock and crops. As a result of the raid, 750 enslaved people were liberated.
Records in the National Archives relating to Harriet Tubman include documents relating to her Civil War pension claims, military service records of her husband Nelson Davis (Charles), legislation establishing and images from dedicating the Harriet Tubman and Underground Railroad National Parks, images from the Harriet Tubman Underground Railroad Byway, and applications for designating places and areas for the National Register of Historic Places related to Tubman.
Search the Catalog for records relating to Harriet Tubman Social Networks and Archival Context - Harriet Tubman

Harriet Tubman, after the Civil War ( NAID 7718799 )
Underground Railroad Resources
National Park Service: What is the Underground Railroad?
The Underground Railroad Byway
Digital Public Library of America: Underground Railroad and the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850
Last Seen: Finding Family After Slavery Project
National Underground Railroad Freedom Center
Harriet Tubman Resources
DocsTeach: Key Figures Who Worked to End Slavery
DocsTeach: Documents relating to Harriet Tubman
Legislative Archives: Congress and Harriet Tubman's Claim for Pension
Library of Congress: Harriet Tubman Resource Guide
National Park Service: Harriet Tubman sites
US House of Representatives: The "Very Deserving Case" of Harriet Tubman
Harriet Tubman: Timeline of Her Life, Underground Rail Service and Activism
In addition to freeing slaves, Tubman was also a Civil War spy, nurse and supporter of women's suffrage.

After escaping slavery on her own in 1849, Harriet Tubman helped others journey on the Underground Railroad . From 1850 to 1860 she made an estimated 13 trips and rescued around 70 enslaved people, including many members of her family. She also provided information so that others could find their way north to freedom. Tubman aided so many in escaping slavery that she was called "Moses."
Wanting to bring an end to slavery, Tubman also coordinated with abolitionists. During the Civil War , she became a nurse and a spy for the Union. And despite her ongoing financial struggles, she continued to fight for equality and justice by speaking out against prejudice and advocating women's suffrage. It's clear Tubman led a momentous life that made the world a better place.
c. 1822: Tubman is born as Araminta "Minty" Ross in Maryland's Dorchester County
Her parents, Ben Ross and Harriet "Rit" Green, are both enslaved, meaning Ross had the same status at birth.
Though her birthdate has often been listed as around 1820, a record from March 1822 lists that a midwife had been paid for tending to Green, which suggests the birth may have taken place in February or March of that year.
c. 1828: Tubman is about five or six years old when her enslavers hire her out to tend to an infant. She is whipped for any perceived mistakes.
c. 1829: Around the age of seven, Tubman is again hired out. Her duties include walking into wet marshes to check muskrat traps. She becomes ill with measles and returns to her mother to recover.
c. 1834-36: An overseer throws a two-pound weight at another slave but hits Tubman's head. She barely survives the devastating injury and experiences headaches for the remainder of her life. It's possible this injury led to her suffering from temporal lobe epilepsy , which could explain her visions and sleeping spells.
c. 1835: Tubman works as a field hand, which she prefers to inside tasks.
c. 1830s: Two of Tubman's older sisters are sold and transported out of Maryland.
1840: Tubman's father is freed from slavery.
1844: She weds John Tubman, a free Black man, though her status as a slave means the union is not legally recognized. Upon marriage, Tubman adopts her mother's name of Harriet.
March 7, 1849: Tubman's owner dies, which makes her fear being sold.
September 17, 1849: Tubman heads north with two of her brothers to escape slavery. However, the men become nervous and convince their sister to return.
October 1849: Tubman runs away
She follows the North Star and makes it to Philadelphia. As Pennsylvania is a free state, she has escaped enslavement.
September 18, 1850: The Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 passes. It requires all parts of the United States, even states that had outlawed slavery, to participate in the return of runaway slaves.
December 1850: Tubman helps rescue a niece and her niece's children after learning they are supposed to be sold at auction.
1851: Tubman tries to bring her husband north, but he decides to remain with his second wife, a free Black woman. Tubman instead guides another group to Canada, where they will be outside the reach of the Fugitive Slave Act.
December 1854: Tubman helps a group that includes three of her brothers travel to Canada.
READ MORE: How Harriet Tubman and William Still Helped the Underground Railroad
June 1857: Tubman brings her parents from Maryland to Canada
Her father is in danger because he has been helping the Underground Railroad.
April 1858: In Canada, Tubman meets abolitionist John Brown . She learns of his plans to spark a slave rebellion in the United States and agrees to gather recruits for the cause.
October 16, 1859: Brown's raid on the federal armory at Harper's Ferry in Virginia (now West Virginia) takes place. Tubman does not participate, perhaps due to illness.
1859: Tubman purchases a property in Auburn, New York, from antislavery politician William H. Seward . Having been unhappy in Canada, her parents join Tubman there.

April 27, 1860: In Troy, New York, Tubman helps former slave Charles Nalle elude the U.S. marshals who intend to return him to his enslaver.
December 1860: Tubman makes her last trip on the Underground Railroad
1862: Following the start of the Civil War, Tubman joins Union troops in South Carolina. She becomes a nurse, while also running a wash house and working as a cook to earn money.
c. 1863: Tubman serves as a spy for the Union
She coordinates with former slaves from the area to gather information about the opposing Confederate forces.
READ MORE: Harriet Tubman's Service as a Union Spy
June 1-2, 1863: Tubman leads an armed raid up the Combahee River raid in South Carolina. The mission destroys Confederate supplies and frees more than 700 enslaved people. Tubman is the first woman to head a military expedition in the United States.
July 1863: After the 54th Massachusetts Infantry, whose soldiers were African American volunteers, suffers devastating losses during a bloody battle at Fort Wagner, Tubman helps bury the dead and aids survivors.
June 1864: Tubman is granted a furlough and goes to Auburn to visit her parents.
1865: Tubman nurses Black soldiers at Fort Monroe in Virginia. After the Civil War ends, she visits Washington, D.C., and informs the surgeon general that Black soldiers are experiencing harsh conditions in military hospitals.
READ MORE: Inside Harriet Tubman's Life of Service After the Underground Railroad
July 1865: Tubman asks Seward, who is secretary of state, to help her receive payment for her work during the war. She is not successful, due in part to the turmoil of President Abraham Lincoln's assassination and Seward's ongoing recovery from stab wounds suffering during an assassination attempt.
October 1865: Tubman is traveling home by train when a conductor orders her, using a racial slur , to go to a different car. She defends her rights but is forcibly removed.
December 1868: Scenes in the Life of Harriet Tubman , a biography by Sarah Bradford is published (though the official publication date is listed as 1869). The book has multiple inaccuracies but sales raise approximately $1,200 for a financially struggling Tubman.

March 18, 1869: Tubman weds Nelson Davis, a 25-year-old former slave and Civil War veteran.
1873: Tubman is robbed by men who trick her into believing they could provide her with Confederate gold.
1874: Tubman and her husband adopt a daughter, whom they name Gertie Davis.
June 1886: Tubman buys 25 acres of land next to her home in Auburn to create a nursing home for Black Americans.
October 1886: A revised Tubman biography, Harriet, the Moses of Her People , is published.
October 18, 1888: Tubman's husband dies after suffering from tuberculosis.
1890s: Tubman becomes more involved in the movement for women's suffrage.
June 1890: Tubman applies for a pension as a Civil War widow.
October 16, 1895 : Tubman is approved for a war widow pension of $8 a month .
July 1896: Tubman speaks at the founding conference of the National Association of Colored Women.
November 1896: Tubman is introduced by Susan B. Anthony at a suffrage convention in Rochester, New York.
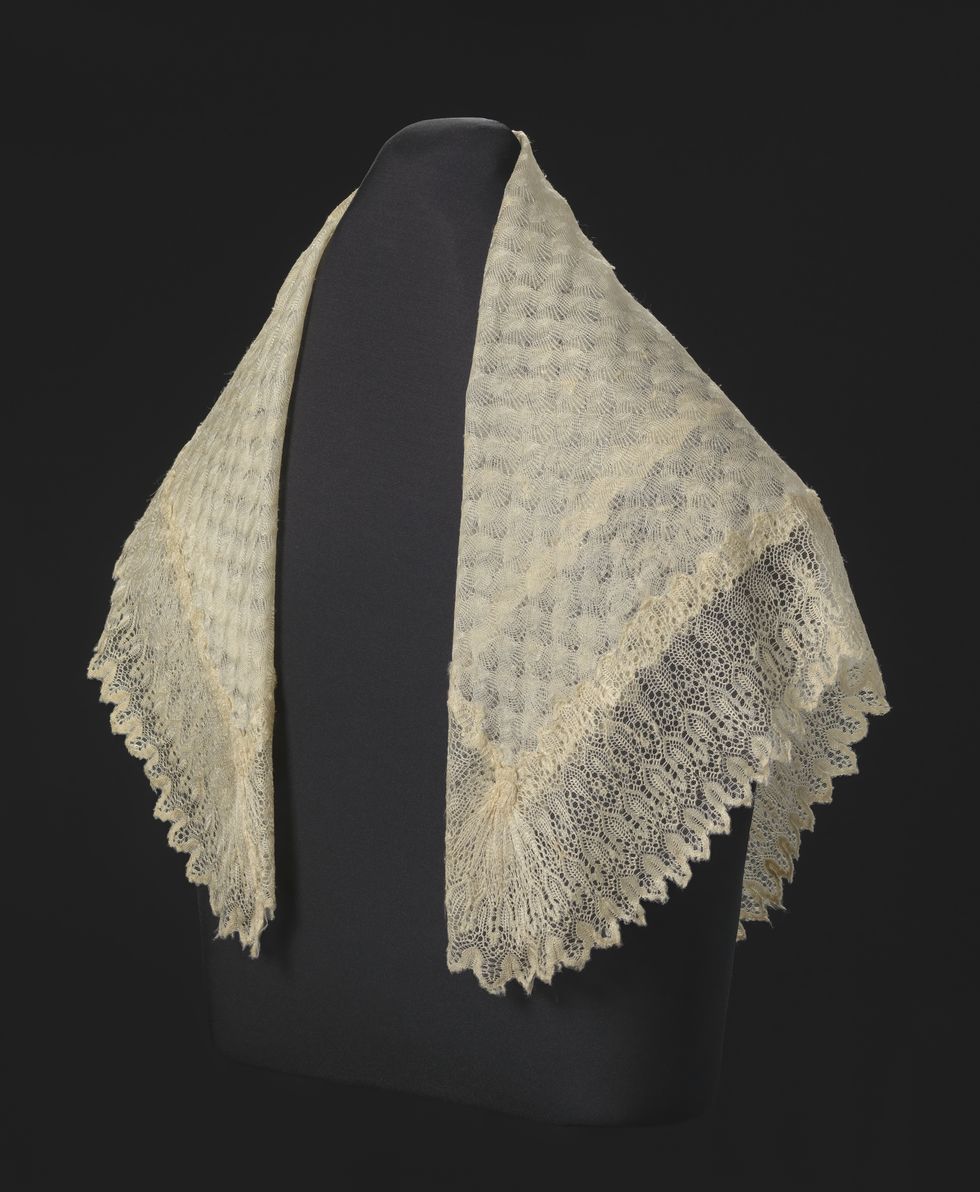
1897: Queen Victoria sends Tubman a shawl and a medal in celebration of her Diamond Jubilee. The queen also invites Tubman to visit England to celebrate her birthday, but Tubman's straitened finances make this an impossibility.

Late 1890s: Tubman undergoes brain surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital in an attempt to alleviate her painful headaches.
1899: Congress raises Tubman's pension to $20 per month, but the increase is for her services as a nurse instead of her military work.

June 23, 1908: Tubman attends the opening ceremony for the Harriet Tubman Home for the Aged. It will be operated by AME Zion Church, which has taken over the deed to the property.
May 19, 1911: An ailing Tubman becomes a resident of the Harriet Tubman Home. Supporters raise funds to finance her care.
March 10, 1913: Tubman dies following a battle with pneumonia
March 13, 1913: Tubman is buried with military honors.

Black History

Kamala Harris

Donald Glover

MLK Almost Didn’t Say “I Have a Dream”

Ray Charles

Whoopi Goldberg

Stevie Wonder

Sylvia Rivera

Jesse Owens

Opal Lee: The “Grandmother of Juneteenth”

13 Powerful Marsha P. Johnson Quotes

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Harriet Tubman (born c. 1820, Dorchester county, Maryland, U.S.—died March 10, 1913, Auburn, New York) was an American bondwoman who escaped from slavery in the South to become a leading abolitionist before the American Civil War.She led dozens of enslaved people to freedom in the North along the route of the Underground Railroad—an elaborate secret network of safe houses organized for ...
Later Life and Legacy During her time with the Union Army, Tubman met her second husband, Nelson Davis. The couple married in 1869 in Auburn, NY where he, Tubman, and her freed family members (one of which was their adopted daughter, Gertie), would live out their days (NPS n.d.).
Harriet Tubman was born around the year 1820 in Dorchester County, Maryland. Her parents named her Araminta Ross. Her mother, Harriet Green, was an enslaved woman owned by Mary Pattinson Brodess. Her father, Ben Ross, was an enslaved man owned by Anthony Thompson. They were brought together when Mary and Anthony got married.
Bradford, an admirer, penned her 1868 biography, Scenes in the Life of Harriet Tubman, with the proceeds going to Tubman and her family. Tubman continued to give freely despite her economic woes.
Harriet Tubman (born Araminta Ross, c. March 1822 [1] - March 10, 1913) was an American abolitionist and social activist. [2] [3] After escaping slavery, Tubman made some 13 missions to rescue approximately 70 enslaved people, including her family and friends, [4] using the network of antislavery activists and safe houses known collectively as the Underground Railroad.
In 2009, Charles L. Blockson, a historian and expert on the Underground Railroad, donated to the Museum a collection of items relating to Harriet Tubman's life and legacy that were collected and given to him by Tubman's descendants. Items such as a fork and knife from the Tubman household demystify and ground Tubman, giving her a sense of ...
Pneumonia took Harriet Tubman's life on March 10, 1913, but her legacy lives on. ... Harriet Tubman Biography. Biography. Harriet Tubman Home for the Aged, Residence, and Thompson AME Zion Church.
Harriet Tubman Underground Railroad Byway hoto reit e rietian Harriet Tubman—Underground Railroad conductor, abolitionist, Civil War spy and nurse, suffragist, and humanitarian. Born into slavery in early 1822 in Dorchester County, Maryland, Tubman rose above horrific childhood adversity to emerge with a will of steel.
Harriet Tubman, born Araminta Ross in Dorchester County, Maryland, was one of the most famous conductors on the Underground Railroad, an abolitionist, suffragist, activist, and served in the Civil ... Tubman's early life was spent enslaved in the Eastern Shore region of Maryland, where she was made to do various tasks including childcare ...
December 1868: Scenes in the Life of Harriet Tubman, a biography by Sarah Bradford is published (though the official publication date is listed as 1869). The book has multiple inaccuracies but ...