- Website Examples
- Website Builder Comparisons
- Hosting Comparisons
- WooCommerce
- Everything Business
- HTTP Errors
- WordPress Errors

Financial Plan in Business Plan: Essential Steps for Success

Executive summary of a financial plan
Revenue streams and sales forecasts, expense breakdown and management, cash flow analysis, capital and funding requirements, budget allocation and financial controls, financial statements overview, profitability and net worth, market analysis and forecasting, liabilities and risk management, financial planning and performance metrics, exit strategy and long-term financial planning.
Creating a financial plan in a business plan is a crucial step that can determine the success or failure of your venture. Whether you’re looking to attract investors, secure loans, or simply ensure long-term growth, a well-crafted financial plan provides the roadmap. It not only showcases your current financial health but also forecasts the potential profitability of your business. This article will summarize the key components and steps to help you craft a comprehensive financial plan aligning with your overall business goals.
Understanding how to incorporate a financial plan into your business strategy can set you apart. By learning the essentials, you’ll be better equipped to manage cash flow, estimate profits, and navigate financial challenges.
What is a financial plan in business planning?
What are the elements of a financial plan?
How to write a financial plan in a business plan?
What should be included in a financial plan?
What is the financial part of the business plan?
How do I write a financial plan?
How to write a financial summary for a business plan?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a financial plan?

Create your online store in minutes!
Looking to sell online? Develop and launch your store with 10Web AI Ecommerce Website Builder.
What is a financial plan in a business plan?
A financial plan is a key part of a business plan . It shows the money side of a business idea. This plan helps owners and investors see if the business can make money.
A financial plan has several important parts. It starts with a sales forecast that predicts how much money the business will make.
Next, it lists all the costs of running the business. This includes things like rent, supplies, and worker pay.
The plan also shows cash flow. This tells when money comes in and goes out of the business. It helps make sure there’s always enough cash to pay bills.
Profit and loss statements are another big piece. They show if the business is making or losing money over time.
The balance sheet lists what the business owns and owes.
Lastly, the plan may include goals for sales growth or profit. It might also have ways to reach these goals. All these parts work together to paint a clear money picture of the business.
Elements of a financial plan in a business plan
The elements of a financial plan in a business plan are essential to understanding your company’s financial health and future potential. They provide a detailed picture of revenue generation, cost management, and profitability.
A financial plan needs clear revenue projections. Sales forecasts help predict future income. This section examines how to make these forecasts and what numbers to include.
Sales forecasting methodology
Sales forecasts use past data and market trends. Start by looking at your sales history. Check for patterns in monthly or yearly sales. Then, factor in things that might change sales. This could be new products, more marketing, or changes in the market.
Use a simple model to start. Take last year’s sales and add expected growth.
As you get more data, you can make your model more complex. Some businesses forecast by product line. Others look at sales channels or customer types.
Remember to account for seasonal changes. Many businesses have busy and slow periods. Your forecast should reflect these ups and downs.
Projected sales numbers
Your sales projections should cover at least the next 12 months. Break this down by month. For years 2 and 3, you can use yearly totals.
Be realistic in your numbers. Aiming low and exceeding your goals is better than aiming too high.
Include unit sales and prices in your forecast. This helps you see if growth comes from selling more or raising prices. If you have multiple products, show sales for each one.
Here’s a simple example of a sales forecast table:
This table shows sales growth for two products over time. It’s a clear way to present your projected income.
A good expense breakdown helps businesses track and control costs. It shows where money goes and helps find ways to save.
Fixed and variable costs
Fixed costs stay the same each month. These include rent, insurance, and salaries.
Variable costs change based on sales or production. Examples are raw materials and shipping fees.
To manage fixed costs:
- Look for cheaper office space
- Negotiate better deals with suppliers
- Cut unneeded services
For variable costs:
- Buy in bulk for discounts
- Find more efficient ways to make products
- Use cheaper shipping methods when possible
Tracking both types of costs helps businesses plan better and save money.
Operational expenses analysis
This looks at the day-to-day costs of running a business. It includes things like:
- Office supplies
- Employee travel
To analyze these expenses:
- List all costs
- Group them by type
- Look at trends over time
- Compare to industry standards
This helps find areas to cut costs. For example, a business might see high utility bills and decide to use energy-saving light bulbs.
Regular expense reviews can lead to big savings. Even minor cuts in daily costs add up over time.
Cash flow analysis helps businesses track money coming in and going out. It shows if a company can pay its bills and invest in growth. This analysis uses cash flow statements and looks at investing and financing activities.
Cash flow statements
A cash flow statement shows how cash moves through a business. It has three parts: operations, investing, and financing.
The operations section shows money from sales and day-to-day activities. This part is key for seeing if the business makes enough to cover costs.
Cash flow statements also show changes in assets and debts. They help spot cash shortages before they happen.
Managers use these statements to plan for slow periods and growth.
Investing and financing activities
Investing activities involve buying or selling long-term assets. This includes things like equipment or property.
Financing activities show how a business raises and repays money.
Examples of financing activities are:
- Taking out loans
- Selling stock
- Paying dividends
These activities affect cash flow but aren’t part of regular operations. They’re important for growth and expansion. Businesses must balance investing in the future with having cash for daily needs.
Money is key for new businesses. You need to figure out how much cash you need and where to get it. This helps you start strong and grow.
Estimates for seed capital
Seed capital is the money to get your business going. You need to add up all your costs. Think about things like:
- Permits and licenses
Make a list of everything you’ll need to buy. Get price quotes when you can. Add some extra for surprise costs. This gives you a good guess at your total seed money needs.
Having enough cash for at least 6 months of expenses is smart. This helps if sales are slow at first.
Investor funding strategy
Once you know how much money you need, plan how to get it. You have a few choices:
- Use your own savings
- Ask family and friends
- Look for angel investors
- Try crowdfunding
- Apply for a business loan
Most new businesses use a mix of these. Your choice depends on how much cash you need and how fast your business might grow.
Make a strong pitch to investors. Show them why your business idea is great. Tell them how you’ll use their money and when they might see returns.
Be ready to give up some control of your business if you take investor money. Decide how much of your company you’re willing to sell.
A business plan needs a strong budget and financial controls. These help a company use its money wisely. Good budgets split cash between different parts of the business.
Budget allocation means giving money to each department. This is based on what the company wants to do. Some areas may get more money than others.
Here’s a simple example of how a small business might split its budget:
Financial controls are rules that keep spending in check. They make sure money is used as planned. This can include:
- Approval steps for big purchases
- Regular budget reviews
- Tracking of all income and spending
These controls help catch problems early. They also show where a company might save money.
Good budget allocation and controls lead to smart financial decisions. They help a business use its resources well. This can give the company an edge over others in its field.
Regular budget checks are key. They let a business change its plans if needed. This keeps the company on track to meet its goals.
Financial statements show a company’s money situation. They help business owners and investors see how well a company is doing. These statements include income, balance sheet, and profit and loss information.

Income statement details
The income statement shows how much money a company makes and spends. It lists sales, costs, and profits over a set time. This could be a month, quarter, or year.
The income statement starts with total sales. Then, it takes away costs like supplies and employee pay. What’s left is the profit.
Sales numbers come from what the company thinks it will sell. Expense numbers come from expected costs.
The difference between sales and expenses is gross profit. Take away other costs like taxes to get net profit. This final number tells if the company made or lost money.
Balance sheet insights
A balance sheet shows what a company owns and owes at a certain time. It has three main parts: assets, liabilities, and equity.
The company owns assets like cash, equipment, and buildings. Liabilities are what the company owes, like loans or bills. Equity is the money left over for owners if all debts are paid.
The balance sheet must always balance. This means assets must equal liabilities plus equity. If they don’t, there’s a mistake somewhere.
A strong balance sheet shows more assets than liabilities. This means the company can pay its bills and has room to grow.
Profit and loss statement analysis
The profit and loss statement (P&L) is like the income statement. It shows if a company made money over time.
The P&L starts with sales and takes away all costs. What’s left is the profit or loss.
This statement helps owners see where money comes from and where it goes.
The P&L can show trends over time. For example, it might show that sales go up in summer. Or it might show that some costs are too high.
A business financial plan shows how much money a company expects to make and keep. It also looks at the total value of the business.
Gross margin and net income projections
Gross margin is the money left after paying for materials and labor. It’s found by subtracting the cost of goods sold from total sales. A higher gross margin means the business is more profitable.
Net income is the profit after all expenses are paid. To project net income:
- Estimate sales for each month or quarter
- Subtract all costs and expenses
- Account for taxes
These numbers help owners see if the business will make money. They also show when cash might be tight.
Shareholder equity calculation
Shareholder equity is the company’s net worth. It’s what’s left after subtracting debts from assets. To calculate it:
- Add up all assets (cash, inventory, equipment)
- Subtract all liabilities (loans, bills to pay)
The result is shareholder equity. A growing net worth over time is a good sign. It means the business is becoming more valuable.
Investors look at this number to see how much their company share is worth. A strong net worth can help attract new investors or get loans.
Market analysis and forecasting help businesses understand their industry and plan for the future. These tools give key insights into competitors, trends, and financial projections.
Competitive market research
Businesses need to know who they’re up against. Market research looks at other companies selling similar products or services. This research covers things like:
- Competitor prices
- Product features
- Marketing strategies
- Market share
Understanding the competition helps a business find ways to stand out. It also shows gaps in the market that a company could fill.
Market research uses surveys, focus groups, and data analysis. These methods give a clear picture of what customers want and how much they’ll pay.
Trends affecting financial projections
Economic shifts and industry changes impact a company’s financial future. Some key trends to watch are:
- New technologies
- Consumer behavior changes
- Government regulations
- Economic growth or recession
These trends shape financial forecasts. For example, a new law might increase costs. Or a tech breakthrough could boost sales.
Financial forecasting uses past data and future predictions. It creates estimates for:
- Sales revenue
Good forecasts help with budgeting and planning. They also show potential investors what to expect.
A financial plan needs to address both liabilities and risks. Liabilities are what a business owes to others. Common liabilities include:
- Credit card balances
- Accounts payable
Tracking liabilities helps businesses understand their true financial position. It’s important to list all debts and when they’re due.
Risk management aims to protect a business from financial losses. Some key risks are:
- Economic downturns
- Property damage
- Data breaches
To manage risks, businesses can:
- Get insurance
- Create emergency funds
- Diversify income streams
- Have backup suppliers
A good risk management plan looks at what could go wrong and how to respond. It helps keep a business stable when facing challenges.
Businesses should review their liabilities and risks regularly. This allows them to spot issues early and make changes as needed. With careful planning, companies can reduce their financial risks and build a stronger future.
Financial planning and performance metrics are key tools for businesses to track their financial health and progress. They provide valuable insights into a company’s efficiency, profitability, and overall financial position.
Key financial ratios
Financial ratios help analyze different aspects of a business’s finances. The debt-to-equity ratio shows how much a company relies on debt versus equity funding. A lower ratio is often seen as better. The current ratio measures a firm’s ability to pay short-term debts. A ratio above 1 is good.
Profit margin is the percentage of sales that turn into profit. A higher margin means more efficient operations. Return on assets (ROA) shows how well a company uses its assets to generate profit. A higher ROA is better.
The inventory turnover ratio reveals how quickly a business sells its inventory. A higher ratio may indicate strong sales or good inventory management.
Performance benchmarking
Benchmarking compares a company’s performance to industry standards or competitors. It helps identify areas for improvement and set realistic goals.
The revenue growth rate is a key benchmark. It shows how fast a company expands compared to others in its industry. Gross profit margin compares a firm’s pricing and production costs to peers.
Market share is another important metric. It reveals a company’s position relative to competitors. Customer acquisition cost and retention rate are vital for assessing marketing effectiveness and customer satisfaction.
Employee productivity metrics, such as revenue per employee, can highlight operational efficiency compared to industry norms.
A business exit strategy is a plan for selling or leaving a company. It helps owners prepare for the future.
Exit plans are part of long-term financial planning.
There are several types of exit strategies:
- Selling to a buyer
- Passing the business to family
- Going public with an IPO
- Merging with another company
- Closing the business
Owners should think about their goals when choosing an exit strategy. Some may want to keep the business in the family. Others might prefer to sell for the highest price.
Exit planning takes time. Experts say to start 3-5 years before leaving.
This gives time to boost the company’s value. It also allows for finding the right buyers or successors.
A good exit plan includes:
- Business valuation
- Financial records
- List of assets
- Growth plans
- Potential buyers
Long-term financial planning helps with exit strategies. It involves setting goals and making plans to reach them.
This might include saving money, investing, or growing the business.
Regular financial check-ups are important. They help track progress toward exit goals.
Owners should review their plans yearly and adjust as needed.
A solid financial plan in your business plan is not just about crunching numbers— it’s about creating a clear path toward growth and stability.
Every component plays a role in guiding your business toward profitability, from financial statements to cash flow projections. Whether seeking funding or simply aiming to understand your finances better, a well-thought-out financial plan is indispensable.
Develop and launch your store with 10Web AI Ecommerce Website Builder.
Short Term Goals for a Business: Driving Success in the Next Quarter
Short-term goals help businesses stay on track and make progress. These goals focus on what a company wants to achieve in the near future, usually within a few weeks or months. Setting clear short-term goals gives your business direction and helps you measure success. Short-term goals can cover many areas of a business. They may relate to sales, customer service,…
How to Start a Business in Rhode Island: A Guide for Entrepreneurs
How to start a business in oklahoma: a guide for beginners, how to start a business in new hampshire: a guide to success, how to start a business in nevada: your guide to success, how to start a business in wyoming: a guide to your new venture, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Your email address will never be published or shared. Required fields are marked *
Email address *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get a head start on website creation with AI
Create a custom website tailored to your business needs 10X faster with 10Web AI Website Builder!
🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!
How to Write a Financial Plan for a Business Plan

Noah Parsons
4 min. read
Updated July 11, 2024

Creating a financial plan for a business plan is often the most intimidating part for small business owners.
It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts.
Here is everything you need to include in your business plan’s financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid , and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan in business plans
A sound financial plan for a business plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, you’ll need to include a few additional pieces of information as part of your business plan’s financial plan example.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios.
While including these metrics in your financial plan for a business plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Key financial terms you should know
It’s not hard. Anybody who can run a business can understand these key financial terms. And every business owner and entrepreneur should know them.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
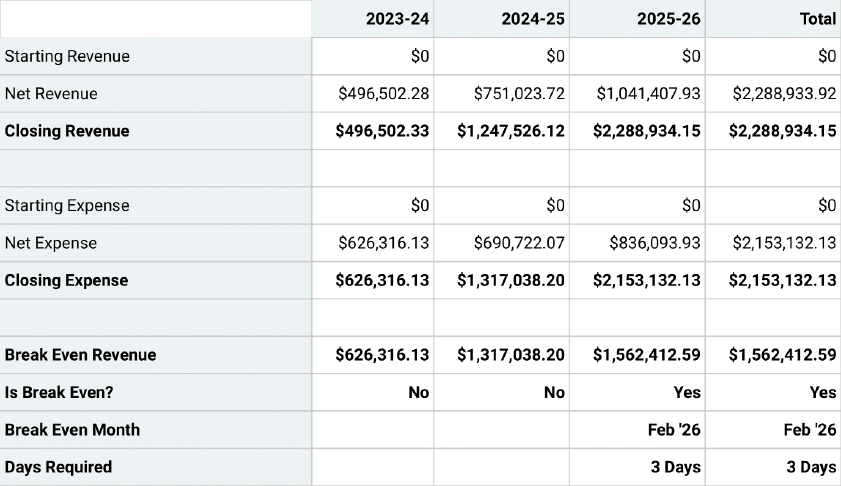
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- How to improve your financial plan
Your financial statements are the core part of your business plan’s financial plan that you’ll revisit most often. Instead of worrying about getting it perfect the first time, check out the following resources to learn how to improve your projections over time.
Common mistakes with business forecasts
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with startup financial projections. I read about 100 business plans per year, and I have this list of mistakes.
How to improve your financial projections
Learn how to improve your business financial projections by following these five basic guidelines.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

10 Min. Read
How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
AI Research Assist Your go-to AI-powered research assistant
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Plan Writing & Consulting We create a business plan for you
Business Plan Review Get constructive feedback on your plan
Financial Forecasting We create financial projections for you
SBA Lending Assistance We help secure SBA loans for your business
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
- 13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis, and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup or small business, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup or small business.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your small business and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan for your business plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

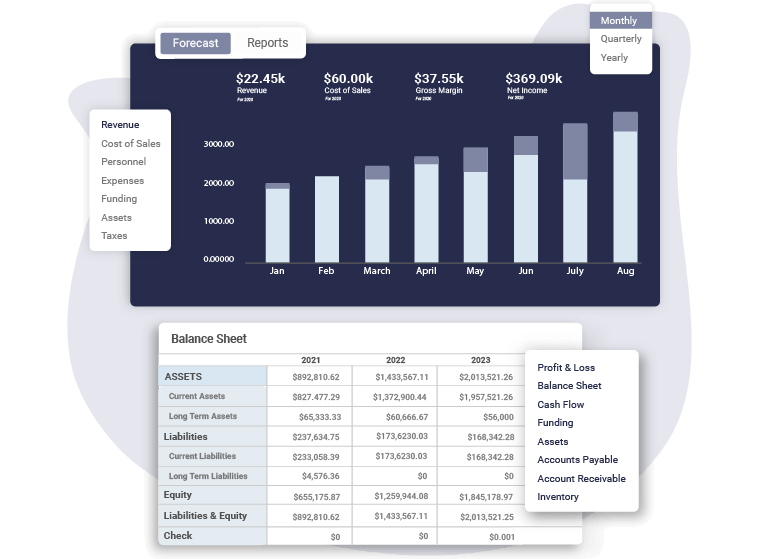
Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.

6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan for your small business, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
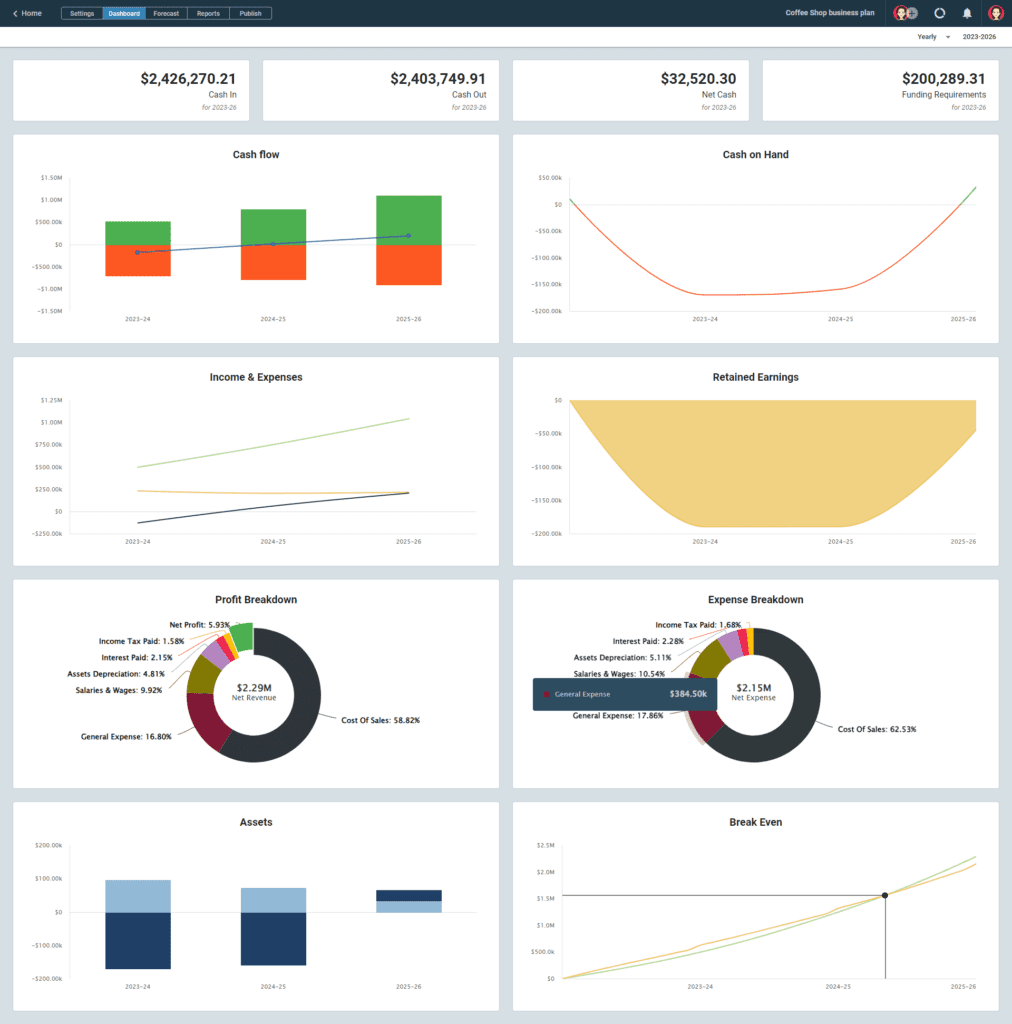
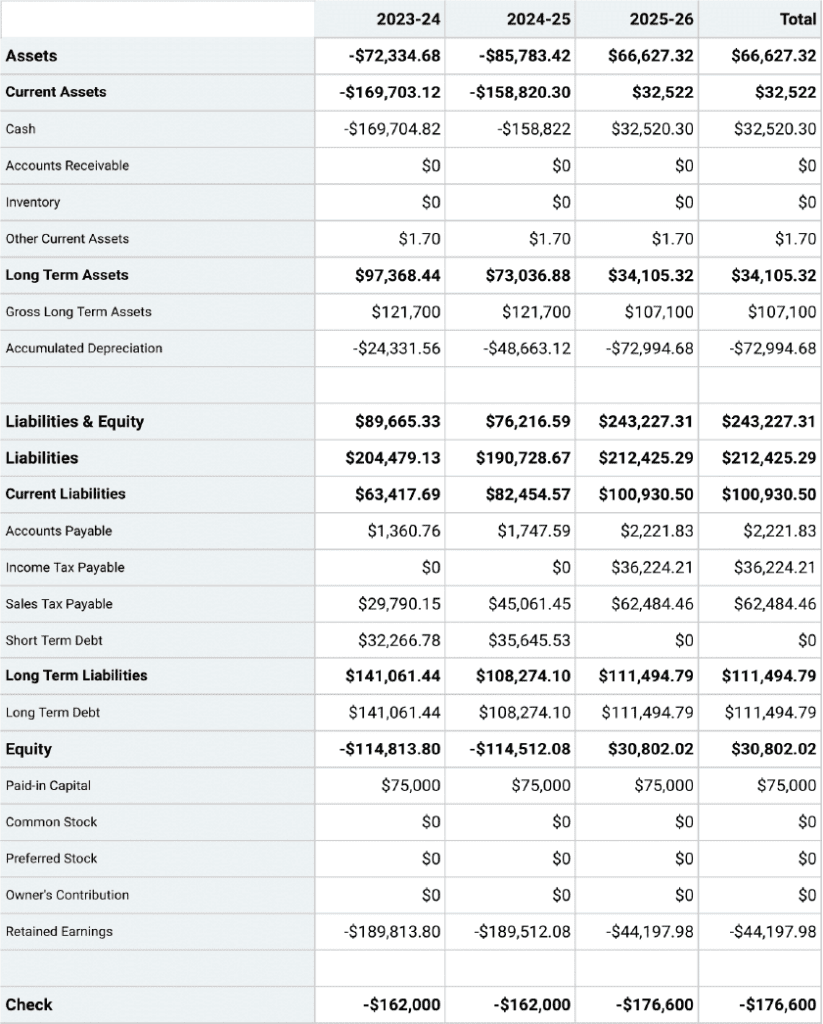
Projected Balance Sheet
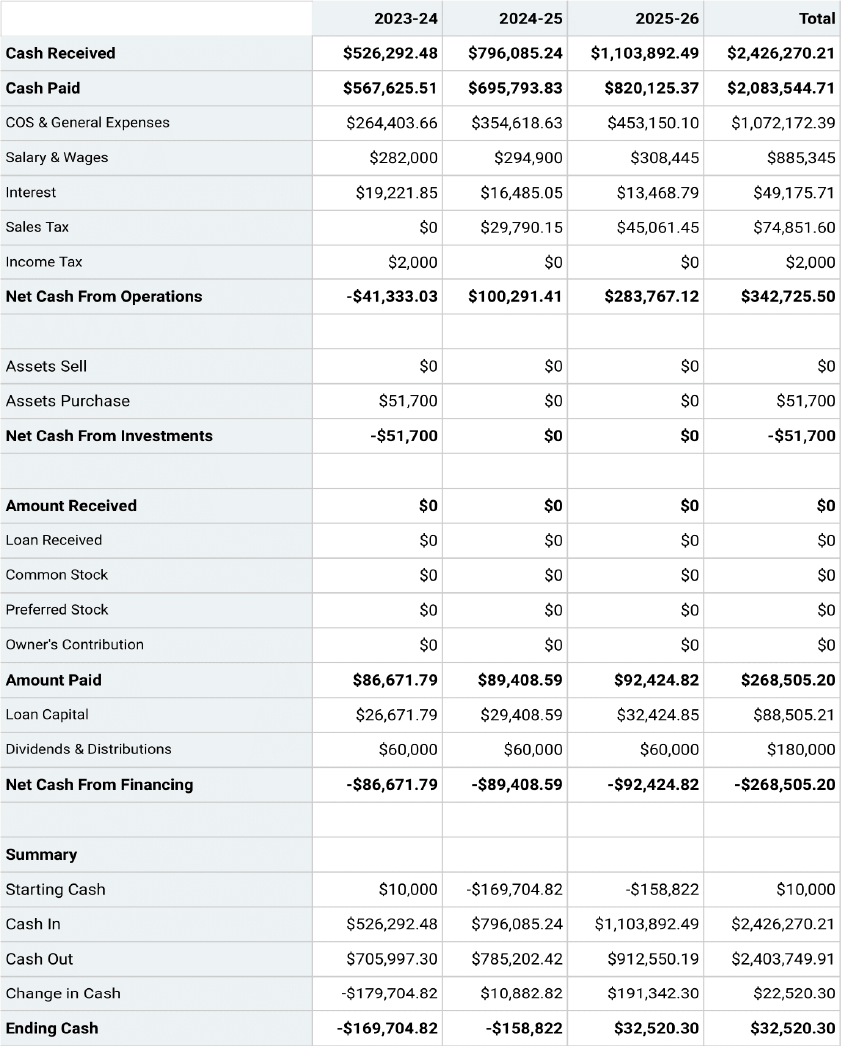
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
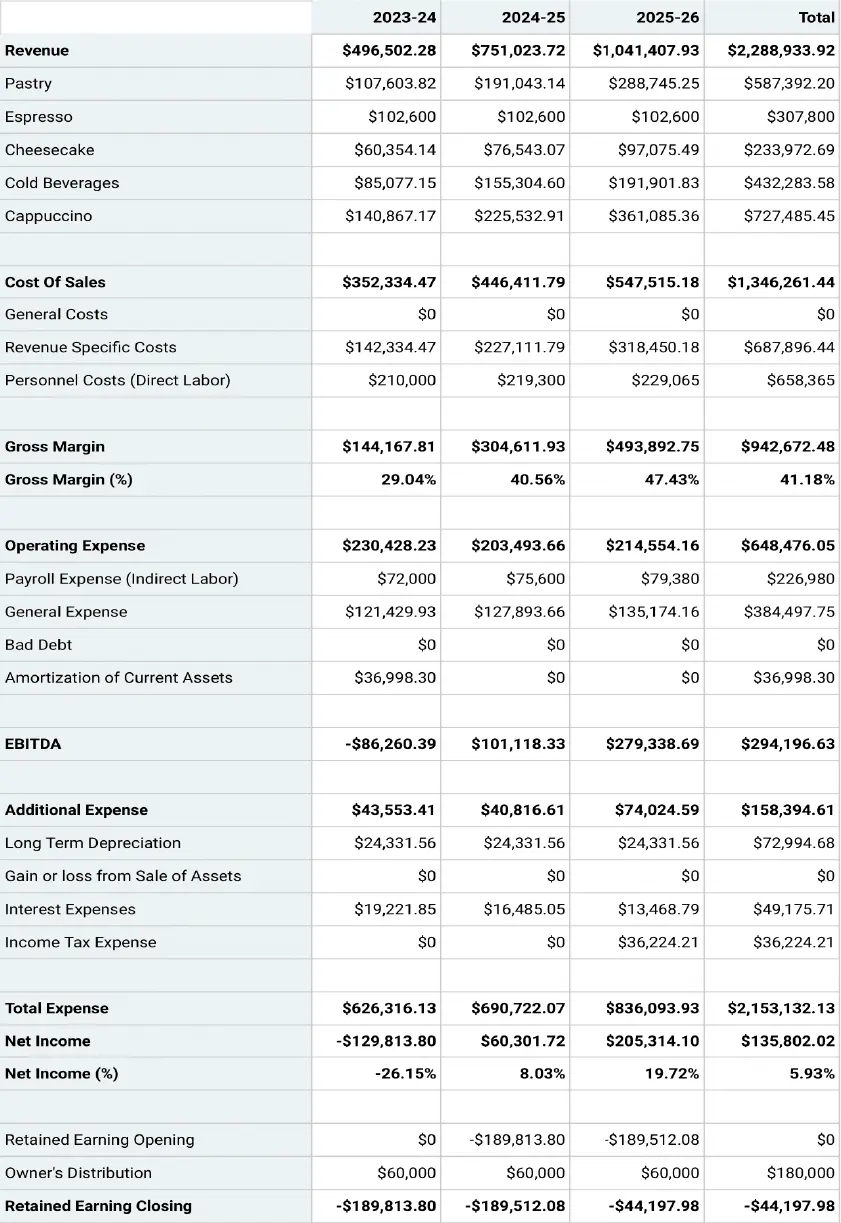
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
Break Even Analysis
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or small businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author
Ajay is the Head of Content at Upmetrics. Before joining our team, he was a personal finance blogger and SaaS writer, covering topics such as startups, budgeting, and credit cards. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

How to Develop a Small Business Financial Plan
By Andy Marker | April 29, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Financial planning is critical for any successful small business, but the process can be complicated. To help you get started, we’ve created a step-by-step guide and rounded up top tips from experts.
Included on this page, you’ll find what to include in a financial plan , steps to develop one , and a downloadable starter kit .
What Is a Small Business Financial Plan?
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth.

Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ideas. Craig Hewitt, Founder of Castos , shares that “creating a financial plan will show you if your business ideas are sustainable. A financial plan will show you where your business stands and help you make better decisions about resource allocation. It will also help you plan growth, survive cash flow shortages, and pitch to investors.”
Why Is It Important for a Small Business to Have a Financial Plan?
All small businesses should create a financial plan. This allows you to assess your business’s financial needs, recognize areas of opportunity, and project your growth over time. A strong financial plan is also a bonus for potential investors.

Mark Daoust , the President and CEO of Quiet Light Brokerage, Inc., explains why a financial plan is important for small businesses: “It can sometimes be difficult for business owners to evaluate their own progress, especially when starting a new company. A financial plan can be helpful in showing increased revenues, cash flow growth, and overall profit in quantifiable data. It's very encouraging for small business owners who are often working long hours and dealing with so many stressful decisions to know that they are on the right track.”
To learn more about other important considerations for a small business, peruse our list of free startup plan, budget, and cost templates .
What Does a Small Business Financial Plan Include?
All small businesses should include an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement in their financial plan. You may also include other documents, such as personnel plans, break-even points, and sales forecasts, depending on the business and industry.

- Balance Sheet: A balance sheet determines the difference between your liabilities and assets to determine your equity. “A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business’s financial position at a particular moment in time,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “It adds up everything your business owns and subtracts all debts — the difference reflects the net worth of the business, also referred to as equity .” Yüzbaşıoğlu explains that this statement consists of three parts: assets, liabilities, and equity. “Assets include your money in the bank, accounts receivable, inventories, and more. Liabilities can include your accounts payables, credit card balances, and loan repayments, for example. Equity for most small businesses is just the owner’s equity, but it could also include investors’ shares, retained earnings, or stock proceeds,” he says.
- Cash Flow Statement: A cash flow statement shows where the money is coming from and where it is going. For existing businesses, this will include bank statements that list deposits and expenditures. A new business may not have much cash flow information, but it can include all startup costs and funding sources. “A cash flow statement shows how much cash is generated and used during a given period of time. It documents all the money flowing in and out of your business,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Break-Even Analysis: A break-even analysis is a projection of how long it will take you to recoup your investments, such as expenses from startup costs or ongoing projects. In order to perform this analysis, Yüzbaşıoğlu explains, “You need to know the difference between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are the expenses that stay the same, regardless of how much you sell or don't sell. For example, expenses such as rent, wages, and accounting fees are typically fixed. Variable costs are the expenses that change in accordance with production or sales volume. “In other words, [a break-even analysis] determines the units of products or services you need to sell at least to cover your production costs. Generally, to calculate the break-even point in business, divide fixed costs by the gross profit margin. This produces a dollar figure that a company needs to break even,” Yüzbaşıoğlu shares.
- Personnel Plan: A personnel plan is an outline of various positions or departments that states what they do, why they are necessary, and how much they cost. This document is generally more useful for large businesses, or those that find themselves spending a large percentage of their budget on labor.
- Sales Forecast: A sales forecast can help determine how many sales and how much money you expect to make in a given time period. To learn more about various methods of predicting these figures, check out our guide to sales forecasting .
How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan
Writing a financial plan begins with collecting financial information from your small business. Create income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, and any other documents you need using that information. Then share those documents with relevant stakeholders.
“Creating a financial plan is key to any business and essential for success: It provides protection and an opportunity to grow,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “You can use [the financial plan] to make better-informed decisions about things like resource allocation on future projects and to help shape the success of your company.”
1. Create a Plan
Create a strategic business plan that includes your business strategy and goals, and define their financial impact. Your financial plan will inform decisions for every aspect of your business, so it is important to know what is important and what is at stake.
2. Gather Financial Information
Collect all of the available financial information about your business. Organize bank statements, loan information, sales numbers, inventory costs, payroll information, and any other income and expenses your business has incurred. If you have not already started to do so, regularly record all of this information and store it in an easily accessible place.
3. Create an Income Statement
Your income statement should display revenue, expenses, and profit for a given time period. Your revenue minus your expenses equals your profit or loss. Many businesses create a new statement yearly or quarterly, but small businesses with less cash flow may benefit from creating statements for shorter time frames.
4. Create a Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a snapshot of your business’s financial status at a particular moment in time. You should update it on the same schedule as your income statement. To determine your equity, calculate all of your assets minus your liabilities.
5. Create a Cash Flow Statement
As mentioned above, the cash flow statement shows all past and projected cash flow for your business. “Your cash flow statement needs to cover three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities,” suggests Hewitt. “Operating activities are the movement of cash from the sale or purchase of goods or services. Investing activities are the sale or purchase of long-term assets. Financing activities are transactions with creditors and investments.”
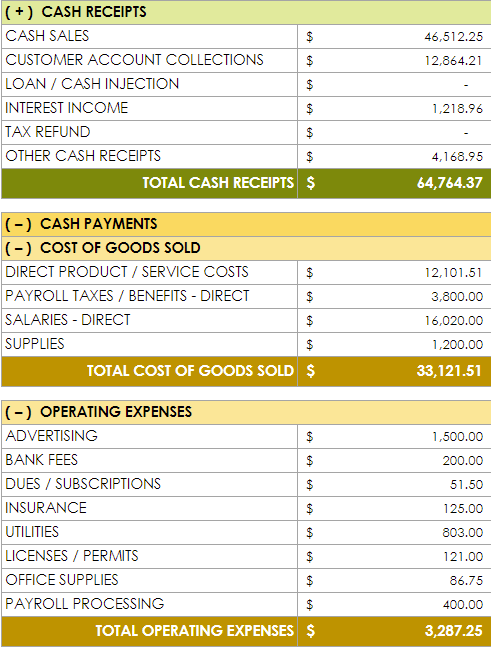
6. Create Other Documents as Needed
Depending on the age, size, and industry of your business, you may find it useful to include these other documents in your financial plan as well.
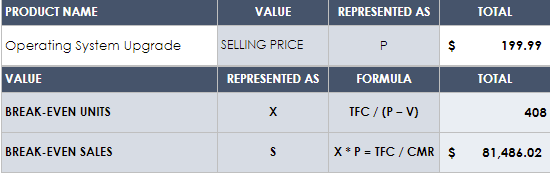
- Sales Forecast: Your sales forecast should reference sales numbers from your past to estimate sales numbers for your future. Sales forecasts may be more useful for established companies with historical numbers to compare to, but small businesses can use forecasts to set goals and break records month over month. “To make future financial projections, start with a sales forecast,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “Project your sales over the course of 12 months. After projecting sales, calculate your cost of sales (also called cost of goods or direct costs). This will let you calculate gross margin. Gross margin is sales less the cost of sales, and it's a useful number for comparing with different standard industry ratios.”
7. Save the Plan for Reference and Share as Needed
The most important part of a financial plan is sharing it with stakeholders. You can also use much of the same information in your financial plan to create a budget for your small business.

Additionally, be sure to conduct regular reviews, as things will inevitably change. “My best tip for small businesses when creating a financial plan is to schedule reviews. Once you have your plan in place, it is essential that you review it often and compare how well the strategy fits with the actual monthly expenses. This will help you adjust your plan accordingly and prepare for the year ahead,” suggests Janet Patterson, Loan and Finance Expert at Highway Title Loans.
Small Business Financial Plan Example
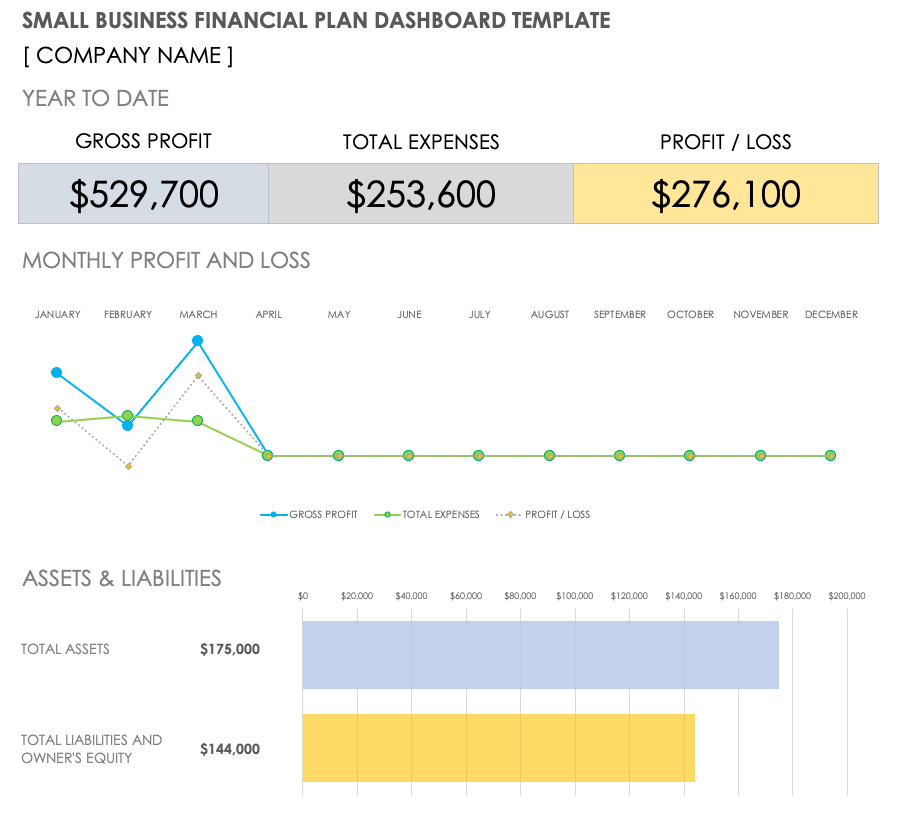
Download Small Business Financial Plan Example Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Here is an example of what a completed small business financial plan dashboard might look like. Once you have completed your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements, use a template to create visual graphs to display the information to make it easier to read and share. In this example, this small business plots its income and cash flow statements quarterly, but you may find it valuable to update yours more often.
Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
Download Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
We’ve created this small business financial plan starter kit to help you get organized and complete your financial plan. In this kit, you will find a fully customizable income statement template, a balance sheet template, a cash flow statement template, and a dashboard template to display results. We have also included templates for break-even analysis, a personnel plan, and sales forecasts to meet your ongoing financial planning needs.
Small Business Income Statement Template
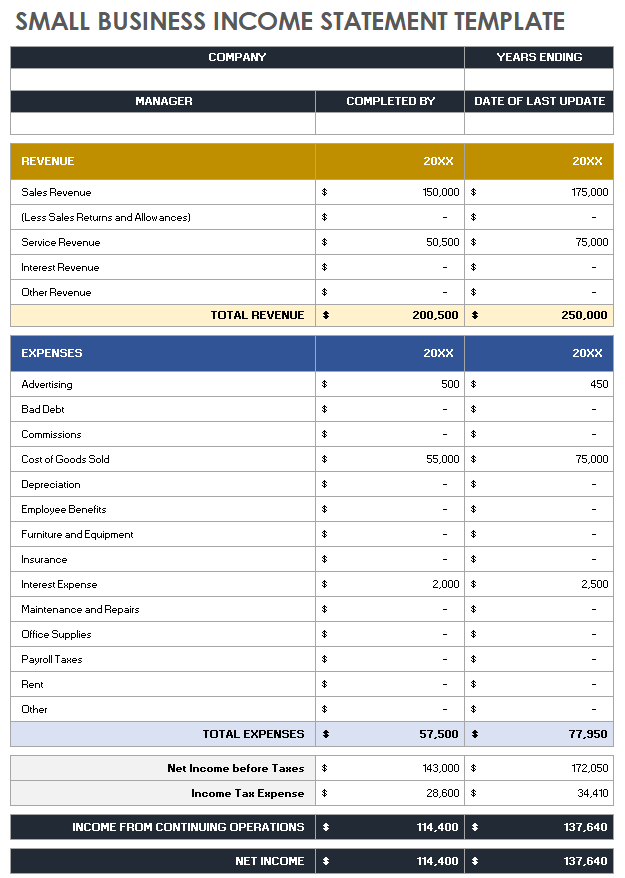
Download Small Business Income Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business income statement template to input your income information and track your growth over time. This template is filled to track by the year, but you can also track by months or quarters. The template is fully customizable to suit your business needs.
Small Business Balance Sheet Template
Download Small Business Balance Sheet Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This customizable balance sheet template was created with small businesses in mind. Use it to create a snapshot of your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity quarter over quarter.
Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template
Download Small Business Cash Flow Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable cash flow statement template to stay organized when documenting your cash flow. Note the time frame and input all of your financial data in the appropriate cell. With this information, the template will automatically generate your total cash payments, net cash change, and ending cash position.
Break-Even Analysis Template
Download Break-Even Analysis Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This powerful template can help you determine the point at which you will break even on product investment. Input the sale price of the product, as well as its various associated costs, and this template will display the number of units needed to break even on your initial costs.
Personnel Plan Template
Download Personnel Plan Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this simple personnel plan template to help organize and define the monetary cost of the various roles or departments within your company. This template will generate a labor cost total that you can use to compare roles and determine whether you need to make cuts or identify areas for growth.
Sales Forecast Template
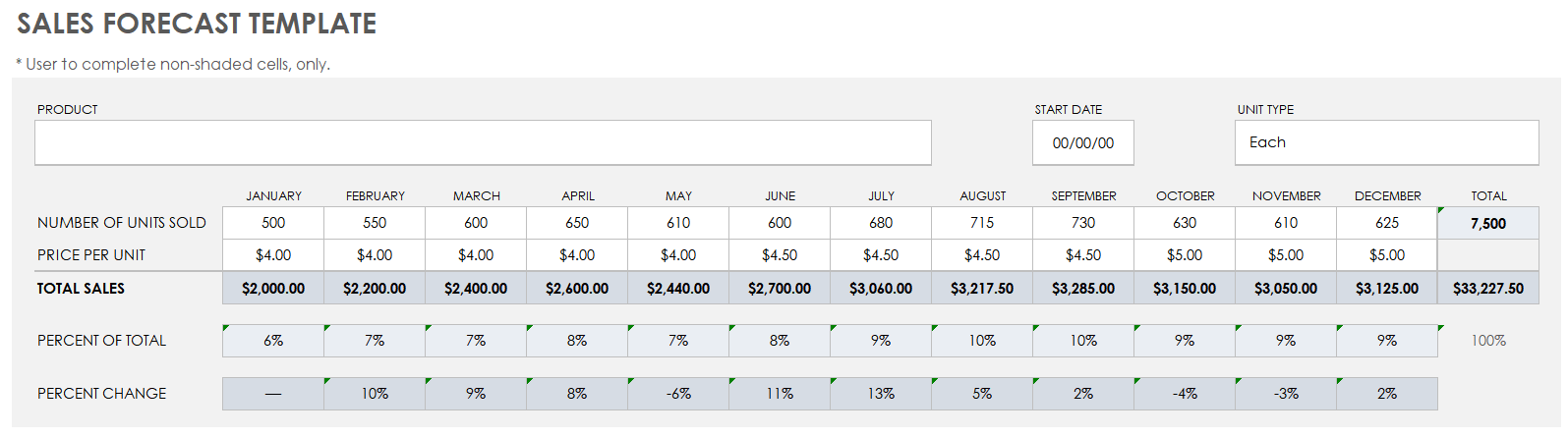
Download Sales Forecast Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable template to forecast your sales month over month and determine the percentage changes. You can use this template to set goals and track sales history as well.
Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template
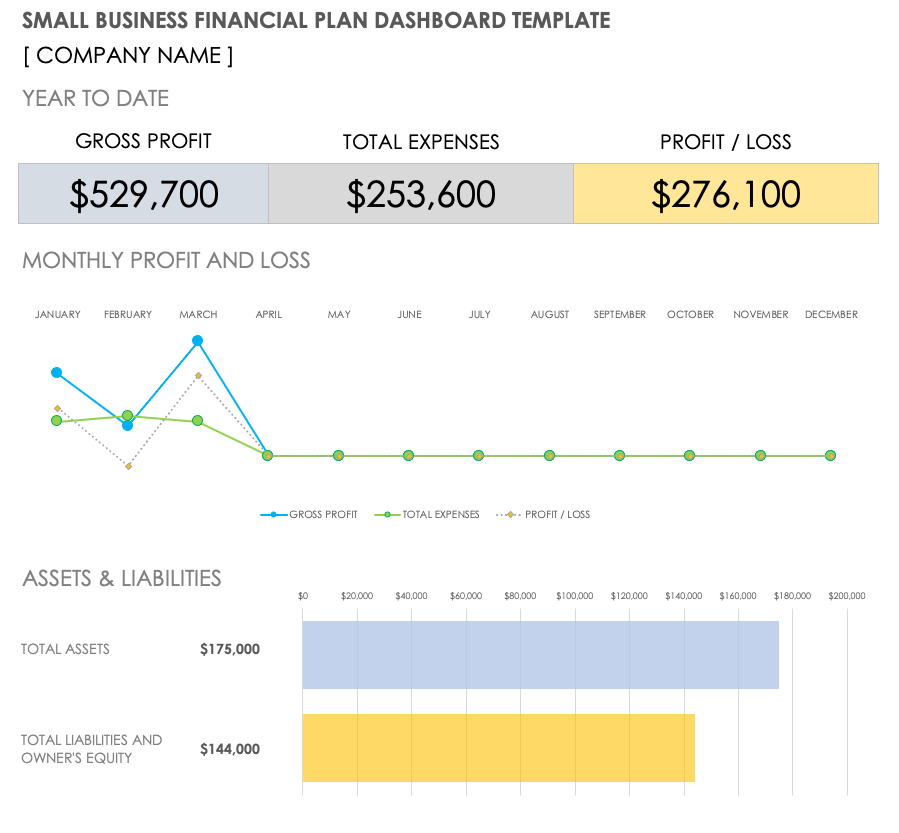
Download Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This dashboard template provides a visual example of a small business financial plan. It presents the information from your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in a graphical form that is easy to read and share.
Tips for Completing a Financial Plan for a Small Business
You can simplify the development of your small business financial plan in many ways, from outlining your goals to considering where you may need help. We’ve outlined a few tips from our experts below:

- Outline Your Business Goals: Before you create a financial plan, outline your business goals. This will help you determine where money is being well spent to achieve those goals and where it may not be. “Before applying for financing or investment, list the expected business goals for the next three to five years. You can ask a certified public accountant for help in this regard,” says Thé. The U.S. Small Business Administration or a local small business development center can also help you to understand the local market and important factors for business success. For more help, check out our quick how-to guide on writing a business plan .
- Make Sure You Have the Right Permits and Insurance: One of the best ways to keep your financial plan on track is to anticipate large expenditures. Double- and triple-check that you have the permits and insurances you need so that you do not incur any fines or surprise expenses down the line. “If you own your own business, you're no longer able to count on your employer for your insurance needs. It's important to have a plan for how you're going to pay for this additional expense and make sure that you know what specific insurance you need to cover your business,” suggests Daost.
- Separate Personal Goals from Business Goals: Be as unbiased as possible when creating and laying out your business’s financial goals. Your financial and prestige goals as a business owner may be loftier than what your business can currently achieve in the present. Inflating sales forecasts or income numbers will only come back to bite you in the end.
- Consider Hiring Help: You don’t know what you don’t know, but fortunately, many financial experts are ready to help you. “Hiring financial advisors can help you make sound financial decisions for your business and create a financial roadmap to follow. Many businesses fail in the first few years due to poor planning, which leads to costly mistakes. Having a financial advisor can help keep your business alive, make a profit, and thrive,” says Hewitt.
- Include Less Obvious Expenses: No income or expense is too small to consider — it all matters when you are creating your financial plan. “I wish I had known that you’re supposed to incorporate anticipated internal hidden expenses in the plan as well,” Patterson shares. “I formulated my first financial plan myself and didn’t have enough knowledge back then. Hence, I missed out on essential expenses, like office maintenance, that are less common.”
Do Small Business Owners Need a Financial Planner?
Not all small business owners need a designated financial planner, but you should understand the documents and information that make up a financial plan. If you do not hire an advisor, you must be informed about your own finances.
Small business owners tend to wear many hats, but Powell says, “it depends on the organization of the owner and their experience with the financial side of operating businesses.” Hiring a financial advisor can take some tasks off your plate and save you time to focus on the many other details that need your attention. Financial planners are experts in their field and may have more intimate knowledge of market trends and changing tax information that can end up saving you money in the long run.
Yüzbaşıoğlu adds, “Small business owners can greatly benefit from working with a financial advisor. A successful small business often requires more than just the skills of an entrepreneur; a financial advisor can help the company effectively manage risks and maximize opportunities.”
For more examples of the tasks a financial planner might be able to help with, check through our list of free financial planning templates .
Drive Small Business Success with Financial Planning in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.
- Financial Advisor
- Financial Planning
Financial Planning: What It Is and How to Make a Plan
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Financial and Investment Planning
- How to Create a Plan
Investment Planning 101
- Benefits of Making a Plan
- When to Create a Plan
The Bottom Line
Liz Manning has researched, written, and edited trading, investing, and personal finance content for years, following her time working in institutional sales, commercial banking, retail investing, hedging strategies, futures, and day trading.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/LizManning-INV-BW-3a1ec9a776ef4fc09313c125ed6598f3.jpg)
Gordon Scott has been an active investor and technical analyst or 20+ years. He is a Chartered Market Technician (CMT).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/gordonscottphoto-5bfc26c446e0fb00265b0ed4.jpg)
Ariel Courage is an experienced editor, researcher, and former fact-checker. She has performed editing and fact-checking work for several leading finance publications, including The Motley Fool and Passport to Wall Street.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ArielCourage-50e270c152b046738d83fb7355117d67.jpg)
- Financial Planning: What It Is and How to Make a Plan CURRENT ARTICLE
- Conduct a Financial Checkup
- How to Manage Lifestyle Inflation
- Annual Financial Planning Checklist
- DIY Financial Planning
- Making an Annual Plan
- Planning for Retirement
- Financial Security Before 30
- Retire as a Millionaire
- Pay Yourself First
- Budgeting for Short- and Long-term Expenses
- Balance Your Portfolio
- Financial New Year's Resolutions
- When Someone Needs a Financial Intervention
What Is Financial Planning?
An investment plan starts with a financial plan. Both identify your financial goals and address the financial resources you have available to meet them.
A financial plan is a document that details a person’s current financial circumstances, their short- and long-term monetary goals, and their strategies to achieve those goals. It can help you to establish and plan for income and spending, debt reduction, and fundamental needs such as managing life's risks such as those involving health or disability.
A financial plan can provide financial guidance so you're prepared to meet your obligations and objectives. It can also help you track your progress throughout the years toward financial well-being.
Investment planning involves a thorough evaluation of your money situation including income, spending, debt, saving, and expectations for the future. It can be created independently or with the help of a certified financial planner.
Key Takeaways
- An investment plan documents an individual’s short- and long-term financial goals and includes a strategy to achieve them.
- The plan should be comprehensive and highly customized.
- It should reflect an individual’s personal and family financial needs, investment risk tolerance, and a plan for saving and investing.
- Planning in finance starts with a calculation of one’s current net worth and cash flow.
- A solid investment plan provides guidance over time and serves as a way to track progress toward your goals.
The Fundamentals of Financial Plans
How to create an investment plan.
Certain steps are necessary to create a financial plan and an investment plan .
1. Do It Yourself or Get Professional Help
Decide whether you'll create your financial and investment plans on your own or with the help of a licensed financial planner . You can certainly build a financial plan but a financial pro can help ensure that your plan covers all the essentials.
2. Build an Emergency Cash Fund
Start setting aside money in a liquid account based on what your cash flow allows. Your goal should be to save enough to cover all your expenses for three to six months at a minimum but preferably for longer in case you find yourself without income due to unexpected events.
3. Plan to Reduce Debt and Manage Expenses
The faster and more effectively you can eliminate debt, the better for the growth of your savings, your standard of living, and for the achievement of your specific investment objectives.
Make it a habit to cut expenses whenever and wherever possible so you can add to your savings. Stay on top of those that you know you'll have, such as taxes, so you always meet those obligations on time.
4. Manage Potential Risks
Your financial well-being can be affected when accidents, health problems, or the death of a loved one strike. Plan to put into place the appropriate insurance coverage that will protect your financial security at such times. This coverage can include home, property , health, auto, disability, personal liability , and life insurance.
5. Begin to Invest
Take part in a retirement plan at work that automatically deducts contributions from your paychecks. Plan to maximize your tax-advantaged investing with a personal IRA if and when your income allows.
Consider how you might allocate any other available income to a taxable investment account that can add to your net worth over time. Your plan for investing should take into account your investment risk tolerance and future income needs.
6. Include a Tax Strategy
Address the goal of reducing your income taxes with tax deductions, tax credits, tax loss harvesting, and any other opportunities that are legally available to taxpayers.
7. Consider an Estate Plan
It's important to make arrangements for the benefit and protection of your heirs with an estate plan . The details will depend on your stage in life and whether you're married, have children, or have other legacy goals. Again, a professional such as an attorney can help here.
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Plan
Revisit your plan at least yearly on your own or with a financial professional. Do it more often if a change in circumstances affects your financial situation. Keep it working efficiently and effectively by adjusting it as necessary.
Investopedia / Nez Riaz
Whether you’re going it alone or with a financial planner, it's necessary to understand how important financial and investment plans can be to your financial future. They can provide the guidance that assures your financial success.
Start your planning effort by gathering information from your various financial accounts into a document or spreadsheet. Then make some basic calculations that establish where you stand financially.
1. Calculate Your Net Worth
To calculate your current net worth , subtract the total of your liabilities from the total of your assets. Begin by listing and adding up all of the following:
- Your assets : An asset is property of value that you own. Assets may include a home, a car, cash in the bank, money invested in a 401(k) plan , and other investment accounts.
- Your liabilities : A liability is something you owe. Liabilities may include outstanding bills, credit card debt, student debt, a mortgage, and a car loan.
2. Determine Your Cash Flow
Cash flow is the money you take in measured against the money you spend. You must know your income as well as how and when your money is spent to create a financial plan and then an investment plan. Documenting your cash flow will help you determine how much you need every month for necessities, how much is available for saving and investing, and where you can cut back on spending.
Review your checking account and credit card statements. They should provide a fairly complete history of your income and spending in a wide range of spending categories.
Document how much you’ve paid during the year for housing expenses like rent or mortgage payments, utilities, and credit card interest. Other categories include food, household and clothing, transportation, medical insurance, and non-covered medical expenses. Still others can include your spending on miscellaneous entertainment, dining out, and vacation travel.
You’ll know what your monthly cash flow has been and where you can improve it when you've added up all these numbers for a year and divided the total by 12.
Don’t overlook cash withdrawals that may have been used on sundries like shampoo. ATM withdrawals can also highlight where you can cut unnecessary spending.
3. Establish Your Goals
A major part of an investment plan is your clearly defined goals . They might include funding a college education for the children, buying a larger home, starting a business, retiring on time, or leaving a legacy.
No one can tell you how to prioritize these goals but a professional financial planner should be able to help you finalize a detailed savings plan and specific investing that can help you reach them one by one.
The main elements of a financial plan include a retirement strategy, a risk management plan, a long-term investment plan, a tax reduction strategy, and an estate plan.
Benefits of Making a Financial Plan
- A financial plan involves a thorough examination of your income and spending.
- It can improve your understanding of your financial circumstances at all times.
- It establishes important short- and long-term financial goals upon which you can base your investment planning.
- It clarifies the actions required to achieve your various financial goals.
- A financial plan can focus your attention on important immediate steps such as reducing debt and building your savings for emergencies.
- It enhances the probability that you'll achieve financial milestones and overall financial success.
- It can guide your efforts over time and provide a means to monitor your progress.
- It can keep you out of financial trouble and reduce any stress and worry you might have experienced in the past.
Financial planning is a smart way to keep your financial house in order. It's a money tool regardless of your age, earnings, net worth, or financial dreams. It provides a way to document your financial goals and corresponding investment goals.
When to Create a Financial Plan
A financial plan is always an advantage for those who want to make sure they manage their finances in ways that are best suited for them. You can create one at any time whether you've just joined the workforce or you've been working for years.
Some circumstances can call for the creation and use of a financial plan, however. They can also serve as signals to adjust existing plans.
- A new job that results in added income, new expenses, or new opportunities
- An income change that can affect your ability to pay expenses, pay off debt, or save
- Major life events such as marriage, children, or divorce that can change financial objectives, spending needs, and obligations
- Health adversities that result in redirecting income and spending away from existing goals
- An income windfall such as an inheritance or insurance payment that can affect your efforts to reach your financial goals, such as by providing more money for investing
What Is the Purpose of a Financial Plan?
A financial plan should help you make the best use of your money and achieve long-term financial goals such as investments, sending your children to college, buying a bigger home, leaving a legacy, or enjoying a comfortable retirement.
How Do I Create an Investment Plan?
You can write an investment plan yourself or enlist the help of a professional planner. Begin with a financial plan. The first step is to calculate your net worth and identify your spending habits. Consider your longer-term objectives and decide on ways to achieve them when this has been accomplished and documented.
What Are the Key Components of a Financial Plan?
Financial plans aren't one-size-fits-all but the good ones tend to focus on the same things. You can explore your financial goals and ways to achieve them after you've calculated your net worth and spending habits. This usually involves some form of budgeting , saving, and investing each month.
Your goal is to ensure that you live comfortably and financially stress-free for the rest of your life. Areas to focus on include an emergency savings plan, a retirement plan, risk management, a tax minimization plan, and then a long-term investment strategy.
What Are the Five Key Areas of Financial Planning?
The five key areas of financial planning are estate planning, retirement planning, self-protection/risk management such as insurance, tax planning, and investment planning.
A financial plan is an essential tool for your financial well-being, both now and into the future. It involves setting down the current state of your finances, your various financial goals, and methods that can help you achieve them.
It's never too early or too late to create a financial plan. It can help you to determine the best way to put it to work so that you can meet your financial needs through all of your life stages, no matter the amount of money you might have.
Yahoo! Finance. " How Much Money Should I Have in an Emergency Savings Account? "
Forbes Advisor. " Estate Planning Checklist: Get Your Affairs in Order ."
Fidelity Investments. " What Is Net Worth? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TheDeepDiveThumbnailYT-RichBerthy-51eb279f0b114ca7830a34ceb87d13e1.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

COMMENTS
A financial plan in business planning is a detailed projection of a company’s future economic performance. It includes revenue, expenses, and profitability estimates, guiding the business in managing its finances and planning for growth.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts. Here is everything you need to include in your business plan’s financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid, and free templates.
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Your business plan is the tool you’ll use to convince people that working with you — or investing in your company — is a smart choice. Pick a business plan format that works for you. There’s no right or wrong way to write a business plan. What’s important is that your plan meets your needs.
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth.
A financial plan is a document that details a person’s current financial circumstances, their short- and long-term monetary goals, and their strategies to achieve those goals.